| Demographics of Zimbabwe | |
|---|---|
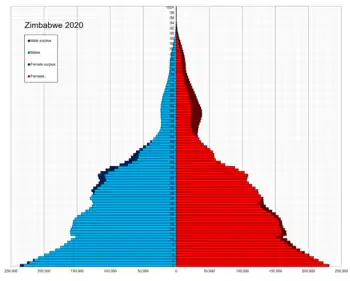 Population pyramid of Zimbabwe in 2020 | |
| Population | 15,121,004 (2022 est.) |
| Growth rate | 1.95% (2022 est.) |
| Birth rate | 33.07 births/1,000 population |
| Death rate | 8.76 deaths/1,000 population |
| Life expectancy | 63.32 years |
| • male | 61.18 years |
| • female | 65.52 years |
| Fertility rate | 3.89 children |
| Infant mortality rate | 28.53 deaths/1,000 live births |
| Net migration rate | -4.83 migrant(s)/1,000 population |
| Sex ratio | |
| Total | 0.97 male(s)/female (2022 est.) |
| At birth | 1.03 male(s)/female |
| Nationality | |
| Nationality | Zimbabwean |
| Major ethnic | African - 99.4% |
| Language | |
| Official | Shona, Ndebele, English and 13 other minority languages |
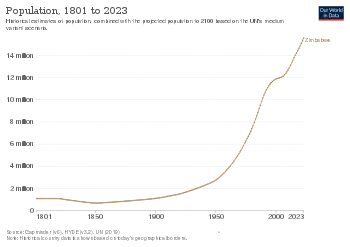
Demographic features of the population of Zimbabwe include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
Population
The population of Zimbabwe has grown during the 20th century in accordance with the model of a developing country with high birth rates and falling death rates, resulting in relatively high population growth rate (around 3% or above in the 1960s and early 1970s). After a spurt in the period 1980-1983 following independence, a decline in birth rates set in. Since 1991, however, there has been a jump in death rates from a low of 10 per 1000 in 1985 to a high of 25 per 1000 in 2002/2003. It has since subsided to just under 22 per 1000 (estimate for 2007) a little below the birth rate of around 27 per 1000.[1][2]
The high death rate is a result of poor medical facilities. This leads to a small natural increase of around 0.5%. Deaths due to HIV/AIDS have reduced due to improved methods of protection. However, outward migration rates of around 1.5% or more have been experienced for over a decade, therefore actual population changes are uncertain. Because of the high number of unaccounted emigrants, the recent increase of emigration and the death toll from AIDS, the total population might be declining to as low as 8 million according to some estimates.[3]
Census data
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1982 | 7,608,432 | — |
| 1992 | 10,412,548 | +36.9% |
| 2002 | 11,631,657 | +11.7% |
| 2012 | 13,061,239 | +12.3% |
| 2022 | 15,178,957 | +16.2% |
| Source:[4] | ||
Historical data of Southern Rhodesia
| Year | Black | White | Coloured | Asian |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1911 | 744,558 | 23,606 | 2,912 | |
| 1921 | 862,319 | 33,620 | 1,998 | 1,250 |
| Year | Black | White |
|---|---|---|
| 1890 | 700,000 | |
| 1910 | 900,000 | 20,000 |
| 1927 | 922,000 | 38,200 |
| 1930 | 1,300,000 | |
| 1945 | 1,400,000? | 140,000 |
| 1946 | 1,640,000 | 80,500 |
Current estimates
Based on the 2022 revision of the World Population Prospects[5][6], the population of Zimbabwe was estimated by the United Nations at 15,993,524 in 2021. About 38.9% comprised youths under 15, while another 56.9% grouped persons aged between 15 and 65 years. Only around 4.2% of citizens were apparently over 65.[7]
