Penny, British Columbia | |
|---|---|
Locality | |
 Location of Penny in British Columbia | |
| Coordinates: 53°51′00″N 121°17′00″W / 53.85000°N 121.28333°W | |
| Country | Canada |
| Province | British Columbia |
| Land District | Cariboo |
| Regional District | Fraser-Fort George |
| Geographic Region | Robson Valley |
| Elevation | 632 m (2,073 ft) |
| Area code(s) | 250, 778, 236, & 672 |
Penny, between Longworth and Dome Creek on the northeast side of the Fraser River in central British Columbia, offers an access point for outdoor recreational activities.[1][2] With a community hall and 15 permanent residents,[3] No utilities infrastructure exists. Prior to the post office permanently closing on 31 December 2013, the community was the only one in Canada that still relied upon the railway for its postal service.
Transportation
A trackside signpost marks the flag stop for Via Rail's Jasper – Prince Rupert train.[4] The immediate Via Rail stops are Longworth to the northwest and Bend to the southeast.
History
Railway
Penny lies at mile 69.5, Fraser Subdivision.[5] Previously designated as Mile 159 during the line's construction, it was the area headquarters for Foley, Welch and Stewart, the prime contractor.[6][7][8] The Siems-Carey headquarters,[9] and a work camp existed at Mile 160.[6] Mr. Flannigan, a contractor at this camp, who considered all the camps maintained exceptional sanitary conditions, complained of IWW agitators seeking better wages and camp conditions.[10] The government sanitary inspector, who described camp conditions as fair, destroyed 20,000 lbs. of beef at about Mile 160, and bacon unfit for human consumption at other camps. He advised contractors to stop dumping garbage into the Fraser River.[11] Soon after, typhoid and diphtheria cases filled the medical outpost. In one 10-day period, the facility treated five victims of dump-car accidents, and the latest patient from Camp 162 had been cut in two.[12] The Miles 160 and 162 camps were both large, and a hospital was mentioned at Mile 160.[6][13] The true location of the hospital was likely Mile 73 (formerly around Mile 162.5).[3]
Not a planned station on the Grand Trunk Pacific Railway (the Canadian National Railway after nationalization), Penny remained absent from the 1916 timetable.[14] Exclusion from the 1919[15] and 1921[16] Official Guides probably reflects that only the employee timetables initially listed it as a footnote. Mention in the 1918 BC towns directory,[17] and on a c.1919 map,[18] suggest a 1917 or 1918 opening date for the station.
The settlement developed between Lindup to its northwest, and Guilford to its southeast. The name, a surname that emerged by the beginning of the 13th century,[19] was selected for unknown reasons.[20] Commonly claimed as an English place name on the list prepared by Josiah Wedgwood (submitted at the request of William P. Hinton, the railway's general manager),[21] no such location existed in the United Kingdom. Furthermore, the name Penny, in use by 1914, predated the station by at least three years. Formerly it was known just as the Engineers' Camp.[8]
Trains sometimes struck straying livestock,[22] but slowed to a crawl if sighted in time.[23] A passenger shelter likely existed prior to replacement in 1927 by a converted section tool house from Miworth. In 1947, the latter burned to the ground.[24] Transported the 5.5 miles (8.9 km) by railway flatcar,[25] Lindup exchanged its standard-design Plan 100-152 (Bohi's Type E)[26][27] station building for Penny's Plan 110-101 converted sectionmen's bunkhouse.[28] The CNR appointed the first station agent at this time.[29]
A burned out journal box on a freight car immobilized a train at Penny for seven hours in 1955.[30] During the 1960s, 18 cars derailed from an eastbound 98-car freight train in the vicinity, which delayed the westbound passenger train for three hours.[31] In another incident, a head-on collision with a bull moose, just outside Penny, derailed 23 cars of a westbound 50-car freight train.[32]
In 1970, CNR closed its section shop.[33] Isolated communities, like Penny, suffered when the Prince George–McBride way freight ceased operations in 1977.[34] The next year, Penny was one of the 11 communities between Prince Rupert and the Alberta border, where the CNR replaced its agent-operator position[35] with a resident serving as CN Express agent.[36]
The deep snow of the 1981/82 winter near Penny caused hundreds of collisions between moose and trains.[37] By this time, the station was boarded up apart from a small waiting room.[38] In 1988, an ice bridge was built across the Fraser River to carry the station by flatbed truck to its new home, the Prince George Railway & Forestry Museum.[39] Using a raft 18 months earlier, volunteers transported a heritage railway speeder shed and tool shed from Penny to that site.[40]
The remaining passenger shelter was removed in 1996.[41]
| Service | c.1917–c.1919 | c.1920–c.1921 | c.1921–c.1924 | c.1924–1931 | 1932–1942 | 1943–1977 | 1977–c.1989 | c.1990–present |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [17][42] | [43] | [44][45] | [46] | [47][48][49][50][51] | [52][53][54][55][56][57][58][59][60][61] [62][63][64][65][66][67][68][69][70] | [5][71][72] | [73][74][75][76][77] | |
| Passenger | Flag stop probably | Flag stop | Flag stop | Regular stop | Regular stop | Regular stop | Flag stop | |
| Way freight | Flag stop probably | Flag stop probably | Regular stop | Regular stop | Regular stop | Regular stop |
| Siding | Mile No. | 1922 | 1933 | 1943 | 1960 | 1965–72 | 1977–92 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Capacity Length) | Cars [44] | Cars [49] | Cars [52] | Cars [59] | Cars [64][67][69] | Feet [5][73][74] | |
| Penny | 69.2 | 54 | |||||
| Penny | 69.4 | 53 | |||||
| Penny | 69.5 | 46 | 52 | 54 | 2,530 |
| Other Tracks | Mile No. | 1920 | 1922 | 1933 | 1943 | 1960 | 1965 | 1968 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Capacity Length) | Cars [43] | Cars [44] | Cars [49] | Cars [52] | Cars [59] | Cars [64] | Cars [67] | |
| Unknown | 68.4 | Unknown | ||||||
| Red Mountain Lumber | 68.9 | Unknown | Unknown | |||||
| Penny Lumber | 69.2 | Unknown | ||||||
| Penny | 69.5 | 20 | 20 | |||||
| Red Mountain Lumber | 69.9 | 21 | ||||||
| Penny Sawmills | 69.9 | 19 | ||||||
| Penny Spruce Sales | 69.9 | 41 | ||||||
| Penny Forest Products | 69.9 | 42 | ||||||
| Eagle Lake Sawmills | 69.9 | 42 |
Map
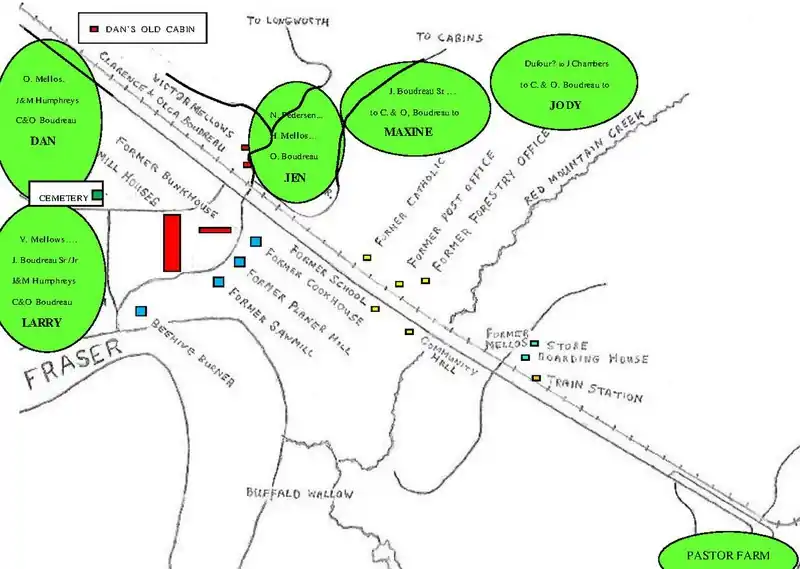
Contents are a composite of source data.[78][79] Clarence & Olga Boudreau's five properties are now owned by their children. . Larry has the former 108-acre Victor Mellows farm on the river. Immediately north, Dan has the former 153-acre Ole Mellos square property, of which 25 acres is north of the track. Jen has the former N. Pedersen 43-acre pentagonal farm, where her parents lived. Maxine has the farm owned by her grandparents. Jody (daughter of Diane Louise) has the former J. Dufour farm. The latter two are each 160 acres and square, with southern boundaries at the same latitude as Dan's one.[3][80] In addition to the mill accommodation, forestry, CNR and private dwellings existed.[81]
Hunting & trapping
Trapper Fred Rankin (1879–1964),[82][83] a keen astronomer and resident 1939–1964, who arrived in the district in 1910, had a cabin near the creek bearing his name[84] one-half mile (0.8 km) west of Red Mountain Creek). Resident Charles Hartsell (1862–1937)[85][86][87] was possibly the companion who mistook him for a moose and accidentally shot him in the arm a few miles from Penny in 1919.[88] Onufry Lewoniuk (c.1904–1933),[89] who was staying with the pair while trapping and hunting at Slim Lake about nine miles (14 km) southwest of Penny, died of exposure to the cold at the lake edge.[90]
John (Jack) Evans (1866–1948),[91] a homesteader,[17] had 100-mile (160 km) trapline through Penny in 1912/13.[92] He paddled and poled to Tête Jaune in 1897, continued to Fort George in 1905, and later settled near Penny.[93] A regular contributor to the Red Cross,[94] he lived alone in his cabin, which was about two miles (3.2 km) upstream and across the river. Famed for his horticulture, he was especially popular with the local children for his candy treats.[95][96]
Benjamin (Ben) (1883–1955)[97] & Adelia (Ada) (1886–1977)[98] Sykes had relocated from Slim Creek by 1918.[17] Their children were Bessie (1906–43),[99][100] David (1909–31),[101][102] Alice (c.1911–2003),[103][104] Mary (1913–?), Thelma (1915–?), Marjory (1918–?),[105] Leona (1922–80),[106] and Faye Lucille (c.1923–2003).[107][108] When the family left in 1924, the school closed owing to insufficient pupils.[109]
By 1921, the recognized guides for big game hunters in the Penny area were B. T. Sykes,[110] C. Hartsell and J. R. Norboe (c.1853–1921) (Narboe alternate spelling).[17][111] Ben had guided with John Norboe,[112] who died of a seizure in Nels Pedersen's house . John's brother Mac drowned that year at Eaglet Lake,[3] but was misreported as Slim Lake.[113]
