| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
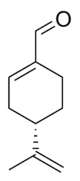
| IUPAC name
(S)-4-(1-Methylethenyl)-1-cyclohexene-1-carboxaldehyde | |||
| Other names
Perilla aldehyde; 4-Mentha-1,8-dien-7-al | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.639 | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C10H14O | |||
| Molar mass | 150.221 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 0.953 g/mL (20 °C) | ||
| Boiling point | 237 °C (459 °F; 510 K) (745 mmHg) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
Perillaldehyde, perillic aldehyde or perilla aldehyde, is a natural organic compound found most abundantly in the annual herb perilla, but also in a wide variety of other plants and essential oils. It is a monoterpenoid containing an aldehyde functional group.
Perillaldehyde, or volatile oils from perilla that are rich in perillaldehyde, are used as food additives for flavoring and in perfumery to add spiciness. Perillaldehyde can be readily converted to perilla alcohol, which is also used in perfumery. It has a mint-like, cinnamon odor and is primarily responsible for the flavor of perilla.
The oxime of perillaldehyde is known as perillartine or perilla sugar and is about 2000 times sweeter than sucrose and is used in Japan as a sweetener. It is presented in lower concentrations in the body odor of persons suffering from Parkinson's disease.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Merck Index, 12th Edition, 7308.
- ↑ Trivedi, Drupad K.; Sinclair, Eleanor; Xu, Yun; Sarkar, Depanjan; Walton-Doyle, Caitlin; Liscio, Camilla; Banks, Phine; Milne, Joy; Silverdale, Monty; Kunath, Tilo; Goodacre, Royston; Barran, Perdita (2019). "Discovery of Volatile Biomarkers of Parkinson's Disease from Sebum". ACS Central Science. 5 (4): 599–606. doi:10.1021/acscentsci.8b00879. PMC 6487537. PMID 31041379.
External links
 Media related to Perillaldehyde at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Perillaldehyde at Wikimedia Commons