Phatthalung
พัทลุง | |
|---|---|
 Wang Chao Mueang Phatthalung | |
 Flag  Seal | |
 Map of Thailand highlighting Phatthalung province | |
| Country | Thailand |
| Capital | Phatthalung |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Kukiat Wongkraphan (since 2017) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 3,424 km2 (1,322 sq mi) |
| • Rank | Ranked 58th |
| Population (2018)[2] | |
| • Total | 525,044 |
| • Rank | Ranked 51st |
| • Density | 153/km2 (400/sq mi) |
| • Rank | Ranked 28th |
| Human Achievement Index | |
| • HAI (2017) | 0.5679 "somewhat low" Ranked 56th |
| GDP | |
| • Total | baht 36 billion (US$1.2 billion) (2019) |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (ICT) |
| Postal code | 93xxx |
| Calling code | 074 |
| ISO 3166 code | TH-93 |
| Website | www |
Phatthalung (Thai: พัทลุง, pronounced [pʰát.tʰā.lūŋ]) is one of the southern provinces (changwat) of Thailand.[5] Neighboring provinces are (from north clockwise) Nakhon Si Thammarat, Songkhla, Satun, and Trang. Phatthalung is essentially a landlocked province, one of the only two in southern Thailand, the other being Yala.[6]
Geography

