| Painted Desert | |
|---|---|
 | |
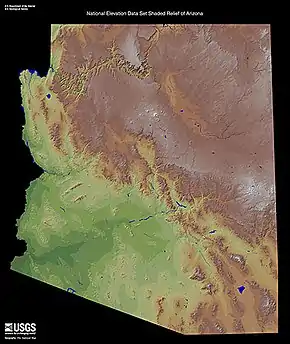 Relief map showing arc-shaped desert north and northeast of Mogollon Plateau and Mogollon Rim. | |
| Length | 160 miles |
| Area | 93500 acres |
| Naming | |
| Native name | El Desierto Pintado (Spanish) |
| Geography | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Arizona |
| Borders on | Little Colorado and Puerco rivers |
| Coordinates | 35°30′N 110°05′W / 35.500°N 110.083°W [1] |
The Painted Desert is a United States desert of badlands in the Four Corners area,[2] running from near the east end of Grand Canyon National Park and southeast into Petrified Forest National Park. It is most easily accessed from the north portion of Petrified Forest National Park. The Painted Desert is known for its brilliant and varied colors: these include the more common red rock, but also shades of lavender.
History
The Painted Desert was named by a Spanish expedition under Francisco Vázquez de Coronado during his 1540 quest to find the Seven Cities of Cibola. He located these some 40 miles (60 km) east of Petrified Forest National Park. Finding the cities were not made of gold, Coronado sent an expedition to find the Colorado River to gain supplies. Passing through the wonderland of colors, they named the area El Desierto Pintado ("The Painted Desert").[3]
Much of the Painted Desert within Petrified Forest National Park is protected as Petrified Forest National Wilderness Area, where motorized travel is limited.[4] The park offers both easy and longer hikes into the colored hills. The Painted Desert continues north into the Navajo Nation, where off-road travel is allowed only by permit.
Geology
The desert is composed of stratified layers of siltstone, mudstone, and shale of the Triassic Chinle Formation, which erode easily. These fine-grained rock layers contain abundant iron and manganese compounds, which provide the pigments for the various colors of the region. Thin, resistant lacustrine limestone layers and volcanic flows cap the mesas. Numerous layers of silicic volcanic ash occur in the Chinle and provide the silica for the petrified logs of the area. The erosion of these layers has resulted in the formation of the badlands topography of the region.[5][6][7]
In the southern portions of the desert, the remains of a Triassic period coniferous forest have fossilized over millions of years. Wind, water and soil erosion continue to change the face of the landscape by shifting sediment and exposing layers of the Chinle Formation. An assortment of fossilized prehistoric plants and animals are found in the region, as well as ancient dinosaur tracks and evidence of early human habitation.
Area and climate
The Painted Desert extends roughly from Cameron–Tuba City southeast to past Holbrook and the Petrified Forest National Park. The desert is about 120 miles (190 km) long by about 60 miles (100 km) wide, making it roughly 7,500 square miles (19,420 km2) in area.[8] Bordering southwest and south is the Mogollon Plateau, and on the plateau's south border the Mogollon Rim, the north border of the Arizona transition zone.
Owing to the strong rain shadow of the Mogollon Rim, the Painted Desert has a cold desert climate (Köppen BWk), with hot, dry summers and chilly (though virtually snow-free) winters. The annual precipitation is the lowest in northern Arizona and in many places is lower even than Phoenix.[9]
| Climate data for Petrified Forest National Park, Arizona, 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1973–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 67 (19) |
73 (23) |
84 (29) |
89 (32) |
101 (38) |
103 (39) |
104 (40) |
101 (38) |
100 (38) |
90 (32) |
79 (26) |
69 (21) |
104 (40) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 60.1 (15.6) |
67.8 (19.9) |
75.2 (24.0) |
82.1 (27.8) |
89.7 (32.1) |
98.9 (37.2) |
99.0 (37.2) |
96.1 (35.6) |
91.4 (33.0) |
82.6 (28.1) |
72.4 (22.4) |
62.7 (17.1) |
100.1 (37.8) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 47.6 (8.7) |
52.5 (11.4) |
60.7 (15.9) |
68.4 (20.2) |
77.6 (25.3) |
88.6 (31.4) |
91.5 (33.1) |
88.4 (31.3) |
82.0 (27.8) |
70.5 (21.4) |
58.2 (14.6) |
46.5 (8.1) |
69.4 (20.8) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 35.0 (1.7) |