Forestry
A. Roy Spurr (1885–1954),[105][114] who arrived at the Tête Jaune railhead in 1911, was a fur trader, who operated a store, café and accommodation, and provided a bookkeeping service, at camps during the railway construction. Using his savings, he opened a sawmill at Penny in 1917,[115][116] later buying out his partners. The mill lay south of the village on the riverbank. As early as the 1920s, fellow lumber operators recognized his sawmilling and business expertise and sought his advice.[117] Spurr's Red Mountain Lumber Co and the Penny Lumber Co. were both in operation by 1918,[17][118] but a later misconception that the former opened years later possibly inspired the questionable claim that Spurr also had an ownership interest in the latter.[119]
In bankruptcy by 1921,[120] the assets of the Penny Lumber were acquired by company president, George H. Lipsett (1866–1955).[87][121][122][123] Located south of the CNR track on Rankin Creek,[124] it operated as Penny Lumber,[125] and then as G.H. Lipsett Lumber,[126] until fire totally destroyed the mill in 1926.[127]
The narrow strip of accessible spruce forest bordering the railway that stretched some 100 miles (160 km) east of Prince George was known as the East Line.[128] In the 1920s, with logging limited to the winter and fall seasons to facilitate the hauling of logs over snow and ice, loggers were transient. However, year round work existed in sawmill towns such as Giscome, Aleza Lake, Hutton, Penny, and Longworth.[129] Injuries and death were common in sawmills and logging camps. Sawyer Laughlin McKenzie (1856–1923)[130] was killed when a saw severed his body from head to hips at the Red Mountain Lumber Co.[131]
The proceeds from selling Red Mountain Lumber Co. during the 1928[132] boom year provided Spurr with the funds to acquire other mills at bargain prices during the Great Depression.[133] The purchasers, who were owners of Cranbrook Sawmills, dismantled their mill at Otway, and either sold or relocated the machinery to Penny.[134] Like other sawmills during 1930–32, the Penny mill, then owned by the Joseph Campbell and John (Jack) Myers (1881–1960)[135] partnership,[136][137] scarcely operated.[13] In 1932, fire completely destroyed the sawmill and yard lumber.[138] At the time, Newlands, Snowshoe and Sinclair Mills were the only ones sawing, the latter having a big logging camp at Penny.[139]
During the 1920s, W. Langmuir was the district forester.[83][140] The forest ranger, residing in Penny for the Penny Ranger District covered an area that stretched from Dewey to Rider. His dispersed field staff,[141] which were seasonal from spring to fall, travelled by boat or speeder.[142] In 1948, two forestry speeders carrying 17 men to a forest fire at Loos collided near Bend. While the two most seriously injured went by freight train to Prince George, an amphibian plane later landed on the river at Penny to fly five of the less seriously injured for medical treatment.[143] The ranger position was eliminated in the mid-1960s.[144]
In 1933 Myers bought out his partner,[145] and the following year rebuilt the Red Mountain Lumber Co. mill.[146] In 1940, the 50,000-foot per shift capacity sawmill was again destroyed by fire, but the planing mill and processed lumber piles escaped conflagration.[147] Fulfilling his prior commitment,[148] Myers sold the mill to John F. McMillan and C. Earl Jaeck (1904–52), formerly at Bend,[149][150] who changed the name to the Penny Sawmills.[151] Jaeck died in a train/truck collision.[152]
In 1941, Elizabeth (1906–91)[153] (né Coats of Longworth, C. Earl Jaeck's cousin) & Rory (Roy) R.M. McGillivray (1903–94), formerly at Bend,[154][155] relocated with children S.T. Michael (1930–2015) and Barbara (1935–2015),[156] when Roy became general manager at the Penny mill.[157] Elizabeth headed the local Red Cross fundraising effort during World War II.[158]
In 1942, a new dry kiln was installed,[159] and several new homes and bunkhouses were constructed on the mill site to accommodate the demand from running two shifts.[160] Since the homes mostly lacked indoor plumbing, outhouses were the norm and water came from a tap at the end of the road.[161] The following year, fire destroyed the planing mill boiler room,[162] putting it out of operation for 6 weeks.[163] This may have been the occasion when a passing CNR locomotive rescued part of the building.[164] In 1945, labour shortages closed one logging camp.[165] The company name changed again to Standard Tie and Timber, when Standard Forest Products acquired the mill in late 1945 or early 1946.[166] After an absence, Roy McGillivray returned[167] as general manager.[151][168] The family relocated to Prince George in 1953.[169] On cremation, Roy's ashes were scattered in the Fraser at Penny.[170]
In 1947, the large bunkhouse was constructed at Penny.[171] The following year, the mill burned down,[172] and a portable mill set up at the mouth of the Red Mountain Creek was used until the old mill was rebuilt.[151][173] In 1952, renamed as the Penny Spruce Mills,[174] the Totem Pole group, controlled by the Thurston family, purchased the operations, which included the bunkhouse and 35 family residences.[175] Leboe Bros. of Crescent Spur provided mainly fir logs from the Goat River area, which were floated down the Fraser to the mill.[176]
The mill, which employed about 120 during summer and 45 in winter, plus 40 at the logging camps,[177] was one of the hardest hit by the strike of 1953.[178] In 1955, the mill cookhouse burned to the ground.[179] Closed in 1958,[180] after the Bank of Montreal called the operating loan,[177] the 100,000-foot capacity sawmill, steam and diesel power plants, 78-man bunkhouse, cookhouse, company houses, machine shop, garage, tractor house and various equipment were soon auctioned by court order.[181]
During the 1940s–50s, as many as three sawmills operated in the area.[124][182] The main mill, bought by Eagle Lake Lumber of Giscome, was renamed Penny Forest Products,[183] and continued as a much smaller operation.[180] In 1963, fire destroyed the mill and powerhouse, with only part of the trimmer left standing.[184] Fire damage and outdated equipment made the investment in a rebuild unrealistic.[185] Subsequently, Gordon Geddes ran portable mills until all sawmilling activity ceased in 1965.[124][186] Northwood inherited the defunct Penny mill when it acquired the Eagle Lake mill in 1966.[187] Long abandoned, the beehive burner, one of the largest in BC's history, still stands.[188]
The back-to-the-land movement peaked in the 1970s, with two tree planting companies and fire suppression crews based in Penny.[189] The movement largely comprised hippies, many U.S. draft dodgers, who temporarily settled along the East Line. In addition to occupying vacant houses, a commune existed by the river, which locals called "Buffalo Wallow".[190]
Community
Population estimates were 25 (Rev. W.J. Patton)[191] and 50–85 (Wrigley)[17] for 1918, 200 by 1920,[87] 100 by 1928,[192] 100 by 1934, 203 for 1943 and 1944, and 200 for 1948.[193][194] The population peaked in 1957/58 at 675, which included the logging camps.[180][186]
Commonly, the postmaster in such towns was also a storeowner. Nels Pedersen (c.1885–?),[17][122] the first postmaster 1916–19,[195] ran a general store 1914–27 as a sole proprietorship or in partnership as Johnston & Pedersen.[196] Thomas B. (1877–1952)[197] & Betty Fae (c.1885–1945)[198] Wall were storeowners,[105][199][200][201] and she was postmaster 1919–25. William Birt and Joseph Melling purchased this store, with Birt as postmaster 1926–28.[192][195][202][203]
Samuel (Sam) (1895–1940)[105][204] & Annie (1890–1931)[205] Michaylenko,[206] who arrived as the CNR section foreman around 1919–20, operated a store 1929–31, and apparently applied to be postmaster.[195] Their children were Nettie (1921–?), William (Bill) (1923–58),[207] Helen (1925–?),[208] Joseph (Joe) (1926–99),[209] Florence (1928–?),[210] Jessie (1930–?), and Magdelina (1931–?). When Annie died, Sam assumed responsibility for the children, except Magdelina, whom the Hinsbergers adopted. When Sam died,[211] Nettie cared for her siblings.[212] On adulthood, the children left Penny.[213]
Siblings Ole (1882–1956),[214] Halvor (1891–1973),[215][216] and Ingeborg L. (1884–1952)[217][218] Mellos relocated from neighbouring Guilford in 1927.[219] While the brothers developed a farm,[220] Ingeborg purchased the Pedersen general store,[192] and was postmaster 1929–38.[195] In 1929, Halvor Mellos formed the Mellos & Johnson Logging Co.[221] Halvor, who became Ingeborg's business partner, was postmaster 1938–48.[195] Together, they purchased the Bert and Melling store and sold their original property.[222]