| Total population | Population aged 0–14 (%) | Population aged 15–64 (%) | Population aged 65+ (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 2 747 000 | 42.0 | 54.8 | 3.2 |
| 1955 | 3 204 000 | 43.8 | 52.9 | 3.3 |
| 1960 | 3 752 000 | 45.3 | 51.4 | 3.4 |
| 1965 | 4 422 000 | 47.7 | 49.0 | 3.3 |
| 1970 | 5 206 000 | 48.1 | 48.7 | 3.2 |
| 1975 | 6 170 000 | 48.4 | 48.5 | 3.1 |
| 1980 | 7 289 000 | 48.9 | 48.1 | 3.0 |
| 1985 | 8 855 000 | 47.9 | 49.1 | 3.0 |
| 1990 | 10 469 000 | 46.1 | 50.9 | 3.0 |
| 1995 | 11 685 000 | 44.3 | 52.5 | 3.2 |
| 2000 | 12 509 000 | 41.7 | 54.9 | 3.4 |
| 2005 | 12 710 000 | 40.1 | 56.1 | 3.8 |
| 2010 | 13 080 000 | 38.9 | 56.9 | 4.2 |
Population Estimates by Sex and Age Group (01.VII.2020) (Projections based on the 2012 Population Census.):[8]
| Age Group | Male | Female | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 7 439 221 | 8 034 602 | 15 473 818 | 100 |
| 0–4 | 991 893 | 1 022 505 | 2 014 398 | 13.02 |
| 5–9 | 941 990 | 973 625 | 1 915 614 | 12.38 |
| 10–14 | 903 673 | 922 505 | 1 826 178 | 11.80 |
| 15–19 | 831 648 | 839 774 | 1 671 422 | 10.80 |
| 20–24 | 786 263 | 788 910 | 1 575 172 | 10.18 |
| 25–29 | 605 999 | 665 755 | 1 271 754 | 8.22 |
| 30–34 | 506 137 | 627 334 | 1 133 471 | 7.33 |
| 35–39 | 475 942 | 550 399 | 1 026 341 | 6.63 |
| 40–44 | 392 995 | 420 872 | 813 866 | 5.26 |
| 45–49 | 309 988 | 314 677 | 624 665 | 4.04 |
| 50–54 | 206 545 | 207 935 | 414 480 | 2.68 |
| 55–59 | 130 120 | 182 182 | 312 301 | 2.02 |
| 60–64 | 115 990 | 180 661 | 296 650 | 1.92 |
| 65-69 | 91 696 | 126 950 | 218 646 | 1.41 |
| 70-74 | 63 617 | 90 849 | 154 466 | 1.00 |
| 75-79 | 42 079 | 57 802 | 99 881 | 0.65 |
| 80+ | 42 646 | 61 867 | 104 513 | 0.68 |
| Age group | Male | Female | Total | Percent |
| 0–14 | 2 837 556 | 2 918 635 | 5 756 191 | 37.20 |
| 15–64 | 4 361 627 | 4 778 499 | 9 140 126 | 59.07 |
| 65+ | 240 038 | 337 468 | 577 506 | 3.73 |
Vital statistics
Registration of vital events in Zimbabwe is not complete. The Population Department of the United Nations prepared the following estimates.[9]
| Period | Mid-year Population | Live births | Deaths | Natural change | CBR* | CDR* | NC* | TFR* | IMR* | Life expectancy (in years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 2 791 000 | 141 000 | 46 000 | 95 000 | 50.4 | 16.6 | 33.8 | 7.10 | 102.2 | 49.64 |
| 1951 | 2 882 000 | 144 000 | 48 000 | 96 000 | 49.9 | 16.7 | 33.2 | 7.10 | 101.4 | 49.86 |
| 1952 | 2 974 000 | 147 000 | 49 000 | 98 000 | 49.5 | 16.5 | 33.1 | 7.11 | 99.8 | 50.22 |
| 1953 | 3 068 000 | 151 000 | 50 000 | 101 000 | 49.1 | 16.2 | 32.9 | 7.12 | 98.1 | 50.62 |
| 1954 | 3 165 000 | 155 000 | 50 000 | 104 000 | 48.8 | 15.9 | 32.8 | 7.13 | 96.4 | 51.01 |
| 1955 | 3 264 000 | 158 000 | 51 000 | 107 000 | 48.4 | 15.7 | 32.7 | 7.14 | 95.0 | 51.28 |
| 1956 | 3 365 000 | 162 000 | 52 000 | 110 000 | 48.1 | 15.4 | 32.7 | 7.16 | 93.6 | 51.70 |
| 1957 | 3 470 000 | 166 000 | 53 000 | 114 000 | 47.9 | 15.1 | 32.8 | 7.17 | 92.2 | 52.06 |
| 1958 | 3 579 000 | 171 000 | 53 000 | 118 000 | 47.7 | 14.8 | 32.8 | 7.19 | 90.6 | 52.40 |
| 1959 | 3 691 000 | 175 000 | 54 000 | 122 000 | 47.4 | 14.5 | 32.9 | 7.20 | 88.8 | 52.84 |
