 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
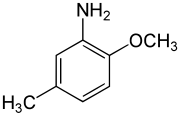
2-Methoxy-5-methylaniline | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.018 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H11NO | |
| Molar mass | 137.179 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Melting point | 51.5 °C (124.7 °F; 324.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 235 °C (455 °F; 508 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
para-Cresidine is an organic compound with the formula CH3OC6H3(CH3)NH2. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. The compound features both amine and methoxy functional groups. It is used as an intermediate in preparation of dyes and pigments.
Synthesis and reactions
The compound is obtained in several steps from 4-chlorotoluene. Nitration gives mainly 3-nitro-4-chlorotoluene, which reacts with methoxide sources to give 4-methoxy-2-nitrotoluene. Reduction of this nitro compound affords the aniline.[1]
Sulfonation with oleum gives 4-amino-5-methoxy-2-methylbenzenesulfonic acid. This sulfonic acid is a precursor to allura red AC, a red food coloring.[1]

Allura Red AC is a popular food coloring agent made from para-cresidine.
References
- 1 2 P. F. Vogt, J. J. Gerulis, "Amines, Aromatic" in Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_037
External links
- International Chemical Safety Card, Center for Disease Control
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.