In geometry, the Parry point is a special point associated with a plane triangle. It is the triangle center designated X(111) in Clark Kimberling's Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers. The Parry point and Parry circle are named in honor of the English geometer Cyril Parry, who studied them in the early 1990s.[1]
Parry circle
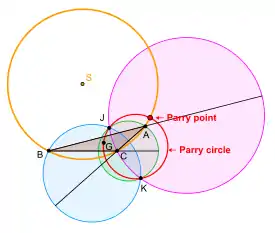
Let △ABC be a plane triangle. The circle through the centroid and the two isodynamic points of △ABC is called the Parry circle of △ABC. The equation of the Parry circle in barycentric coordinates is[2]
The center of the Parry circle is also a triangle center. It is the center designated as X(351) in the Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers. The trilinear coordinates of the center of the Parry circle are
Parry point
The Parry circle and the circumcircle of triangle △ABC intersect in two points. One of them is a focus of the Kiepert parabola of △ABC.[3] The other point of intersection is called the Parry point of △ABC.
The trilinear coordinates of the Parry point are
The point of intersection of the Parry circle and the circumcircle of △ABC which is a focus of the Kiepert hyperbola of △ABC is also a triangle center and it is designated as X(110) in Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers. The trilinear coordinates of this triangle center are
See also
References
- ↑ Kimberling, Clark. "Parry point". Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- ↑ Yiu, Paul (2010). "The Circles of Lester, Evans, Parry, and Their Generalizations" (PDF). Forum Geometricorum. 10: 175–209. Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W. "Parry Point". MathWorld—A Wolfram Web Resource. Retrieved 29 May 2012.