| 1960 | 3 806 000 | 180 000 | 54 000 | 126 000 | 47.3 | 14.2 | 33.0 | 7.22 | 87.1 | 53.24 |
| 1961 | 3 926 000 | 185 000 | 55 000 | 130 000 | 47.0 | 13.9 | 33.1 | 7.23 | 85.3 | 53.62 |
| 1962 | 4 050 000 | 190 000 | 55 000 | 135 000 | 46.9 | 13.6 | 33.3 | 7.26 | 83.3 | 54.07 |
| 1963 | 4 178 000 | 195 000 | 55 000 | 140 000 | 46.6 | 13.2 | 33.4 | 7.25 | 81.3 | 54.55 |
| 1964 | 4 310 000 | 200 000 | 56 000 | 145 000 | 46.4 | 12.9 | 33.5 | 7.26 | 79.2 | 54.99 |
| 1965 | 4 447 000 | 206 000 | 56 000 | 150 000 | 46.2 | 12.6 | 33.7 | 7.26 | 77.1 | 55.46 |
| 1966 | 4 589 000 | 212 000 | 56 000 | 155 000 | 46.1 | 12.3 | 33.8 | 7.24 | 75.2 | 55.89 |
| 1967 | 4 735 000 | 218 000 | 57 000 | 161 000 | 45.9 | 12.0 | 33.9 | 7.22 | 73.5 | 56.19 |
| 1968 | 4 886 000 | 225 000 | 58 000 | 167 000 | 45.9 | 11.8 | 34.1 | 7.19 | 72.1 | 56.46 |
| 1969 | 5 044 000 | 232 000 | 59 000 | 174 000 | 46.0 | 11.6 | 34.3 | 7.14 | 71.0 | 56.71 |
| 1970 | 5 203 000 | 240 000 | 60 000 | 181 000 | 46.1 | 11.4 | 34.6 | 7.09 | 70.1 | 57.03 |
| 1971 | 5 363 000 | 248 000 | 61 000 | 187 000 | 46.2 | 11.4 | 34.8 | 7.06 | 69.6 | 57.20 |
| 1972 | 5 533 000 | 258 000 | 63 000 | 195 000 | 46.5 | 11.3 | 35.2 | 7.06 | 69.3 | 57.40 |
| 1973 | 5 713 000 | 269 000 | 65 000 | 204 000 | 47.0 | 11.3 | 35.7 | 7.07 | 69.1 | 57.37 |
| 1974 | 5 904 000 | 279 000 | 67 000 | 212 000 | 47.2 | 11.3 | 35.9 | 7.04 | 69.0 | 57.49 |
| 1975 | 6 097 000 | 289 000 | 69 000 | 220 000 | 47.3 | 11.3 | 36.0 | 6.98 | 69.2 | 57.55 |
| 1976 | 6 288 000 | 297 000 | 73 000 | 224 000 | 47.1 | 11.6 | 35.6 | 6.91 | 69.3 | 56.94 |
| 1977 | 6 453 000 | 304 000 | 77 000 | 227 000 | 46.7 | 11.8 | 34.9 | 6.85 | 69.3 | 56.29 |
| 1978 | 6 549 000 | 309 000 | 84 000 | 226 000 | 46.6 | 12.6 | 34.0 | 6.77 | 69.0 | 54.59 |
| 1979 | 6 656 000 | 310 000 | 84 000 | 226 000 | 46.3 | 12.6 | 33.8 | 6.70 | 68.5 | 55.04 |
| 1980 | 7 050 000 | 317 000 | 76 000 | 241 000 | 46.2 | 11.1 | 35.1 | 6.61 | 66.9 | 58.67 |
| 1981 | 7 507 000 | 349 000 | 76 000 | 273 000 | 46.5 | 10.1 | 36.4 | 6.51 | 64.8 | 59.33 |
| 1982 | 7 804 000 | 358 000 | 76 000 | 282 000 | 45.9 | 9.8 | 36.1 | 6.38 | 62.0 | 59.88 |
| 1983 | 8 106 000 | 366 000 | 77 000 | 289 000 | 45.1 | 9.4 | 35.7 | 6.25 | 59.2 | 60.25 |
| 1984 | 8 399 000 | 365 000 | 75 000 | 290 000 | 43.4 | 8.9 | 34.5 | 6.08 | 55.7 | 61.05 |
| 1985 | 8 691 000 | 365 000 | 74 000 | 291 000 | 42.0 | 8.5 | 33.5 | 5.90 | 52.9 | 61.62 |
| 1986 | 8 983 000 | 364 000 | 73 000 | 290 000 | 40.5 | 8.2 | 32.3 | 5.70 | 50.8 | 62.02 |
| 1987 | 9 277 000 | 363 000 | 75 000 | 288 000 | 39.2 | 8.1 | 31.0 | 5.50 | 49.5 | 61.77 |
| 1988 | 9 569 000 | 356 000 | 78 000 | 278 000 | 37.2 | 8.2 | 29.0 | 5.29 | 49.2 | 61.32 |
| 1989 | 9 846 000 | 350 000 | 83 000 | 267 000 | 35.6 | 8.4 | 27.2 | 5.08 | 49.7 | 60.40 |
| 1990 | 10 114 000 | 352 000 | 88 000 | 263 000 | 34.8 | 8.7 | 26.0 | 4.87 | 50.9 | 59.43 |
| 1991 | 10 378 000 | 357 000 | 96 000 | 261 000 | 34.4 | 9.3 | 25.2 | 4.71 | 52.6 | 58.09 |
| 1992 | 10 642 000 | 363 000 | 106 000 | 257 000 | 34.1 | 9.9 | 24.2 | 4.57 | 54.8 | 56.44 |
| 1993 | 10 795 000 | 361 000 | 118 000 | 243 000 | 33.1 | 10.8 | 22.3 | 4.39 | 57.1 | 54.43 |