In 1932, Halvor married[223][224] Anna Marie Haugen (1908–2008),[225] who arrived in 1930.[226] They raised their own daughter, Katherine, and niece Kathleen Johnson, after the death of Ole's wife Emma (c.1897–1942).[219][227] A 1936 fire destroyed their hotel and store. Recently constructed and equipped with all modern conveniences, it was the most popular accommodation between Longworth and McBride.[228] Their private hydro plant supplied electricity,[229] and unlike most properties relying upon wells, they had running water.[230] Buying the bunkhouse buildings at the abandoned relief camp , and transporting the wood by flatcar, Halvor rebuilt his house, storage and general store.[231]
For many years, Anna Mellos managed their rooming house[92][232] close to the store, which catered to short-term stays.[233] After selling the store, Halvor performed odd jobs in the community.[234] On Katherine's marriage to Jack Clements in 1953, the couple remained in Prince George.[235] Although Kathleen married William Isfan at Penny in 1955, the couple were never residents.[236] Anna resided in Penny 1930–95.[92]
In 1935, the widowed Victor Mellows (1898–1994),[237] his mother Anna (1862–1943),[238][239] and three sons Arne, Ivar and Oscar settled in Penny. Victor initially farmed, then worked at the sawmill. After Ivar and Oscar had left, Victor relocated in 1956.[240] Returning from World War II,[241] Arne Mellows married[242] Carrie Benson (1923–2012) from Bend.[243] Their children raised in Penny were Karen,[244] Lloyd,[245] and Craig.[246]
In 1948, Arne, and brother-in-law Carl A. Benson (1928–2015) from Bend,[247] bought the Mellos' store, trading as Penny Merchants,[248] and then as Penny Mercantile Co.[249] The following year, Carl sold his share to Oscar.[250] Two years later, Arne installed a gas pump for the increasing number of vehicles.[251] Formerly, fuel came by rail in barrels.[3] Arne was postmaster 1948–65,[195] at which time the store closed permanently,[252] and the family departed for Prince George.[253]
Jack Taylor opened a coffee shop in his pool hall,[254] and sold the business to Mr. & Mrs. C. Kirkwood.[202][255]
Philippe (1900–84)[256][257] & Anna (1905–83)[258][259] Michaud, who resided 1952–61, opened the Dew Drop Inn, a coffee shop, poolroom and accommodation for boarders. Their children were Roland, Emile, René, Gisele, Madeleine, Fernande (c.1936–2008),[260] Gilberte, Philip, Lorraine (1942– ),[261] Louis, Louise, and Jeannie.[262] Emile, who married Helen Bechtel,[263] raised three children there.[264] He stayed 1946–60[265] and subsequently remarried. Other adult siblings came and went.[266] Fernande (Fern) married[267] Mike Saiko (1927–98)[268] a local,[269] and their daughter was born in Penny. Gilberte married James (Jim) Kruger,[270] and moved away.[271] René, who played violin, suffered work and sports injuries.[272] Coming and going,[270] he married Teena Teichroeb in 1959. Lorraine married Richmond Lozeau,[273] and moved away. Philip (Phil), who played guitar and sang,[274] remained longer in Penny. Gisele married[266] Bertil Stavely (c.1934–2014),[275] and their three children were born while at Penny. Philippe, Anna and their three youngest left in 1961.[262]
The first school, held in an old bunkhouse behind the sawmill, opened in 1920 or 1921, with Miss H. Thomas (possibly 1903–?)[276] filling in until the arrival of Mrs. L.O. Cameron as the inaugural teacher.[277] Owing to low student numbers, it closed 1925–29. A one-room school was built as a replacement in 1930.[278] To facilitate a second teacher,[279] it was remodelled as two classrooms in 1943.[280] The following year, a teacherage was built on the school grounds,[281] with propane lighting added in 1955.[282]
The last of the three facilities, a two-room school opened for the 1953/54 year,[283] with propane lighting added in 1954.[284] The former building was moved off the grounds.[285] The school closed for six years during the 1970s,[182] but students taking correspondence courses continued to use a classroom.[286] It reopened in 1977 with 13 students.[287] Enrolment for 1945–50 in Grades 1–9 was 27–32, 1953–60 in Grades 1–8 was 31–51, 1963–70 in Grades 1–7 was 6–34, 1970–78 in Grades K–7 was 7–13,[277][288] and 1981–84 in Grades K–7 was 10–12.[289] Having only seven students, the school closed permanently in 1985,[290] with the building ultimately removed.[186]
The community club, formed in 1932,[291] held functions for nine years in the sawmill cookhouse.[292] The community hall was built in 1941.[293] The building, severely damaged by heavy snow in 1946,[294] was repaired and an electrical generator installed two years later.[295] The hall hosted country artists, professional entertainers, movie screenings and many weddings.[296]
John E. (1906–87)[297] & Jean (1909–96)[298][299] Humphreys arrived in late 1946[300] or early 1947. To fill individual customer orders, John, as shipper, coordinated product through the planer mill and into boxcars for delivery. Their children were John A. (1932–2006),[301][302] Jean (1933–2002),[303] James (Jim) (1940–2011),[304] and Jerry (1945– ).[305] John Jr. married Margaret Boudreau. Jean Jr. left,[306] trained as a nurse,[307] and married Arne May.[308] John Sr. rented and showed movies in the community hall. The Friday night screenings were weekly in the summer and biweekly in the winter.[309][310] Admission was 50 cents.[311] Active in the social life,[312] Jean Sr., a registered nurse,[313] delivered 14 of the community babies.[302][314] On buying the Dome Creek store, they left in 1957 (1947 a misprint).[315][316] After boarding away for high school,[317][318] Jim joined his parents at Dome Creek.[319]
Badminton was popular.[320] The hall was a venue for community dances during World War II,[321] when many were in aid of the Red Cross.[322] The post-war dances[323][324] often attracted visitors from surrounding communities.[325] The hall, falling into disuse during the 1960s, was renovated in 1971 and used for badminton during the 1970s–1980s.[326]
In his role as rector of All Saints Anglican, McBride, Rev. Duncan Cameron regularly conducted Sunday evening services in the Penny schoolhouse,[327] as did his predecessor, Rev. J.J. Cowan, each month.[328] A Sunday school commenced in 1946.[329] St. Paul's United Church, McBride, also held evening services in the Penny school.[330] The priest came from Giscome each month to St. James Catholic Church, which opened in 1954.[186] Formerly, their services were conducted in the school,[331] with Catholic, Anglican and United alternating weeks. The deconsecrated Catholic building became a residence.[332]
When the mill closed, most of the population left. Some abandoned their privately owned houses, which had become worthless.[333]
The Penny cemetery, 200–300 feet along the side road where the boat ramp road makes a right angle bend,[334] is on land provided by Halvor Mellos.[335] Volunteer male labour produced the coffins and dug the graves, and the women prepared the bodies.[336]
A homecoming reunion for former residents occurred August 18–20, 1995,[337] for which the book covering the community's history was compiled.[338] At the time, the permanent population of 11[186] was meagre in relation to the 36 dwellings.[339]
Boudreau family
Joseph (Joe) (1889–1969)[340] & Bessie (1894–1983)[341] Boudreau[203] arrived in 1923. They built a house on their preemption in 1928. Joe was a trapper and logger,[342][343] who could play the violin.[302] Bessie, an avid gardener, who delivered many of the community's babies,[344] could play the piano, flute and harp.[302] Their children were M. Isabelle (1923–2001),[345] Eveline (1925–98),[346] Joseph E. (Joe Jr.) (1929–91),[347][348] Clarence (1931– ),[349] E. Jack (1933–2018),[350] Margaret (1934– ),[302] and June. The family made their own entertainment, singing and playing musical instruments, and the community attended these gatherings at their place.[351]
M. Isabelle left, but returned for her wedding to Peter Motiuk (1920–88).[352][353] Never residing as a couple in Penny, their children were Patricia (Pat) and Cary.[354] Isabelle provided a home away from home to family members who came to Prince George for high school.[345]
Eveline married[355] resident Jack McKinley (1924–2017),[356] a talented Prince George piano player. They supplied the music for many events.[357] Their children raised in Penny were Gail,[358] Barry,[359] and Rocky L.,[360] with Melody and Charlene born after the family left in 1956.[361]
Josie married William F. (Bud) Proctor in 1946.[355] Months earlier, Bud, a local logger, suffered a skull fracture when struck by a falling tree.[362] Josie and daughter Sandra[363] spent part of 1947 with Bud in Merritt.[364] Josie returned to Penny prior to the birth of son Dwayne.[365] Tragically, 20-month-old Sandra, died of accidental ingestion of gasoline.[313] Janet A.[366] and J. Mark[367] were born subsequently. In 1956, Josie left permanently to work in Prince George.[368] Remarried,[369] she and Marcien Fisher, of Penny,[370] had three children.[371]
