 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
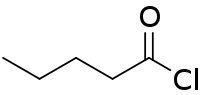
| Preferred IUPAC name
Pentanoyl chloride | |
| Other names
Valeroyl chloride; n-Pentanoyl chloride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.301 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H9ClO | |
| Molar mass | 120.58 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Pentanoyl chloride is an acyl chloride derived from pentanoic acid. It is a colorless liquid that is used to attach the valeroyl group. It is usually produced by chlorination of valeric acid.[1]
Reactions
Like related acyl chlorides, valeryl chloride hydrolyzes readily:
- CH3(CH2)3C(O)Cl + H2O → CH3(CH2)3CO2H + HCl
Alcohols react to give esters:
- CH3(CH2)3C(O)Cl + ROH → CH3(CH2)3CO2R + HCl
Amines react to give amides:
- CH3(CH2)3C(O)Cl + R2NH → CH3(CH2)3C(O)NR2 + HCl
Benzene reacts under conditions of the Friedel-Crafts reaction to give valerophenone:
- CH3(CH2)3C(O)Cl + C6H6 → CH3(CH2)3C(O)C6H5 + HCl
References
- ↑ Helferich, B.; Schaefer, W. (1929). "n-Butyryl Chloride". Org. Synth. 9: 32. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.009.0032.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.