| 1994 | 10 859 000 | 359 000 | 128 000 | 230 000 | 32.8 | 11.8 | 21.1 | 4.27 | 58.9 | 52.59 |
| 1995 | 10 994 000 | 359 000 | 141 000 | 218 000 | 32.6 | 12.8 | 19.8 | 4.15 | 60.5 | 50.53 |
| 1996 | 11 178 000 | 372 000 | 154 000 | 218 000 | 33.2 | 13.8 | 19.4 | 4.11 | 61.8 | 48.96 |
| 1997 | 11 362 000 | 385 000 | 163 000 | 221 000 | 33.8 | 14.4 | 19.4 | 4.06 | 61.7 | 47.99 |
| 1998 | 11 548 000 | 399 000 | 175 000 | 224 000 | 34.5 | 15.2 | 19.4 | 4.03 | 61.4 | 46.82 |
| 1999 | 11 716 000 | 415 000 | 192 000 | 223 000 | 35.3 | 16.3 | 19.0 | 4.01 | 60.6 | 45.21 |
| 2000 | 11 835 000 | 424 000 | 200 000 | 224 000 | 35.6 | 16.8 | 18.8 | 3.97 | 59.9 | 44.69 |
| 2001 | 11 911 000 | 431 000 | 228 000 | 203 000 | 36.0 | 19.0 | 16.9 | 3.95 | 58.9 | 41.96 |
| 2002 | 11 985 000 | 433 000 | 204 000 | 229 000 | 35.9 | 17.0 | 19.0 | 3.89 | 58.3 | 44.57 |
| 2003 | 12 076 000 | 435 000 | 216 000 | 219 000 | 35.9 | 17.8 | 18.1 | 3.82 | 57.7 | 43.39 |
| 2004 | 12 161 000 | 434 000 | 208 000 | 226 000 | 35.5 | 17.0 | 18.5 | 3.74 | 58.1 | 44.50 |
| 2005 | 12 225 000 | 430 000 | 207 000 | 223 000 | 34.9 | 16.8 | 18.1 | 3.67 | 58.5 | 44.77 |
| 2006 | 12 330 000 | 427 000 | 203 000 | 223 000 | 34.5 | 16.4 | 18.1 | 3.62 | 59.5 | 45.36 |
| 2007 | 12 451 000 | 436 000 | 204 000 | 232 000 | 34.8 | 16.3 | 18.5 | 3.65 | 59.9 | 45.61 |
| 2008 | 12 550 000 | 449 000 | 197 000 | 252 000 | 35.6 | 15.6 | 20.0 | 3.77 | 59.9 | 46.72 |
| 2009 | 12 680 000 | 469 000 | 189 000 | 280 000 | 36.7 | 14.8 | 21.9 | 3.95 | 58.1 | 48.06 |
| 2010 | 12 840 000 | 478 000 | 171 000 | 307 000 | 37.1 | 13.3 | 23.8 | 4.03 | 55.0 | 50.65 |
| 2011 | 13 026 000 | 487 000 | 155 000 | 332 000 | 37.2 | 11.9 | 25.3 | 4.10 | 51.9 | 53.35 |
| 2012 | 13 265 000 | 490 000 | 142 000 | 347 000 | 36.8 | 10.7 | 26.1 | 4.10 | 47.2 | 55.63 |
| 2013 | 13 555 000 | 492 000 | 133 000 | 360 000 | 36.2 | 9.8 | 26.5 | 4.06 | 44.0 | 57.46 |
| 2014 | 13 856 000 | 488 000 | 127 000 | 361 000 | 35.1 | 9.1 | 26.0 | 3.96 | 42.0 | 58.85 |
| 2015 | 14 155 000 | 482 000 | 124 000 | 357 000 | 34.0 | 8.8 | 25.2 | 3.85 | 41.1 | 59.59 |
| 2016 | 14 453 000 | 480 000 | 122 000 | 358 000 | 33.2 | 8.4 | 24.7 | 3.77 | 39.6 | 60.31 |
| 2017 | 14 751 000 | 481 000 | 122 000 | 358 000 | 32.5 | 8.3 | 24.3 | 3.71 | 38.7 | 60.71 |
| 2018 | 15 052 000 | 484 000 | 120 000 | 364 000 | 32.1 | 8.0 | 24.1 | 3.66 | 37.4 | 61.41 |
| 2019 | 15 355 000 | 485 000 | 124 000 | 361 000 | 31.5 | 8.0 | 23.5 | 3.60 | 37.2 | 61.29 |
| 2020 | 15 670 000 | 486 000 | 128 000 | 359 000 | 31.0 | 8.1 | 22.9 | 3.55 | 36.8 | 61.12 |
| 2021 | 15 994 000 | 489 000 | 145 000 | 344 000 | 30.5 | 9.1 | 21.5 | 3.49 | 36.8 | 59.25 |
| * CBR = crude birth rate (per 1000); CDR = crude death rate (per 1000); NC = natural change (per 1000); IMR = infant mortality rate per 1000 births; TFR = total fertility rate (number of children per woman) | ||||||||||
Fertility and births
Total Fertility Rate (TFR) (Wanted Fertility Rate) and Crude Birth Rate (CBR):[10]
| Year | CBR (Total) | TFR (Total) | CBR (Urban) | TFR (Urban) | CBR (Rural) | TFR (Rural) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1982-1984 | 6.66 | 5.33 | 7.28 | |||
| 1985-1988 | 5.31 | 3.86 | 6.06 | |||