Joe Jr. married Edith (Penny) Lammle (1934–2011)[372] at Penny.[373] Their children raised there were Rhoda,[374] Donna (1953–2009),[375] Judy,[376] and William. Joe, a sawfiler then millwright, departed with his family to pursue other work opportunities.[377]
Clarence married Olga Horn (1932– ),[378] one of the two teachers who had arrived for the 1950/51 school year.[379] Their children Dan,[380] Diane Louise (1954–2009),[381] Larry,[382] Maxine, and Jenny, attended the Penny school, as well as three of the grandchildren.[383] Dan has authored five books,[384] When 15, Clarence joined his father and older brother in driving their horse team that hauled logs for milling. In 1956, he bought a Caterpillar D6 to clear their land for potato farming.[385] When cattle ranching proved unprofitable, he focused on logging, land clearing and snowplowing. He was fire warden for many years, and ran (1980–1996)[386] the salmon hatchery (1980–2006) located on their property.[387] In retirement, he voluntarily maintained the Longworth–Penny road with his Cat D6,[386] and remained a resident for nearly 80 years.[349] During the 1970s, when the school closed temporarily, Olga supervised the correspondence course children.[388] Although away from teaching while raising her children, she did substitute when needed. She worked in, and did the bookkeeping for, the hatchery. She also kept a large garden and canned the produce.[386] They acquired their first electricity generator in 1982. Diane Louise is the most recent burial at the cemetery. Clarence, having resided for 80 years, the couple left in 2011.[3]
E. Jack and ex-wife, Andreen E. Spoklie (1942–2015), had two children, Kelly and Kim.,[389] Jack worked various jobs in the mill and in driving logs down the river.[390] In 1967, residents protested the closure of their post-office and it reopened after six weeks.[391] Jack was postmaster 1967–76,[202][392] chair of the citizens committee,[393] and remained a resident.[394] He left in 1976.[395] He finished his career elsewhere as a licensed scaler, an industrial first-aid attendant, and forest firefighter mostly with the Ministry of Forests.[350][396] In 1999 on retirement, he wrote the first of his 10 published books on the region's history and personalities.[350]
Margaret married logger[397] John A. Humphreys.[398] Their children were David J.,[367] James (Jim) C.,[399] and Allan. By 16, Margaret could harness and work her father's horse team. Starting work at 15, John spent about 15 years at the lumber camps or the mill.[334] The family left in 1965.[302]
June Boudreau worked briefly in Prince George,[368] before marrying William (Bill) Benedict (1928–2013),[3] and having children Julie[400] (died of SIDS at six months), Shirley (Allannah), Darlene, and Wayne. The Penny station was busy for most of Bill's tenure as CNR station agent 1954–65, but the family departed after sawmilling activity ceased. In 1993, he returned to live in Penny for a number of years,[186][401] and his ashes were spread at the cemetery.[3] Remarried, June Vandermark has been a prolific writer of letters to the editor, which criticize mainline religious,[402] environmental,[403] and sundry matters.[404]
Pastor family, scouts, guides & polio outbreak
Joseph Pastor (1896–1982)[405][406] settled in 1934. His wife Mary (1900–84),[407] and children Mary E. (1920–86),[408] Theresa (Terry) M. (1921–84),[409] and Joseph (Joe) (1925–2006),[410] joined him from Hungary.[411] Although he worked in the sawmill[412] during the earlier years, the farm[413] was his primary involvement. Mary Sr. delivered milk, cream, butter and cheese to residents.[414] On retiring in 1973, they left.[415]
Joseph was also a hunting guide, who had been shot during World War I and the bullet was removed from his elbow in 1944.[416] His Hungarian friend, Joseph Kobra (1902–65),[417] a sometime Penny resident since the 1940s,[418][419] followed him from Lindup, remaining in the Penny/Lindup area for 40 years.[420]
In 1937, Mary married[421] Gustof (Gus) Frenkel (1905–83),[422] but they never resided as a couple in Penny. Their children were John, Margaret, Sheila and Marie.[414][423]
In 1943, Terry married[424] J. Earl Lousier (1924–2011).[425] Initially a sawmill blade tooth setter, Earl became a sawyer after two years. Danny, their son, was born in Penny,[426] with Theresa (Terry) Ann, Bonita (Bonnie), and Lorraine born after the family left in 1952.[427][428]
During the mid-1940s, a Scout troop and Wolf Cub pack operated. Charles (Charlie) Adcock, the CNR section foreman, was scoutmaster, and Earl Lousier was his assistant. Thurston Berg led the Cubs.[429] On Charlie's transfer,[193] Larry Willington became scoutmaster and Alice Sinclair had taken charge of the cubs,[430] but these activities soon folded.[431]
In 1946, Joe Jr. married[432] Marie Jopp (1924–2014).[433] Joe, who played trumpet at the dances,[434] months earlier had lost two toes in a logging accident.[355] Marie was one of the two teachers for the 1944/45 to 1946/47 school years, after which she was available as a substitute.[435] During the mid-to-late 1940s, she led the Girl Guides,[436] who were involved in a range of events.[437][438] In 1950, Marie was briefly confined to hospital in Prince George with suspected polio,[439] before convalescing at home.[440] Their children raised in Penny were Gary (1948– ),[441] Richard (Ritchie) (1949–2004),[410][442] Shirley (1961– ),[443] Stewart (1953–93),[444] and Terry-Lynn (1955– ),[445] with Ronnie born after the family left in 1955.[446][447]
In 1952, Mrs. R. Clark and Mrs. A. Ward are recorded as teachers for the Girl Guides and Brownies,[448] the latter company having been recently organized,[431] but these groups are not mentioned after 1953.[449]
John Kuz (1913–50)[450] was the only Penny resident to die of polio. He had arrived in Penny in 1937, where his wife Anne (probably 1917–2003) and baby Harold (probably 1937–2016)[451] soon joined them. They were active in community life,[452] and their subsequent children raised in Penny were Leona (1939– ),[453] M. Elaine (1943– ),[454] and John (1949– ). Initially a logger, John Sr. became a mill labourer, oiler, and finally millwright, where in 1943 he lost three toes in a mill accident.[455] In 1949, a 12-foot fall required a hospital visit.[456] On John's death in hospital at Prince George, public functions in Penny were cancelled and the school closed as a precaution,[439] which was repeated during another polio outbreak two years later.[457] The community collected almost $1,100 for the family,[458] who left in 1951.[459]
Riggs & Finer families
In 1928, widower Frederick (Dick) R. Finer (1884–1952)[460] arrived in Penny. The following year, his children Mabel (1914–2007),[461] Irene (1916–2002), and Allen (1918–2010), joined him. Mabel married[462] Wilbert (Bert) Riggs (1912–99) of Longworth[463] in 1932, where they homesteaded, before residing off and on in Penny from 1936. Bert was a logger, sawmill worker, and with Mabel, ran their small farm.
In 1937, Irene Finer left and married[464] N. Wilfrid Appleyard (c.1901–?).[465] Allen R. Finer enlisted during World War II,[466] was wounded,[467] married,[468] and settled in Vancouver.[469] His father soon followed.[470]
In 1942, the Riggs resettled in Penny.[471] Their children were Clarence (1933–45),[472] Lelia, Keith (1937– ),[473] Patricia (Pat) (1945– ),[474] and Juanita (Nita) (1947– ).[475] Clarence drowned at Guilford Lumber mill.[476] Mabel Riggs operated an iced confectionary booth from her front porch during the summertime.[477][478] Bert Riggs was hospitalized several times,[479] being evacuated by amphibian plane on one occasion.[480] After relocating to and from Prince George for a couple of years,[481] the family, except Lelia,[482] returned.[483] Keith left for work,[484] and Lelia I. married[369] Lawrence B. Tindill. (1927–2003).[485] Bert relocated for work in 1958, and Mabel, Pat and Nita joined him in 1963.[486][487] Nita married David Solecki,[488] and Pat married Cornelius Evert (Casey) Van Beek.[489]
Crime, calamity & safety measures
During the 1927 forest fire, women and children were temporarily evacuated by special train to Dome Creek.[3]
A sudden death in 1934 prompted an investigative visit by the coroner and a constable from Prince George.[490]
Logger G. Edward Hooker (1915–36), formerly at Bend,[491] slipped and drowned while breaking up a logjam. His body was found over seven months later downriver at Sinclair Mills.[492]
In 1944 and 1945, the police arrested the offenders responsible for break and entries at the store.[493]
A rolling log fatally crushed William Gorrick (1915–48).[494]
Although limited mentions of houses burning to the ground,[495] it was likely a common occurrence.