38.9 (3.8) |
45.4 (7.4) |
51.7 (10.9) |
60.6 (15.9) |
70.8 (21.6) |
75.5 (24.2) |
73.3 (22.9) |
66.6 (19.2) |
55.2 (12.9) |
43.1 (6.2) |
34.0 (1.1) |
54.2 (12.3) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 22.3 (−5.4) |
25.3 (−3.7) |
30.1 (−1.1) |
35.0 (1.7) |
43.6 (6.4) |
52.9 (11.6) |
59.6 (15.3) |
58.3 (14.6) |
51.3 (10.7) |
39.9 (4.4) |
28.1 (−2.2) |
21.5 (−5.8) |
39.0 (3.9) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 5.1 (−14.9) |
9.9 (−12.3) |
17.4 (−8.1) |
24.2 (−4.3) |
31.2 (−0.4) |
43.9 (6.6) |
53.3 (11.8) |
52.4 (11.3) |
40.5 (4.7) |
26.1 (−3.3) |
14.9 (−9.5) |
8.2 (−13.2) |
4.1 (−15.5) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −7 (−22) |
−5 (−21) |
8 (−13) |
16 (−9) |
24 (−4) |
31 (−1) |
38 (3) |
46 (8) |
30 (−1) |
11 (−12) |
−3 (−19) |
2 (−17) |
−7 (−22) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 0.93 (24) |
0.65 (17) |
0.70 (18) |
0.39 (9.9) |
0.46 (12) |
0.26 (6.6) |
1.36 (35) |
1.74 (44) |
1.12 (28) |
0.96 (24) |
0.62 (16) |
0.76 (19) |
9.95 (253.5) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 0.7 (1.8) |
0.1 (0.25) |
0.2 (0.51) |
0.2 (0.51) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.3 (0.76) |
0.1 (0.25) |
1.6 (4.08) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 4.3 | 4.3 | 4.3 | 3.1 | 3.3 | 2.1 | 8.0 | 8.6 | 5.6 | 4.8 | 4.2 | 5.0 | 57.6 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 1.6 |
| Source 1: NOAA[10] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: National Weather Service (mean maxima/minima 2006–2020)[11] | |||||||||||||
Accessibility
Much of the region is accessible only by foot or unpaved road though major highways and paved roads cut across the area. The towns of Cameron and Tuba City, both on the Navajo Nation, are two major settlements. A permit is required for all backroad travel on the Navajo Nation.[12]
Gallery
 The Painted Desert, Petrified Forest National Park
The Painted Desert, Petrified Forest National Park The gray and red colored bands across the landform are typical of most geologic features in the Painted Desert.
The gray and red colored bands across the landform are typical of most geologic features in the Painted Desert. Painted Desert with logs of petrified wood, Petrified Forest National Park
Painted Desert with logs of petrified wood, Petrified Forest National Park- 360° panorama at Tiponi Point
See also
References
- ↑ "Painted Desert". Geographic Names Information System. USGS. February 8, 1980. Retrieved May 5, 2013.
- ↑ Jaeger, Edmund C. The North American Deserts. (cited by Trimble. The Sagebrush Ocean. p. 10.)
- ↑ Granger, Byrd H. (1960). Arizona Place Names. University of Arizona Press. p. 18. Retrieved 6 December 2011.
- ↑ "Wilderness camping" (PDF). Petrified Forest National Park. NPS.
- ↑ Chronic, Halka, Pages of Stone: Geology of Grand Canyon & Plateau Country National Parks & Monuments, Mountaineers Books; 2nd ed., 2004, pp. 131–34 ISBN 978-0-89886-680-3
- ↑ Baars, Donald L., Navajo Country, University of New Mexico Press, 1995 pp. 47–53 ISBN 0-8263-1587-9
- ↑ Baars, Donald L., The Colorado Plateau: a Geologic History, University of New Mexico Press, 1983, pp. 163–68 ISBN 0-8263-0599-7
- ↑ "Grand Canyon and Other Spectacular Sights in Arizona", on-the-matrix.com, "North America on the Matrix: Grand Canyon, Painted Desert, Petrified Forest, Monument Valley". Archived from the original on 2013-02-20. Retrieved 2012-05-05.
- ↑ Arizona Annual Precipitation Map
- ↑ "U.S. Climate Normals Quick Access – Station: Painted Desert NP, AZ". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved March 25, 2023.
- ↑ "NOAA Online Weather Data – NWS Flagstaff". National Weather Service. Retrieved March 25, 2023.
- ↑ "Travel Navajo Nation". Navajo Nation Parks & Recreation. Archived from the original on July 28, 2014. Retrieved May 5, 2013.
External links
- Regional map for Navajo Lands
- Regional Map and Visitor Information for Hopi Lands
- National Park Services Website – Petrified Forest National Park
- Geology of the region
- Grand Canyon and Other Spectacular Sights in Arizona, on-the-matrix.com, (area of Painted Desert, 7500 sq mi
- Ecological Subregions of the United States – US Forest Service
- Petrified Forest Wilderness Area at Wilderness.net