| 1994 | 31.6 | 4.29 (3.5) | 30.5 | 3.09 (2.6) | 32.0 | 4.85 (3.9) |
| 1999 | 30.8 | 3.96 (3.4) | 31.3 | 2.96 (2.6) | 30.5 | 4.57 (3.8) |
| 2005-2006 | 31.0 | 3.8 (3.3) | 28.5 | 2.6 (2.3) | 32.0 | 4.6 (3.9) |
| 2010-2011 | 34 | 4.1 (3.4) | 34 | 3.1 (2.7) | 34 | 4.8 (4.0) |
| 2015 | 32.0 | 4.0 (3.6) | 31.1 | 3.0 (2.7) | 32.7 | 4.7 (4.1) |
Fertility data as of 2010-2011 (DHS Program):[11]
| Province | Total fertility rate | Percentage of women age 15-49 currently pregnant | Mean number of children ever born to women age 40-49 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manicaland | 4.8 | 8.8 | 4.9 |
| Mashonaland Central | 4.5 | 9.1 | 5.0 |
| Mashonaland East | 4.5 | 7.3 | 4.2 |
| Mashonaland West | 4.5 | 8.5 | 5.0 |
| Matabeleland North | 4.1 | 7.7 | 5.2 |
| Matabeleland South | 4.2 | 6.6 | 4.6 |
| Midlands | 4.2 | 7.6 | 4.8 |
| Masvingo | 4.7 | 11.1 | 4.6 |
| Harare | 3.1 | 8.4 | 3.5 |
| Bulawayo | 2.8 | 4.8 | 3.2 |
Life expectancy at birth
Life expectancy from 1950 to 2021 (UN World Population Prospects):[12]
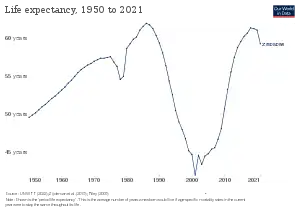
| Period | Life expectancy in Years |
|---|---|
| 1950–1955 | 48.54 |
| 1955–1960 | |
| 1960–1965 | |
| 1965–1970 | |
| 1970–1975 | |
| 1975–1980 | |
| 1980–1985 | |
| 1985–1990 | |
| 1990–1995 | |
| 1995–2000 | |
| 2000–2005 | |
| 2005–2010 | |
| 2010–2015 | |
| 2020 | |
| 2021 |
Ethnic groups
According to 2012 Census report, 99.6% of the population is of African origin.[13] Of the rest of the population, the great bulk—perhaps 30,000 persons[14][15][16]—are White Zimbabweans of European ancestry, a minority which had diminished in size prior to independence.[17]
The vast black majority has grown at a projected annual rate of 4.3% since 1980.[18] Although present figures are difficult to ascertain, the white community once reproduced itself at an annual rate (under 1.5%) similar to that of most totals in developed nations.[19] Of the two major ethnolinguistic categories, Shona speakers formed a decisive plurality at (80<)% and occupied the eastern two-thirds of Zimbabwe.[20] Ndebele speakers constitute about 16%, and none of the other indigenous ethnic groups came to as much as 2% in recent decades.[21] African speakers of nonindigenous languages included migrant workers from Malawi, Zambia, and Mozambique.[22]
Over 90% of White Zimbabweans are of British or British diasporan origin;[19] at various times many emigrated from South Africa and elsewhere.[19] After World War II, Zimbabwe (then Southern Rhodesia) received a substantial influx of emigrants from the United Kingdom—a handful previously resided in other colonies such as India, Pakistan and Kenya. Also represented on a much smaller scale were individuals of Afrikaner, Greek, and Portuguese origin.[17] After Rhodesia's Unilateral Declaration of Independence in 1965, Ian Smith's administration removed technical obstacles to immigration from southern Europe.[19]
A heavily urbanised Coloured population is descended, partially, from early unions between White Rhodesian settlers and local Black African females. Many, however, can also trace their ancestry to the Dutch/Khoisan mulatto clans of the Cape.