In 1957, safecrackers stole $4,000 in cash from the store.[496]
While hunting near Penny, Kalman Malzsencizky mistook his friend, Bela Bill Cservenka (1927–65),[497] for a moose and fatally shot him. First aid was administered immediately and after a boat trip back to the Pastor farm, where the victim died four hours after the incident.[498] At his trial, Malzsencizky pleaded guilty to criminal negligence.[499] Schervenka's widow was awarded $60,719 in damages under the provincial Families Compensation Act.[500]
A self-inflicted rifle wound took a hunter's life on the access road.[501][502][503]
In 1975, Imre Sorban fired shots at a boatload of people on the outskirts of Penny, forced another woman into a car, and later shot out two tires on the vehicle before he was subdued. Another victim sustained leg wounds from a shotgun blast. Midway through his trial, Sorban pleaded guilty to charges of carrying an offensive weapon and illegally confining another person.[504]
When ice jams upstream and downstream blocked the river during the 1980/81 winter, owners could not reach their cars parked on the west bank, and flooding submerged 13 vehicles and carried off several boats.[505] Though the townsite on higher ground was safe, houses in low-lying areas were flooded.[506]
Relief programs during the Great Depression
The Aleza Lake to Tête Jaune highway-construction relief project began in 1931. The seven camps between Aleza Lake and McBride housed 500 workers. Discontent in the camps prompted demands for increased wages, and strike action occurred in April and July 1932, at which time the workers departed for Prince George. In August 1932, the province redirected the men to these isolated locations, now designated as non-work relief camps. Camp 88, Penny,[507] was the largest of the group.[508] On 19 November 1932, a physical confrontation with the camp foreman led to his replacement and a police investigation.[509] On 25 November 1932, police arrested three agitators from the camp for travelling without railway tickets and they received one-month prison sentences. By month end, the camp held its full complement of 108 men. The camp closed in October 1933.[510]
The Penny location at about Mile 72 occupied the former GTP construction camp (formerly about Mile 162). In 1934, Edward (Ed) V. (1888–1951)[511] & Elsie (1904–95)[512] Chambers moved from Lindup to the camp, where Ed was employed, and by 1936, he worked at a logging camp across the river. Their children were D. Bernice (c.1923–?),[513] James (Jim) (1924–?), Marie (possibly 1926–2010),[514] Lillian Jean (c.1928–2002),[515] Charles Lindburgh (Lindy) (1929–79),[516] M. Jean (1930–2012),[517] and Bette.
The family settled in Penny just before World War II, with the children spending varying periods of their adult lives there.[518] Ed remained until his death, and Elsie stayed.[519] Bernice married Len Gagnon (1909–59),[520] who worked in the sawmill.[521] James (Jim) E. enlisted 1942–46,[522] married Marion Hooker (1924–2002) of Bend,[523] and settled in Vancouver.[524] Marie moved to Jasper,[525] and enlisted 1944–46.[522] She lived in Vancouver and married J. McNeil.[526] Lillian Jean enlisted 1944–45,[522] married[468] Chester Whelen (c.1921–2012),[527] and settled in Alberta,[528] but later married Michael Kosteck.[515] Lindy remained based in Penny,[529] married Alice Taylor, but later moved.[530] M. Jean married local Charles (Charlie) F. Benton.[531][532] Bette left for Vancouver and married.[533]
Roads
In 1947, Standard Tie and Timber graded a one-mile (1.6 km) road through the town. By 1951, there were 21 cars in the community, but still only one mile of road.[534] When Highway 16, linking Prince George and McBride, opened in 1969,[535] many residents parked their vehicles on the opposite bank of the Fraser River. In winter, the frozen river could usually be crossed by an ice bridge,[536] but if the weather was unusually mild, the train provided the only access.[537] A proposal for a reaction ferry or bridge access divided the community.[538] In 1995, volunteers upgraded a 12-kilometre (7.5 mi) logging road, and for the next 20 years, maintained this only road access to the community.[539] In 2017, the province agreed to maintain the private road to Longworth for two years.[540] A replacement contract is under consideration.[541]
Electricity, broadcast transmissions & communications devices
From 1929, the CNR telephone lines opened for public usage, linking Dome Creek with Prince George.[542] Fifty years later, the CN lines from Giscome still served Penny's crank-style phones[543] on a party line.[170] In the 1990s, the service continued to be erratic, because Telus could not justify the cost of dedicated lines for so few customers.[544]
Using a 150-foot wire strung between two 50-foot poles as an aerial, predominantly battery-powered radios received better reception from certain stations in Calgary or the U.S. west coast.[545][546]
Some places had diesel[182] or alternately powered generators.[547] Otherwise, oil or gas lamps provided light and wood-burning stoves heat.[548][549] Around 1950, the sawmill wired and supplied electricity to many company houses,[550][551] which ceased when the mill closed. There are no BC Hydro transmission lines.[92][552]
A new transmitter, installed by CKPG-TV on Mount Tabor in 1964, provided reception as far southeast as Longworth & Penny.[553]
Completed in 2014, the Telus cell tower near Dome Creek also serves over 16 kilometres (9.9 mi) of Highway 16 between Penny and Dome Mountain.[554]
Footnotes
- ↑ "Penny Red Mountain". www penny-redmountain.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 17 Jul 2010
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Clarence & Olga Boudreau recollections, Dec 2019
- ↑ "Penny flag stop". www.viarail.ca.
- 1 2 3 "1977 Timetable" (PDF). www.cwrailway.ca. p. 79.
- 1 2 3 Fort George Herald, 17 May 1913
- ↑ "Engineer's camps c.1913". www.gent.ca.
- 1 2 Diary of Ada Adelia Sykes
- ↑ Fort George Herald, 21 Jun 1913
- ↑ Fort George Herald, 12 Apr 1913
- ↑ Fort George Herald, 31 May 1913
- ↑ Fort George Herald, 7 Jun 1913
- 1 2 PRC 1995, p. 2.
- ↑ Waghorn's Guide. The Guide Co. Ltd. 1916. p. 74.
- ↑ The Official Guide. The National Railway Publication Company. 1919. p. 875.
- ↑ "The Official Guide" (PDF). www.cprr.org. 1921. p. 950.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "1918 BC Directory". www.bccd.vpl.ca.
- ↑ "Map of the Central Section of British Columbia / Shewing the Country Served by the Grand Trunk Pacific Railway". www.utoronto.ca.
- ↑ "Last name: Penny". www.surnamedb.com.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 27 Jan 1984 (44)
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 27 May 1957
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 15 Jun 1944
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 25 Apr 2000
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 38.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 4 Sep 1947, 16 Oct 1947 & 8 Jul 1989
- ↑ "Type "E" Mythology". www.oil-electric.com.
- ↑ "Vanishing BC GTP Railway stations". www.michaelkluckner.com.
- ↑ Bohi, Charles W.; Kozma, Leslie S. (2002). Canadian National's Western Stations. Fitzhenry & Whiteside. pp. 121, 136 & 141. ISBN 1550416324.
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 37.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 1 Sep 1955
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 14 & 15 Dec 1961
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 17 Jan 1967
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 24 Jun 1970
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 25 Jul 1977
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 2 & 8 Aug 1978
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 3 Oct 1978 & 13 Mar 1980
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 15 & 17 Sep 1982
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 23 Jan 1985
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 11 & 12 Feb 1988
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 19 & 21 Jul 1986
- ↑ Prince George Free Press, 21 Jan 1996
- ↑ "1919 BC Directory". www.bccd.vpl.ca.
- 1 2 1920 Timetable. Bulkley Valley Museum. p. 8.
- 1 2 3 1922 Timetable. Northern BC Archives. p. 8.
- ↑ 1923 Timetable. p. 70.
- ↑ 1925 Timetable. p. 105.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 12 & 19 Nov 1931
- ↑ 1932 Timetable. p. 58.
- 1 2 3 1933 Timetable. Northern BC Archives. p. 8.
- ↑ 1935 Timetable. p. 60.
- ↑ 1942 Timetable. p. 58.
- 1 2 3 1943 Timetable. Northern BC Archives. p. 9.
- ↑ 1945 Timetable. p. 61.
- ↑ "1946 Timetable". www.scribd.com. p. 59.
- ↑ 1949 Timetable. p. 59.
- ↑ "1950 Timetable". www.scribd.com. p. 59.
- ↑ "1956 Timetable" (PDF). www.streamlinermemories.info. p. 53.
- ↑ "1957 Timetable". www.traingeek.ca. p. 53.
- 1 2 3 1960 Timetable. Northern BC Archives. pp. 21–22
- ↑ "1961 Timetable (main)" (PDF). www.streamlinermemories.info. p. 39.
- ↑ "1961 Timetable (way freight)" (PDF). www.streamlinermemories.info. p. 48.
- ↑ "1963 Timetable" (PDF). www.streamlinermemories.info. p. 42.
- ↑ 1964 Timetable. Northern BC Archives. p. 44
- 1 2 3 1965 Timetable. Northern BC Archives. pp. 25–26
- ↑ "1966 Timetable". www.traingeek.ca. p. 38.
- ↑ 1967 Timetable. Northern BC Archives. p. 38
- 1 2 3 1968 Timetable. Northern BC Archives. pp. 25–26
- ↑ "1971 Timetable" (PDF). www.streamlinermemories.info. p. 19.
- 1 2 1972 Timetable. Northern BC Archives. pp. 25–26
- ↑ 1973 Timetable. Northern BC Archives. p. 18
- ↑ "1986 Timetable". www.scribd.com. p. 50, but scan p. 52.
- ↑ "1988 Timetable". www.scribd.com. p. 55, but scan p. 52.
- 1 2 1990 Timetable. Northern BC Archives. pp. 95–97
- 1 2 1992 Timetable. Northern BC Archives. pp. 103–105
- ↑ "1996 Timetable" (PDF). www.streamlinermemories.info. p. 40.
- ↑ "2011 Timetable". www.scribd.com. p. 44, but scan p. 24.
- ↑ Recent timetables
- ↑ Saville 2000, pp. prologue map, 9 & 10.
- ↑ May 2000, p. prologue map.
- ↑ Saville 2000, pp. prologue map & 7.
- ↑ Trolian, Sandra (2000). "Upper Fraser Historical Geography Project Transcript" (PDF). www.nbca.unbc.ca. p. 2.
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Fred RANKIN)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- 1 2 "1922 BC Directory". www.bccd.vpl.ca.
- ↑ PRC 1995, pp. 1 & 153–154.
- ↑ "Cemetery Project (Charles HARTSELL)". www.geneofun.on.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 27 May 1937
- 1 2 3 "1920 BC Directory". www.bccd.vpl.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 8 Oct 1919
- ↑ "Death Certificate (O. LEWONIUK)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 4 Jan 1934
- ↑ "Death Certificate (John William EVANS)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- 1 2 3 4 Prince George Citizen, 9 Aug 1995
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 9 Feb 1939
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 30 Jul 1942, 12 Nov 1942, 14 Jan 1943, 11 Mar 1943, 20 May 1943, 15 Jul 1943, 19 Aug 1943, 7 Oct 1943, 17 Feb 1944, 25 May 1944, 20 Jul 1944, 12 Oct 1944, 21 Dec 1944, 22 Feb 1945, 5 & 26 Apr 1945, & 7 Mar 1946
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 10 Jan 1946, 15 Jan 1948, 22 Jan 1948, & 12 Feb 1948
- ↑ PRC 1995, pp. 103–104.
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Benjamin Silas SYKES)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Ada Adelia SYKES)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Marriage Certificate (DAVIS/SYKES)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Bessie Rebecca DAVIS)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Marriage Certificate (SYKES/FOLLIS)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Death Certificate (David Benj SYKES)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Marriage Certificate (MARRINGTON/SYKES)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Obituary (Alice MARRINGTON)". www.abbynews.com.
- 1 2 3 4 "1921 Census". www.bac-lac.gc.ca.
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Leona Blanche WARDS)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Marriage Certificate (KANOPSKI/SYKES)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Obituary (Faye KANOPSKI)". www.abbynews.com.
- ↑ PRC 1995, pp. 165–168.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 12 Oct 1920
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 13 Sep 1921
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 3 Sep 1919
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 18 Jan 1921
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Albert Roy SPURR)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Fort George Herald: 9 Nov 1912 & 13 Sep 1913
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 16 Aug 1954
- ↑ Drushka, Ken (1998). Tie Hackers to Timber Harvesters. Harbour Publishing. p. 83. ISBN 9781550171891.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 2, 16 & 23 Aug 1918; & 1 May 1924
- ↑ PRC 1995, pp. 2 & 21.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 7 & 11 Jan 1921; & 1, 8, 15 & 22 Mar 1921
- ↑ "Death Certificate (George Humphries LIPSETT)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- 1 2 "1921 Census". www.bac-lac.gc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 1 May 1924
- 1 2 3 PRC 1995, p. 22.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 30 Aug 1921 & 28 Oct 1921
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 3 Jun 1926
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 10 Jun 1926
- ↑ Hak 1986, p. 14.
- ↑ Hak 1986, p. 137.
- ↑ "Cemetery Project (L.W. McKenzie)". www.geneofun.on.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 19 Jul 1923
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 8 Nov 1928
- ↑ Hak 1986, p. 98.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 2 May 1988(56)
- ↑ "Death Certificate (John Prince MYERS)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "1930 BC Directory". www.bccd.vpl.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 2 May 1988(57)
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 25 Aug 1932
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 11 Aug 1932
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 17 Feb 1922
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 26 Aug 1937, 27 Apr 1944 & 26 May 1949
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 19.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 24 Jun 1948
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 9 Oct 1964
- ↑ Hak 1986, p. 84.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 10 May 1934
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 12 Sep 1940
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 29 Aug 1940
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Charles Earl JAECK)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 21 Nov 1940
- 1 2 3 PRC 1995, p. 21.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 28 Apr 1952
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Elizabeth Forrest McGILLIVRAY)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Rory Roderick McClennan McGILLIVRAY)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 8 Jun 1994
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 16 Jul 1942, 11 Mar 2015 & 8 Jan 2016
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 127.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 4 Jun 1942 & 18 Jan 1945
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 21 May 1942
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 27 Aug 1942
- ↑ May 2000, p. 9.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 22 Jul 1943
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 9 Sep 1943
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 27 Jan 1984 (40)
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 30 Aug 1945
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 22 Aug 1946
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 3 Jan 1946 & 17 Apr 1947
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 28 Oct 1948, 9 Aug 1951 & 27 Nov 1952
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 21 Mar 1929, 28 May 1953, & 22 Jan 1991
- 1 2 PRC 1995, p. 172.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 12 Jun 1947
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 7 Oct 1948
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 16 Dec 1948 & 3 Mar 1949
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 3 Mar 1952
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 27 Nov 1952
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 27.
- 1 2 PRC 1995, p. 28.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 22 Oct 1953
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 29 Sep 1955
- 1 2 3 PRC 1995, p. 3.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 16 Oct 1959
- 1 2 3 Prince George Citizen, 2 May 1985
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 12 Apr 1961 & 24 May 1961
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 22 Mar 1963
- ↑ Boudreau 2000, pp. Interview #5: 2–3.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Prince George Citizen, 19 Aug 1995
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 10 Aug 1973 & 30 Jun 1988
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 25 Aug 1995
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 4.
- ↑ Saville 2000, pp. 1, 2, & 20–21.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 26 Aug 1958
- 1 2 3 "1928 BC Directory". www.bccd.vpl.ca.
- 1 2 Prince George Citizen, 17 Oct 1946
- ↑ PRC 1995, pp. 177–183.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Postmasters". www.bac-lac.gc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 8 Oct 1920, 18 Jan 1921, 30 Oct 1924 & 17 Jul 1941
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Thomas Bell WALL)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Betty Fae WALL)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "1921 BC Directory". www.bccd.vpl.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 14 Feb 1922
- ↑ Prince George Leader, 8 Mar 1923
- 1 2 3 PRC 1995, p. 66.
- 1 2 "1926 BC Directory". www.bccd.vpl.ca.
- ↑ "Cemetery Project (Samuel MICHAYLENKO)". www.geneofun.on.ca.
- ↑ "Cemetery Project (Annie MICHAYLENKO)". www.geneofun.on.ca.
- ↑ "1925 BC Directory". www.bccd.vpl.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 11 Jun 1958
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 4 Jan 1945 & 12 Jul 1951
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 4 Oct 1945 & 9 Jun 1999
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 22 Aug 1946 & 5 Mar 1953
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 23 May 1940
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 6 Nov 1941
- ↑ PRC 1995, pp. 140–142.
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Ole MELLOS)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Halvor MELLOS)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 31 Oct 1973
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Ingeborg K. MELLOS)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 26 Jun 1952
- 1 2 PRC 1995, p. 132.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 22 & 29 Aug 1929, 5 Sep 1929, & 5 Oct 1933
- ↑ "1929 BC Directory". www.bccd.vpl.ca.
- ↑ PRC 1995, pp. 63 & 132.
- ↑ "Marriage Certificate (MELLOS/HAUGEN)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 14 Jul 1932
- ↑ "Cemetery Project (Anna Marie MELLOS)". www.geneofun.on.ca.
- ↑ Mellos 2000, p. 1.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 12 Nov 1942, 10 Dec 1953 & 6 Oct 1955
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 30 Jul 1936
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 15 Jun 1933
- ↑ Mellos 2000, pp. 6 & 10.
- ↑ Mellows 2000, pp. 2–4.
- ↑ PRC 1995, pp. 96, 105 & 133.
- ↑ May 2000, p. 8.
- ↑ May 2000, p. 20.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 10 Dec 1953 & 18 Nov 1954
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 6 Oct 1955 & 24 Jan 1957
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Victor MELLOWS)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 19 Aug 1943
- ↑ PRC 1995, pp. 134–135.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 19 Mar 1953, 25 Mar 1954, 29 Mar 1956, 26 Apr 1956 & 30 Jul 1994
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 4 Oct 1945
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 5 Sep 1946
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 12 Dec 2012
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 15 Mar 1951
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 14 May 1953
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 10 Jan 1955
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 4 Dec 2015
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 27 May 1948
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 26 May 1960
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 81.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 12 Jul 1951
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 64.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 21 Jul 1986 & 12 Dec 2012
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 10 May 1951
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 6 Mar 1952 & 12 May 1952
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Phillippe Joseph MICHAUD)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 16 Jan 1984
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Marie Anna MICHAUD)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 4 Feb 1983
- ↑ "Obituary (Fern SAIKO)". www.edmontonjournal.ca.
- ↑ "Kin (Lorraine MICHAUD)". www.halls-vallees.com.
- 1 2 PRC 1995, pp. 136–140.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 6 Sep 1951
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 17 Jul 1952 & 14 May 1956
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 26 Sep 1960
- 1 2 Prince George Citizen, 19 Jul 1956
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 2 Jul 1953
- ↑ "Grave & kin (Michael SAIKO)". www.billiongraves.com.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 13 & 27 May 1948, 28 Jul 1949, 13 Apr 1950, 22 Jun 1950, 23 Nov 1950, 14 Dec 1950, 18 Feb 1952, 19 Jan 1956 & 18 Mar 1957
- 1 2 Prince George Citizen, 30 Sep 1954
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 19 Jul 1956 & 25 Apr 1957
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 6 Mar 1952 & 19 Mar 1953
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 8 Sep 1959
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 22 Apr 1954
- ↑ "Obituary (Bertil Joseph STAVELY)". www.yourlifemoments.ca.
- ↑ "Marriage Certificate (MUIR/THOMAS)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- 1 2 Hall, Barbara; Nellis, Kris (2012). School District No. 57 (Prince George) historical memories. (Volume II): people, places, programs & services. Prince George Retired Teachers' Association, Education Heritage Committee.
- ↑ PRC 1995, pp. 2 & 46.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 12 Aug 1943
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 15 Jul 1943 & 19 Aug 1943
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 14 Sep 1944
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 8 Dec 1955
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 24 Sep 1953
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 2 Dec 1954
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 20 Oct 1955
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 19 May 1972 & 16 Feb 1977
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 16 Sep 1977
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 2 Sep 1960 & 23 Oct 1963
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 4 Sep 1981, 20 Oct 1982, 21 Apr 1983 & 25 Oct 1984
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 22 May 1985
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 23 Jun 1932
- ↑ PRC 1995, pp. 9 & 229.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 18 Sep 1941; & 4 & 25 Dec 1941
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 7 Mar 1946
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 9.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 7 Oct 1948, 21 Sep 1950, 26 Jul 1951, 15 Nov 1951, 22 May 1952, 9 Sep 1954 & 25 Jul 1977
- ↑ "Death Certificate (John Edward HUMPHREYS)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Jean HUMPHREYS)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 2 Apr 1996
- ↑ Humphreys_b 2000, p. 1.
- ↑ Humphreys_a 2000, p. 1.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Prince George Citizen, 13 Oct 2016
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 9 Mar 2002
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 16 Mar 2011
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 21 Jan 1954
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 24 Apr 1952
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 30 Dec 1952, 7 Apr 1953, 27 May 1954 & 30 May 1955
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 29 Dec 1959
- ↑ Humphreys_b 2000, pp. 2–3.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 12 Aug 1948, 26 Jan 1950, 1 Sep 1955, 9 Jan 1956, & 12 Feb 1987
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 175.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 11 May 1950, 9 Aug 1951, 7 Aug 1952, 28 May 1953, 26 Apr 1956, & 2 May 1957
- 1 2 Prince George Citizen, 9 Sep 1948
- ↑ PRC 1995, pp. 107–109.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 27 Jun 1957 & 12 Feb 1987
- ↑ Humphreys_b 2000, pp. 1–3.
- ↑ Humphreys_b 2000, p. 3.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 28 Oct 1954, 21 Apr 1955, 22 Dec 1955, 5 Apr 1956 & 25 Apr 1957
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 18 Jun 1958 & 22 Oct 1958
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 25 Dec 1941, 10 Jan 1946, 7 Mar 1946, 20 May 1948, 16 Sep 1948 & 3 Nov 1949
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 25 Dec 1941, 5 Feb 1942, 2 Apr 1942, 14 May 1942, 3 Jun 1943, 9 Dec 1943, 6 Jan 1944, 6 Jul 1944, 26 Oct 1944, 4 & 21 Dec 1944, 22 Mar 1945 & 24 May 1945
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 16 & 23 Apr 1942, 4 Jun 1942, 16 Jul 1942, 25 Mar 1943, 23 Mar 1944, 20 Jul 1944 & 5 Jul 1945
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 7 Mar 1946, 16 May 1946, 31 Jul 1947, 13 Nov 1947, 20 & 27 May 1948, 8 Jul 1948, 16 Sep 1948, 6 Jan 1949, 3 & 24 Mar 1949, 2 Jun 1949, 13 Oct 1949, 6 Jul 1950, 14 Dec 1950, 11 Jan 1951, 22 Feb 1951, 6 Sep 1951, 8 Nov 1951, 7 Jan 1954, 13 Jan 1955, 2 Jun 1955 & 28 Mar 1957
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 17.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 6 Sep 1945, 18 Jul 1946, 5 Sep 1946, 4 Sep 1947, 15 Jan 1948, 5 & 26 Aug 1948, & 14 Jul 1955,
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 10.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 27 Mar 1947; 1 May 1947; 12 Jun 1947 (Bishop); 24 Jul 1947; 21 Aug 1947; 16 Oct 1947; 13 Nov 1947; 15 Jan 1948; 12 & 26 Feb 1948; 22 Apr 1948, 27 May 1948; 3 & 17 Jun 1948; 8 Jul 1948; 23 Sep 1948; 7 & 21 Oct 1948; 4 & 18 Nov 1948; 2, 16 & 30 Dec 1948; 27 Jan 1949; 10 & 24 Feb 1949; 3, 10 & 24 Mar 1949; 7 & 21 Apr 1949; 5 & 19 May 1949; 9 Jun 1949; 20 Oct 1949; 17 Nov 1949; 1, 15 & 29 Dec 1949; 12 Jan 1950; 16 Feb 1950; 16, 23 & 30 Mar 1950; 13 & 27 Apr 1950; 4 May 1950; 8 & 15 Jun 1950; 27 Jul 1950; 19 Oct 1950; 9 Nov 1950; 11 & 25 Jan 1951; 8 Feb 1951; 29 Mar 1951; 12 & 26 Apr 1951; 3 & 24 May 1951; & 23 Aug 1951;
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 3 Nov 1938; & 2 & 30 Oct 1941
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 15 Aug 1946
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 24 Jun 1948, 8 Jul 1948, 7 Oct 1954, 6 Oct 1955, 1 Mar 1956, 29 Nov 1956 & 28 Mar 1957
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 24 Jun 1948 & 2 Jul 1953
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 7.
- ↑ Boudreau 2000, pp. Interview #5: 3 & 11.
- 1 2 Humphreys_a 2000, pp. Supplementary Notes.
- ↑ Mellos 2000, p. 13.
- ↑ Boudreau 2000, p. Summary: 7.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 9, 19 & 21 Aug 1995
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 5 Feb 1996
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 22 Oct 1999
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Joseph Edward BOUDREAU)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Bessie May BOUDREAU)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 19 Aug 1995
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 83.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 26 Aug 1983
- 1 2 Prince George Citizen, 11 Apr 2001
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 24 Nov 1998
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Joseph Edward BOUDREAU)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 28 May 1991
- 1 2 Prince George Citizen, 16 Feb 2016
- 1 2 3 Prince George Citizen, 25 Jan 2018
- ↑ Litnosky 2000, p. 15.
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Peter William MOTIUK)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 19 Nov 1951 & 17 Aug 1988
- ↑ PRC 1995, pp. 84–85.
- 1 2 3 Prince George Citizen, 21 Mar 1946
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 10 May 2017
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 8 Apr 1948, 8 Jul 1948, 26 Aug 1948, 2 Dec 1948, 30 Mar 1950, 28 May 1953, 18 Feb 1954, 9 Jun 2016 & 13 Oct 2016
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 3 Apr 1947 & 11 May 1950
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 25 Aug 1949
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 7 Jun 1956
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 21 Jun 1956 & 9 Jun 2016
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 3 Jan 1946
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 19 Dec 1946
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 17 Jul 1947 & 13 Nov 1947
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 15 Jan 1948 & 12 Feb 1948
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 28 Apr 1949 & 9 Jun 1949
- 1 2 Prince George Citizen, 7 Jul 1955
- 1 2 Prince George Citizen, 3 May 1956
- 1 2 Prince George Citizen, 2 May 1957
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 19 & 26 Oct 1950, 9 Nov 1950, 17 Jul 1952, 2 Jul 1953 & 30 Sep 1954
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 3 Mar 1960, 21 Mar 1963 & 5 May 1966
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 9 Nov 2011
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 21 Sep 1950
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 17 Jul 1952
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 14 Dec 1953 & 9 Nov 2011
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 27 Feb 1956
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 85.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 26 Jul 1951 & 16 Feb 2016
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 21 Dec 1950
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 6 Mar 1952 & 24 Sep 1953
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 21 Oct 1954, 19 Aug 1995 & 28 Dec 2009
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 15 Nov 1956
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 106.
- ↑ "Dan Boudreau biography". www.smashwords.com.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 17 May 1956 & 16 May 1957
- 1 2 3 Prince George Citizen, 19 Feb 2013
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 25 May 1985, 10 Apr 1987 & 16 Feb 2016
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 24 Jun1970
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 20 Oct 2015
- ↑ Boudreau 2000, pp. Interview #5: 6–7.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 30 Jun 1967, 7 Jul 1967 & 24 Aug 1967
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 21 Aug 1967
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 22 Sep 1970
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 19 Sep 1977
- ↑ Boudreau 2000, p. Interview #5: 1.
