 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
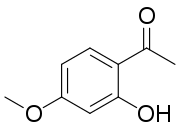
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-(2-Hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)ethan-1-one | |
| Other names
2'-Hydroxy-4'-methoxyacetophenone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.194 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H10O3 | |
| Molar mass | 166.176 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Paeonol is a phenolic compound found in peonies[2] such as Paeonia suffruticosa (moutan cortex),[3][4] in Arisaema erubescens,[5] and in Dioscorea japonica.[6] It is a chemical compound found in some traditional Chinese medicines.[7]
Biological effects
A number of biological effects of paeonol in vitro or in animal models have been observed. Paeonol increases levels of cortical cytochrome oxidase and vascular actin and improves behavior in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease.[8] Paeonol also reduced cerebral infarction involving the superoxide anion and microglia activation in ischemia-reperfusion injured rats.[9]
Paeonol shows antimutagenic activities.[3][6] It also has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects in carrageenan-evoked thermal hyperalgesia.[10] Paeonol inhibits anaphylactic reaction by regulating histamine and TNF-α.[11]
Paeonol has weak MAO-A and MAO-B inhibiting effects with IC50 values of 54.6 μM and 42.5 μM respectively.[12]
Metal complex
Metal complexes of paeonol shows tetrahedral and octahedral coordination geometry in the absence and presence of solvent pyridine respectively.[13]
References
- ↑ "CAS # 552-41-0, Paeonol, 2'-Hydroxy-4'-methoxyacetophenone, 1-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)ethan-1-one".
- ↑ Zhang, L., Li, D. C., & Liu, L. F. (2019). Paeonol: pharmacological effects and mechanisms of action. International immunopharmacology, 72, 413-421. PMID 31030097 doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2019.04.033
- 1 2 Fukuhara Y, Yoshida D (1987). "Paeonol: a bio-antimutagen isolated from a crude drug, moutan cortex". Agricultural and Biological Chemistry. 51 (5): 1441–1442. doi:10.1271/bbb1961.51.1441. INIST 7609719.
- ↑ Wu, Xinan; Chen, Hongli; Chen, Xingguo; Hu, Zhide (2003). "Determination of paeonol in rat plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography and its application to pharmacokinetic studies following oral administration of Moutan cortex decoction". Biomedical Chromatography. 17 (8): 504–8. doi:10.1002/bmc.259. PMID 14648606.
- ↑ Ducki S, Hadfield JA, Lawrence NJ, Zhang X, McGown AT (1995). "Isolation of paeonol from Arisaema erubescens". Planta Medica. 61 (6): 586–587. doi:10.1055/s-2006-959390. PMID 8824957. INIST 2920867.
- 1 2 Miyazawa, Mitsuo; Shimamura, Hideo; Nakamura, Sei-Ichi; Kameoka, Hiromu (1996). "Antimutagenic Activity of (+)-β-Eudesmol and Paeonol fromDioscorea japonica". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 44 (7): 1647–1650. doi:10.1021/jf950792u.
- ↑ Deng, Chunhui; Yao, Ning; Wang, Ben; Zhang, Xiangmin (2006). "Development of microwave-assisted extraction followed by headspace single-drop microextraction for fast determination of paeonol in traditional Chinese medicines". Journal of Chromatography A. 1103 (1): 15–21. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2005.11.023. PMID 16309693.
- ↑ Zhou, Jun; Zhou, Li; Hou, Deren; Tang, Jiaochun; Sun, Juanjuan; Bondy, Stephen C. (2011). "Paeonol increases levels of cortical cytochrome oxidase and vascular actin and improves behavior in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease" (PDF). Brain Research. 1388: 141–7. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2011.02.064. PMID 21377451. S2CID 12668336.
- ↑ Hsieh, Ching-Liang; Cheng, Chin-Yi; Tsai, Tung-Hu; Lin, I-Hsin; Liu, Chung-Hsiang; Chiang, Su-Yin; Lin, Jaung-Geng; Lao, Chih-Jui; Tang, Nou-Ying (2006). "Paeonol reduced cerebral infarction involving the superoxide anion and microglia activation in ischemia-reperfusion injured rats". Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 106 (2): 208–15. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2005.12.027. PMID 16458462.
- ↑ Chou, Tz-Chong (2003). "Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of paeonol in carrageenan-evoked thermal hyperalgesia". British Journal of Pharmacology. 139 (6): 1146–52. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0705360. PMC 1573952. PMID 12871833.
- ↑ Kim, Sung Hoon; Kim, Seung-Ae; Park, Mi-Kyung; Kim, Seung-Hyung; Park, Young-Doo; Na, Ho-Jeong; Kim, Hyung-Min; Shin, Min-Kyu; Ahn, Kyoo-Seok (2004). "Paeonol inhibits anaphylactic reaction by regulating histamine and TNF-α". International Immunopharmacology. 4 (2): 279–87. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2003.12.013. PMID 14996419.
- ↑ Kong, L.D.; Cheng, Christopher H.K.; Tan, R.X. (2004). "Inhibition of MAO A and B by some plant-derived alkaloids, phenols and anthraquinones". Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 91 (2–3): 351–355. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2004.01.013. PMID 15120460.
- ↑ Patel, Mahesh kumar (2019). "Solvent effect on neutral Co (II) complexes of paeonol derivative equalitative and quantitative studies from energy frame work and Hirshfeld surface analysis". Journal of Molecular Structure. 1196: 119–131. Bibcode:2019JMoSt1196..119P. doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.06.050. S2CID 197231895.