With the exception of a select few who were brought to Zimbabwe as railroad workers, most Asians in Zimbabwe arrived from India pursuing employment or entrepreneurship. An educated class, they have traditionally engaged in retail trade or manufacturing.[19]
Languages
Zimbabwe has 16 official languages: Chewa, Tonga, Chibarwe, English, Kalanga, Koisan, Nambya, Ndau, Ndebele, Shangani, Shona, sign language, Sotho, Tonga, Tswana, Venda, Xhosa.[23] English is widely used in administration, law and schools, though less than 2.5%, mainly the white and Coloured (mixed race) minorities, consider it their native language. The rest of the population speak Shona (70%) and Ndebele (20%), Kalanga (2%), etc.[24] Shona has a rich oral tradition, which was incorporated into the first Shona novel, Feso by Solomon Mutswairo, published in 1956.[25] English is spoken primarily in the cities, but less so in rural areas. Television news is broadcast in English, Shona and Ndebele though the local languages time slot falls out of prime viewing time, but radio broadcasts in English, Ndebele, Shona, Kalanga, Nambya, Venda, Suthu and Tonga. English, Ndebele and Shona are given far more airtime.
Religions
85 percent of Zimbabweans are Christian, and of that number, 61 percent regularly attend Christian churches.[26] The largest Christian churches are Anglican, Roman Catholic, Seventh Day Adventist and Methodist. However like most former European colonies, Christianity is often mixed with enduring traditional beliefs. Besides Christianity, ancestral worship (Amadlozi) is the most practised non-Christian religion which involves ancestor worship and spiritual intercession. Under 1% of the population is Muslim, although many Zimbabweans are influenced by Abrahamic food laws.
Health
According to the United Nations World Health Organization, the average life expectancy for men in 2006 was 37 years and for women was 34 years of age, the lowest in the world at the time.[27] An association of doctors in Zimbabwe have made calls for President Mugabe to make moves to assist the ailing health service.[28] Since then it has recovered, and the figures for 2010 to 2015 were 53 and 54 for men and women respectively.[29]
Other demographic statistics
The following demographic statistics of Zimbabwe in 2022 are from the World Population Review.[30]
- One birth every 1 minutes
- One death every 4 minutes
- One net migrant every 7 minutes
- Net gain of one person every 2 minutes
The following demographic statistics are from the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated.[31]
Population
- 15,121,004 (2022 est.)
- 14,030,368 (July 2018 est.)
- 13,805,084 (July 2017 est.)
Religions
Protestant 74.8% (includes Apostolic 37.5%, Pentecostal 21.8%, other 15.5%), Roman Catholic 7.3%, other Christian 5.3%, traditional 1.5%, Muslim 0.5%, other 0.1%, none 10.5% (2015 est.)
Age structure

- 0-14 years: 38.32% (male 2,759,155/female 2,814,462)
- 15-24 years: 20.16% (male 1,436,710/female 1,495,440)
- 25-54 years: 32.94% (male 2,456,392/female 2,334,973)
- 55-64 years: 4.07% (male 227,506/female 363,824)
- 65 years and over: 4.52% (male 261,456/female 396,396) (2020 est.)