The province is on the Malay Peninsula. It borders to the east the large and shallow Songkhla Lake, and to the west the Nakhon Si Thammarat mountain range. Khao Pu–Khao Ya National Park is at the border with Trang.[7] Forests cover 628 km2 (242 sq mi), or 16.3 percent of the province's area.[8]
History
Phatthalung was formerly known as Mardelong (Jawi: مردلوڠ) in Malay, especially during the time when the region came under Malay-Muslim influence.[9]
Phatthalung became one of twelve royal cities during the reign of King Ramathibodi I of the Ayutthaya Kingdom in the 14th century. At the end of the 18th century, King Rama I submitted the city to the Ministry of Defense, which was responsible for all the southern provinces. In 1896, during the administrative reforms of King Chulalongkorn, Phatthalung became part of the Monthon Nakhon Si Thammarat. In 1924, King Rama VI ordered to move the city of Phatthalung to the present-day Khuha Sawan Subdistrict.
Demographics
The majority of the province's populace are Thai Buddhists. Muslims account for 11.1 percent of the population. Many of Phatthalung's Muslims have some ethnic Malay ancestry, but over the centuries they had intermarried with the Thais and adopted Thai cultural norms.[10]
Symbols
The provincial seal shows the 177 meter high Phu Khao Ok Thalu mountain, the symbol of the province. The provincial tree and flower is the sweet shorea (Shorea roxburghii).
Administrative divisions
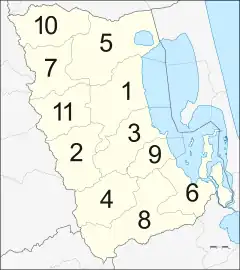
Provincial government
Phatthalung is divided into 11 districts (amphoes). The districts are further divided into 65 subdistricts (tambons) and 626 villages (mubans).
Local government
As of 26 November 2019 there are:[11] one Phatthalung Provincial Administration Organisation (ongkan borihan suan changwat) and 49 municipal (thesaban) areas in the province. Phatthalung has town (thesaban mueang) status. Further 48 subdistrict municipalities (thesaban tambon). The non-municipal areas are administered by 24 Subdistrict Administrative Organisations - SAO (ongkan borihan suan tambon).[2]
Transport
Air
Phatthalung does not have an airport. The nearest airport is Trang Airport, which is 66 km from the center of Phatthalung.
Rail
The main station in the province is the Phatthalung Railway Station.
Human achievement index 2017
| Health | Education | Employment | Income |
| 41 | 38 | 58 | 54 |
| Housing | Family | Transport | Participation |
 |
 |
 |
|
| 23 | 68 | 46 | 22 |
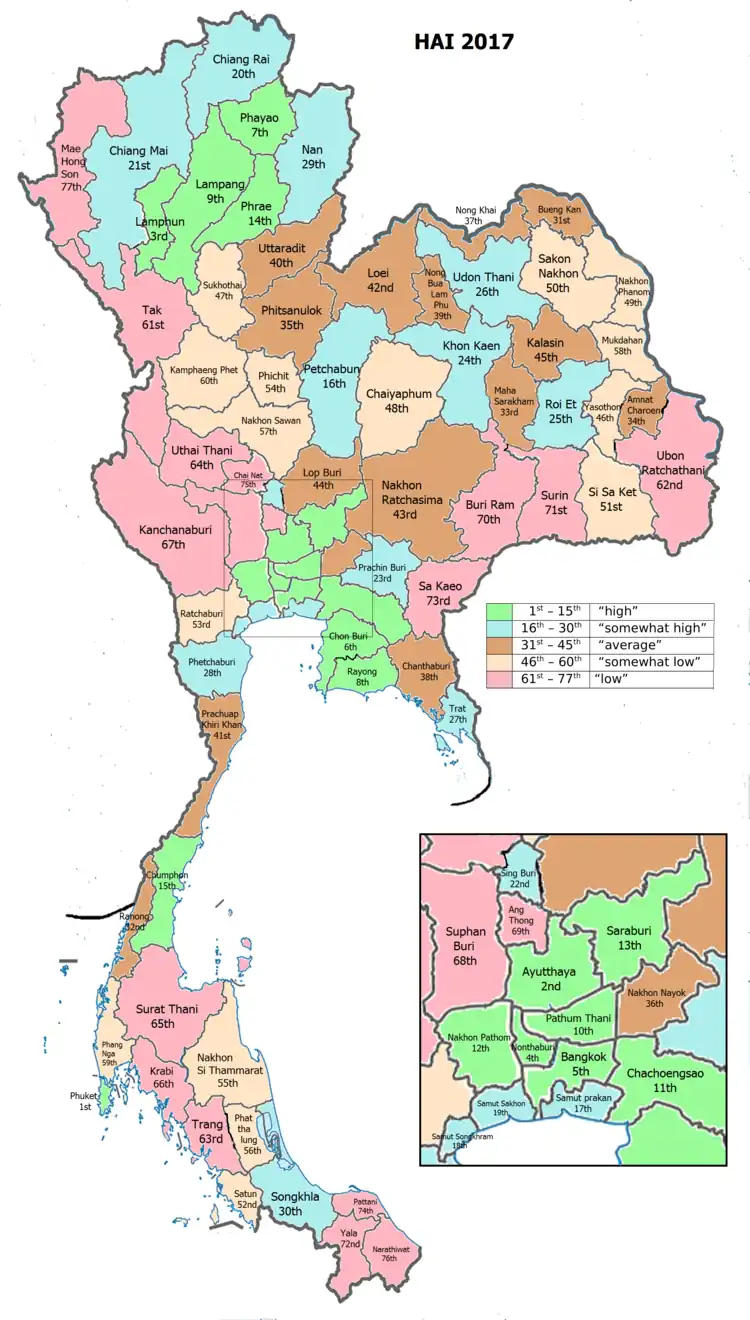
| Province Phatthalung, with an HAI 2017 value of 0.5679 is "somewhat low", occupies place 56 in the ranking. | |||
Since 2003, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in Thailand has tracked progress on human development at sub-national level using the Human achievement index (HAI), a composite index covering all the eight key areas of human development. National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB) has taken over this task since 2017.[3]
| Rank | Classification |
| 1 - 15 | "high" |
| 16 - 30 | "somewhat high" |
| 31 - 45 | "average" |
| 45 - 60 | "somewhat low" |
| 61 - 77 | "low" |
| Map with provinces and HAI 2017 rankings |
 |
Tourism
%252C_Birds%252C_Phatthalung%252C_Thailand.jpg.webp)

Sights
Phraya Thukkharat (Chuai) Monument (อนุสาวรีย์พระยาทุกขราษฎร์ (ช่วย)) - Phraya Thukkharat was a former monk known as Phra Maha Chuai. During the Nine Armies War in the reign of King Rama I, then Phra Maha Chuai had assisted Phraya Phatthalung, who had led a force of villagers to defeat an invading Burmese army. Later, when he had left the monkhood, he was awarded the royal title Phraya Thukkharat and was an assistant to the city's ruler.[12]
Culture

Manora or Nora (มโนราห์หรือโนรา) A local performing art in the south. It was an influence from the south of India, together with Lakhon Chatri (theatrical show by males). However, some dancing patterns were changed to match folk cultures in each province. There are 12 major dancing patterns. The patterns are done to lyrics sung by the dancers, either impromptu or composed in advance.
Talung (ตะลุง) *shadow plays) is a popular folk performance of the south. