 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Pentafluorosulfur hypofluorite | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| SOF6 | |
| Appearance | Colorless gas |
| Density | 1.947 at -47.2 °C[1] |
| Melting point | −86 °C (−123 °F; 187 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | −35.1 °C (−31.2 °F; 238.1 K)[1] |
| Reacts with water | |
| log P | 6.03633-420.35/T-78360/T²[1] |
| Related compounds | |
Related oxohalides |
Thionyl tetrafluoride Thionyl fluoride, sulfonyl fluoride |
Related compounds |
sulfuryl fluoride sulfur hexafluoride pentafluorooxosulfuric acid bis-(pentafluorosulfur) oxide bis-(pentafluorosulfur) peroxide bis-(pentafluorosulfur) trioxide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
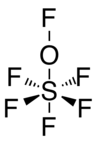
Pentafluorosulfur hypofluorite is an oxyfluoride of sulfur in the +6 oxidation state, with a fluorine atom attached to oxygen. The formula is SOF6. In standard conditions it is a gas.[1]
Synthesis
SOF6 can be made by reacting thionyl fluoride with fluorine at 200 °C with a silver difluoride catalyst.[2]
- SOF2 + 2F2 → SOF6 (+ some SOF4)
Properties
The molecular shape has five fluorine and one oxygen atom arranged around a sulfur atom in an octahedral arrangement. Another fluorine atom is attached to the oxygen in almost a straight line with the S-O connection. So the molecular formula can also be written as SF5OF. The average S-F distance is 1.53 Å. The angles ∠FSF and ∠FSO are 90°.[2]
The 19F nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of SOF6 compared to SF6 has a -131.5 ppm shift for the hypofluorite fluorine, and 1.75 ppm for the opposite F. The other four fluorine atoms have a shift of 3.64 ppm. Spin coupling of o-F to SF4 is 17.4 Hz, between SF4 and opposite (apex) SF 155 Hz, and between apex and hypofluorite it is 0.0.[3]
Reactions
Iodide is oxidised to iodine
- SOF6 + 2I− + H2O → SO2F2 + I2 + 2HF + 2F−
Alkalis such as potassium hydroxide react
- 2SOF6 + 12OH− → O2 + 10F− + 5H2O + 2SO3F−
Alkenes react to add to a double bond, with -OSF5 on one carbon, and -F on the other.
- SOF6 + ClCH=CH2 → FClCH-CH2-O-SF5[5]
- SOF6 + FCH=CH2 → F2CH-CH2-O-SF5[5]
- SOF6 + F2C=CH2 → F3C-CH2-O-SF5[5]
- SOF6 + SOF4 → mixture of SF6, SOF4, bis-(pentafluorosulfur) peroxide F5SOOSF5 and bis-(pentafluorosulfur) oxide F5SOSF5.[4]
Thermal decomposition produces sulfur hexafluoride and oxygen.
- 2SOF6 heat over 210° → 2SF6 + O2.[4]
Some reactions of SOF6 result in fluorination of other molecules
- SOF6 + CO → F2CO + SOF4.[4]
- SOF6 + F2CO → SF5OOCF3[6]
- SOF6 + SO3 → F5SOOSO2F[6]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Dudley, F. B.; Cady, G. H.; Eggers, D. F. (April 1956). "Pentafluorosulfur Hypofluorite and Thionyl Tetrafluoride". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 78 (8): 1553–1557. doi:10.1021/ja01589a013.
- 1 2 Crawford, Roger A.; Dudley, Frank B.; Hedberg, Kenneth (October 1959). "A Verification of the Molecular Structure of Pentafluorosulfur Hypofluorite (SF5OF) by Electron Diffraction". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 81 (20): 5287–5288. doi:10.1021/ja01529a009.
- ↑ Emsley, J. W.; Feeney, J.; Sutcliffe, L. H. (22 October 2013). High Resolution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Elsevier. p. 949. ISBN 9781483184081.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Williamson, Stanley M.; Cady, George H. (August 1962). "Reactions of Pentafluorosulfur Hypofluorite". Inorganic Chemistry. 1 (3): 673–677. doi:10.1021/ic50003a044.
- 1 2 3 Williamson, Stanley M. (1963). "On the Reaction of Pentafluorosulfur Hypofluorite with Unsymmetrical Two-Carbon Alkenes". Inorganic Chemistry. 2 (2): 421–422. doi:10.1021/ic50006a050.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Tattershall, B.W.; Cady, George H. (December 1967). "Reactions of pentafluorosulphur hypofluorite (SF5OF) with Cl2, Br2, I2, NO2, and PF3". Journal of Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry. 29 (12): 3003–3005. doi:10.1016/0022-1902(67)80134-9.