- 0-14 years: 38.62% (male 2,681,192 /female 2,736,876)
- 15-24 years: 20.42% (male 1,403,715 /female 1,461,168)
- 25-54 years: 32.22% (male 2,286,915 /female 2,234,158)
- 55-64 years: 4.24% (male 233,021 /female 361,759)
- 65 years and over: 4.5% (male 255,704 /female 375,860) (2018 est.)
Median age
- total: 20.5 years. Country comparison to the world: 189th
- male: 20.3 years
- female: 20.6 years (2020 est.)
- total: 20.2 years. Country comparison to the world: 190th
- male: 19.9 years
- female: 20.4 years (2018 est.)
Birth rate
- 33.07 births/1,000 population (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 22nd
- 34 births/1,000 population (2018 est.) Country comparison to the world: 25th
- 34.2 births/1,000 population (2017 est.)
Death rate
- 8.76 deaths/1,000 population (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 68th
- 9.9 deaths/1,000 population (2018 est.) Country comparison to the world: 41st
- 10.2 deaths/1,000 population (2017 est.)
Total fertility rate
- 3.89 children born/woman (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 30th
- 3.97 children born/woman (2018 est.) Country comparison to the world: 33rd
Population growth rate
- 1.95% (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 44th
- 1.68% (2018 est.) Country comparison to the world: 60th
- 1.56% (2017 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
- 20 years (2015 est.)
- note: median age at first birth among women 25-29
Contraceptive prevalence rate
- 66.8% (2015)
Net migration rate
- -4.83 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 200th
- -7.3 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2018 est.) Country comparison to the world: 208th
- -8.5 migrants/1,000 population (2017).There is an increasing flow of Zimbabweans into South Africa and Botswana in search of better economic opportunities.
Dependency ratios
- total dependency ratio: 79.5 (2015 est.)
- youth dependency ratio: 74.4 (2015 est.)
- elderly dependency ratio: 5.1 (2015 est.)
- potential support ratio: 19.7 (2015 est.)
Urbanization
- urban population: 66% of total population (2022)
- rate of urbanization: 2.41% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
- urban population: 32.2% of total population (2018)
- rate of urbanization: 2.19% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)
Major infectious diseases
- degree of risk: high (2020)
- food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
- vectorborne diseases: malaria and dengue fever
- water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
- animal contact diseases: rabies
Sex ratio
(2011 est.)
- at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
- under 15 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
- 15-64 years: 0.92 male(s)/female
- 65 years and over: 0.70 male(s)/female
- total population: 0.95 male(s)/female
AIDS
- Adult prevalence rate
- 13.3% (2017 est.)
- 15.3% (2007)
- 33.7% (2001 est.)
- 25% (1999 estimate).
- People living with HIV/AIDS
- 1.3 million (2017 est.)
- 1.3 million (2007 est.)
- 2.3 million (2001 est.)
- Deaths
- 22,000 (2017 est.)
- 140,000 (2007 est.)
- 200,000 (2001 est.)
- 160,000 annually (1999 estimate).
Life expectancy at birth
- total population: 63.32 years. Country comparison to the world: 209
- male: 61.18 years (2022 est.)
- female: 65.52 years (2022 est.)
- total population: 61.1 years
- male
- 59 years
- female: 63.2 years (2018 est.)
- total population 60.4 years
- male 58.3 years
- female 62.5 years (2017 est.)
total population 47.55 years male 47.98 years female 47.11 years (2010 est.)
Physicians density
- 0.08 physicians/1,000 population (2014)
Hospital bed density
- 1.7 beds/1,000 population (2011)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
- 15.5% (2015)
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
- 8.4% (2015)
Education expenditures
- 3.6% of GDP (2018) Country comparison to the world: 122nd
- 7.5% of GDP (2014) Country comparison to the world: 10th
Literacy
definition* age 15 and over can read and write English
- total population: 95%
- male: 96.5%
- female: 90.5% (2022 est.)
- total population* 90.7% (2003 est.), 85% (2000 est.)
- male* 94.2% (2003 est.), 90% (2000 est.)
- female* 87.2% (2003 est.), 80% (1995 est.)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
- total: 11 years
- male: 12 years
- female: 11 years (2013)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24
- total: 27.5%
- male: 25%
- female: 31.4% (2019 est.)