- ↑ Boudreau 2000, p. Interview #5: 7.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 3 Feb 1955
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 19 Nov 1951
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 6 Feb 1956 & 7 Jun 1956
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 30 Jul 1958
- ↑ PRC 1995, pp. 39 & 78–80.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 27 Mar 1986, 18 Sep 1986, 24 Jul 1997, 12 Jan 1999, 19 Aug 2000, 15 & 21 Dec 2000, 21 Jul 2001, 8 Aug 2002, 27 Jan 2010, 1 & 2 Feb 2010, 20 Oct 2010, 30 Nov 2010, 27 Sep 2011, 27 Aug 2012, 25 Nov 2015 & 19 Apr 2016,
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 30 Nov 1985, 21 Jan 1991 & 21 Jan 2002
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 1 Feb 1983, 24 Jul 1984, 24 Jun 1985, 22 Jul 1993, 31 Jan 1994, 6 Mar 1995 & 23 Feb 2000
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Joseph PASTOR)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 22 Nov 1982
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Mary Elizabeth PASTOR)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Mary Elizabeth FRENKEL)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Theresa Mary LOUSIER)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- 1 2 "Obituary (Joseph John PASTOR)". www.ominecaexpress.com.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 22 Nov 1982 & 10 Apr 1984
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 27 Jan 1944
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 3 Oct 1940, 10 Sep 1942, 1 Apr 1948, 27 Mar 1947, 19 May 1955, 17 Jun 1957, 12 Dec 1957 & 4 Aug 1959
- 1 2 PRC 1995, p. 150.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 21 Jun 1979
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 23 Mar 1944
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Joseph KOBRA)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 2 Nov 1944, 26 Jul 1945 & 4 Apr 1957
- ↑ Boudreau, Clarence & Olga. (2003). Into the Mists of Time. Self-published. p. 59
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 29 Jan 1965
- ↑ "Marriage Certificate (FRENKEL/PASTOR)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Gustof FRENKEL)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 14 Oct 1937, 15 Nov 1983, 30 Dec 1986 & 7 Apr 2016
- ↑ "Marriage Certificate (LOUSIER/PASTOR)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 4 Nov 1943, 9 Dec 1943, 28 Aug 1984 & 26 Feb 2011
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 31 Aug 1944
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 21 Feb 1952
- ↑ PRC 1995, pp. 119–123 & 150.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 31 May 1945, 14 & 21 Jun 1945, 2 Aug 1945, 8 Nov 1945, 3 Jan 1946 & 7 Mar 1946
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 1 May 1947
- 1 2 Prince George Citizen, 9 Oct 1952
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 8 Aug 1946
- ↑ "Obituary (Marie Elizabeth PASTOR)". www.ominecaexpress.com.
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 123.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 5 Jul 1945 & 18 Sep 1947
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 21 Jun 1945 & 15 May 1947
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 5 Apr 1945, 24 & 31 May 1945, 5 Jul 1945, 16 Aug 1945, 7 Mar 1946, 7 Aug 1947 & 12 Feb 1948
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 211.
- 1 2 Prince George Citizen, 16 Oct 1950
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 9 Nov 1950
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 5 Feb 1948
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 17 Nov 1949
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 16 Aug 1951
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 15 Jun 1953 & 1 Jun 1993
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 10 Feb 1955
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 1 Dec 1955
- ↑ PRC 1995, pp. 109–110 & 150.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 30 Dec 1952
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 19 Mar 1953 & 27 Apr 1953
- ↑ "Death Certificate (John Harris KUZ)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Obituary (Harold Andrew KUZ)". www.dignitymemorial.com.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 4 Jun 1942, 1 Jul 1943, 24 May 1945, 17 Oct 1946 & 3 Nov 1949
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 8 Jun 1939
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 4 Mar 1943
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 18 Jun 1942
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 7 Jul 1949
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 3 Nov 1952
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 19 Oct 1950
- ↑ PRC 1995, pp. 110–112.
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Frederick Reginald FINER)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Cemetery Project (Mabel J. RIGGS)". www.geneofun.on.ca.
- ↑ "Marriage Certificate (RIGGS/FINER)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Cemetery Project (Wilbert A. RIGGS)". www.geneofun.on.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 14 Oct 1937
- ↑ "Marriage Certificate (APPLEYARD/FINER)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 6 Nov 1941 & 4 Jun 1942
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 21 Oct 1943 & 18 Nov 1943
- 1 2 Prince George Citizen, 13 Sep 1945
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 18 Oct 1945 & 24 Jul 1947
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 12 Jun 1952
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 4 Jun 1942
- ↑ "Cemetery Project (Clarence George RIGGS)". www.geneofun.on.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 19 Aug 1937
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 26 Apr 1945
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 17 Apr 1947
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 19 Jul 1945
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 5 Aug 1948
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 95.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 11 Dec 1947, 7 Sep 1950 & 6 Mar 1952
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 25 Jun 1951
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 28 Aug 1952, 24 Dec 1953 & 18 Feb 1954
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 14 Oct 1954, 18 Nov 1954, 24 Mar 1955, 21 Jul 1955 & 5 Apr 1956
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 6 May 1954
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 5 Jul 1956
- ↑ "Obituary (Lawrence TINDILL)". www.vancouversunandprovince.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 21 Jan 1999
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 159.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 6 Nov 1968
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 21 Nov 1968
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 8 Nov 1934
- ↑ "Cemetery Project (George Edward HOOKER)". www.geneofun.on.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 13 May 1937
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 27 Jan 1944, 3 Feb 1944 & 3 May 1945
- ↑ "Death Certificate (William GORRICK)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 8 Jun 1950
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 25 & 28 Oct 1957
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Bela Tiboi CSERVENKA)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 12 Oct 1965, & 19 & 21 Jan 1966
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 12 May 1966
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 27 Feb 1968
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Kevin Jeffrey BRYAN)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Death Certificate (med) (Kevin Jeffrey BRYAN)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 25 Aug 1994
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 3 Oct 1975; & 2 & 3 Dec 1976
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 19 & 22 Dec 1980
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 18 Dec 1980
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 19 Oct 1933
- ↑ Hak 1986, p. 292.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 24 Nov 1932
- ↑ Hak 1986, p. 296.
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Edward Victor CHAMBERS)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Elsie Louise Christina HEGSTAD)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Marriage Certificate (GAGNON/CHAMBERS)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Obituary (Marie Christina MacNEIL)". www.dignitymemorial.com.
- 1 2 Prince George Citizen, 13 Nov 2002
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Charles Lindburgh CHAMBERS)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ "Obituary (Jean BENTON)". www.inmemoriam.ca.
- ↑ PRC 1995, pp. 90–95.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 15 May 1955
- ↑ "Death Certificate (Leonard Louis Joseph GAGNON)". www.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 17 Apr 1941, 27 Aug 1942, 15 Apr 1943, 28 Sep 1944, 13 Sep 1945, 11 Apr 1946, 3 Apr 1947, 6 May 1948, 30 Mar 1950, 16 Aug 1951, 19 Jun 1952, 2 Mar 1953, 18 Feb 1954, 16 Sep 1954, & 5 & 19 May 1955
- 1 2 3 Prince George Citizen, 3 Oct 1946
- ↑ "Cemetery Project (Marion Margaret CHAMBERS)". www.geneofun.on.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 26 Sep 1946
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 24 Jun 1943
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 17 Jul 1947
- ↑ "Obituary (Chester WHELEN)". www.edmontonjournal.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 22 Aug 1946, 11 Dec 1947, 22 Jan 1948 & 26 Feb 1948
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 8 Apr 1954, 2 May 1957 & 11 Jul 1967
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 10 Aug 1979
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 7 Oct 1948, 11 May 1950, 10 Jan 1952 & 8 Apr 1954
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 82.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 10 Jan 1952
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 9 Aug 1951
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 22 May 1969
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 5 Mar 1980 & 30 Dec 1986
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 23 Feb 1990
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 30 & 31 Jan 1980; 1, 7 18 & 29 Feb 1980; 5 Mar 1980; & 14 Jan 1981
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 9 Aug 1995 & 19 Feb 2013
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 12 Apr 2017
- ↑ "CBC News, 12 Jan 2019". www.cbc.ca.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 20 Jun 1929
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 8 Aug 1978 & 22 Dec 1980
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 9 Aug 1995 & 22 Oct 1999
- ↑ Wlasitz, Steve & Helen (2000). "Upper Fraser Historical Geography Project Transcript" (PDF). www.nbca.unbc.ca. pp. 25–27.
- ↑ Mellows 2000, pp. 8–9.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen, 23 Mar 1950
- ↑ Litnosky 2000, p. 14.
- ↑ PRC 1995, pp. 175 & 251.
- ↑ Litnosky 2000, p. 10.
- ↑ PRC 1995, p. 164.
- ↑ May 2000, p. 10.
- ↑ Prince George Citizen: 27 Oct 1964 & 7 Dec 1964
- ↑ "Rocky Mountain Goat, 6 Jan 2014". www.therockymountaingoat.com. January 7, 2014.
References
- "Penny (community)". BC Geographical Names.
- "Prince George archival newspapers". www.pgpl.ca.
- PRC (1995). A Penny for Your Thoughts... The Penny Reunion Committee.
- Boudreau, Jack (2000). "Upper Fraser Historical Geography Project Transcript" (PDF). www.nbca.unbc.ca.
- Humphreys_b, Jim & Dianne (2000). "Upper Fraser Historical Geography Project Transcript" (PDF). www.nbca.unbc.ca.
- Humphreys_a, John (2000). "Upper Fraser Historical Geography Project Transcript" (PDF). www.nbca.unbc.ca.
- Litnosky, Victor (2000). "Upper Fraser Historical Geography Project Transcript" (PDF). www.nbca.unbc.ca.
- May, Jean (2000). "Upper Fraser Historical Geography Project Transcript" (PDF). www.nbca.unbc.ca.
- Mellos, Anna (2000). "Upper Fraser Historical Geography Project Transcript" (PDF). www.nbca.unbc.ca.
- Mellows, Arne & Carrie (2000). "Upper Fraser Historical Geography Project Transcript" (PDF). www.nbca.unbc.ca.
- Saville, Milly (2000). "Upper Fraser Historical Geography Project Transcript" (PDF). www.nbca.unbc.ca.
- Olson, Raymond (2014). Ghost Towns on the East Line. Self-published. ISBN 9780986924316.
- Hak, Gordon Hugh (1986). "On the Fringes: Capital and Labour in the Forest Economies of the Port Alberni and Prince George Districts, BC, 1910–1939". www.summit.sfu.ca.