Nationality
- noun: Zimbabwean(s)
- adjective: Zimbabwean
Ethnic groups
- African 99.4% (predominantly Shona; Ndebele is the second largest ethnic group)
- White Zimbabweans 0.4%
- Other (primarily Indian) 0.2% [34]
Languages
- Shona (official; most widely spoken), Ndebele (official, second most widely spoken), English (official; traditionally used for official business), 13 minority languages (official; includes Chewa, Chibarwe, Kalanga, Koisan, Nambya, Ndau, Shangani, sign language, Sotho, Tonga, Tswana, Venda, and Xhosa).[35]
References
- ↑ Statesman's Yearbook 2007, Palgrave Macmillan, New York
- ↑ CIA Factbook 2007, CIA Publications, Washington D.C.
- ↑ "The Independent". Independent.co.uk. Archived from the original on December 5, 2008.
- ↑ "2022 Population and Housing Census Preliminary Results". UNFPA - Zimbabwe. Retrieved 13 January 2024.
- ↑ "World Population Prospects 2022". population.un.org. United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved July 17, 2022.
- ↑ "World Population Prospects 2022: Demographic indicators by region, subregion and country, annually for 1950-2100" (XSLX). population.un.org ("Total Population, as of 1 July (thousands)"). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved July 17, 2022.
- ↑ "World Population Prospects, the 2012 Revision". United Nations. Archived from the original on 2011-05-06.
- ↑ "Demographic Yearbook – 2020". New York: United Nations Statistics Division. Retrieved 2022-05-18.
- ↑ United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Division (2022). "World Population Prospects 2022 Demographic indicators by region, subregion and country, annually for 1950-2100" (XLS (91MB)). United Nations Population Division. 27 (Online ed.). New York: United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. rows 3101:3172, cols M,X,AE,S,AH,S,AA,AV,AI. Archived from the original on 2022-08-09.
- ↑ "National Health Survey 1958" (PDF). Dhsprogram.com. Retrieved 2017-08-27.
- ↑ "Zimbabwe Demographic and Health Survey : 2010-11" (PDF). Dhsprogram.com. Retrieved 2017-08-27.
- ↑ "World Population Prospects - Population Division - United Nations". population.un.org. Retrieved 2022-07-13.
- 1 2 "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-09-01. Retrieved 2015-02-16.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "Zimbabwe's only white minster [sic] says insults against whites continue at top government level". Fox News. 2015-03-26.
- ↑ United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. "Refworld - Zimbabwe: Dual citizenship". Refworld.
- ↑ "Teens assaulted in police raid on nightclub". newzimbabwe.com. Archived from the original on 2012-08-19.
- 1 2 Raeburn, Michael. We are everywhere: Narratives from Rhodesian guerillas. pp. 1–209.
- ↑ "Zimbabwe Population growth rate". indexmundi.com.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Nelson, Harold. Zimbabwe: A Country Study. pp. 80–137.
- ↑ "The People of Zimbabwe". Archived from the original on 2007-07-12. Retrieved 2007-11-13.
- ↑ Famighetti, Robert. The World Almanac and Book of Facts, 1996. p. 837.
- ↑ "The Land Act's Losers". postcolonialweb.org.
- ↑ The following languages, namely Chewa, Chibarwe, English, Kalanga, Koisan, Nambya, Ndau, Ndebele, Shangani, Shona, sign language, Sotho, Tonga, Tswana, Venda and Xhosa, are the officially recognised languages of Zimbabwe. (CONSTITUTION OF ZIMBABWE (final draft) Archived 2013-10-02 at the Wayback Machine).
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-03-25. Retrieved 2016-06-01.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ Mother Tongue: Interviews with Musaemura B. Zimunya and Solomon Mutswairo Archived 2018-03-26 at the Wayback Machine University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- ↑ MSN Encarta. Archived from the original on 2009-10-31. Retrieved 2007-11-13.
- ↑ The World Health Organization. "Annex Table 1 - Basic indicators for all Member States" (PDF). The World Health Report 2006.
- ↑ Peta Thornycroft (2006-04-10). "In Zimbabwe, life ends before 40". Sydney Morning Herald. Harare. Retrieved 2006-04-10.
- ↑ "United Nations Statistics Division". Retrieved 17 January 2015.
- ↑ "Zimbabwe Population 2022", World Population Review, 2022
- ↑ Zimbabwe: People, CIA World Factbook, 2022
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-04-02. Retrieved 2014-01-27.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-04-02. Retrieved 2014-01-27.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "Zimbabwe National Statistics Agency". Zimstat.co.zw. Retrieved 2022-05-18.
- 1 2 "Africa :: ZIMBABWE". CIA The World Factbook. 10 May 2022.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook (2024 ed.). CIA. (Archived 2007 edition)
This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook (2024 ed.). CIA. (Archived 2007 edition)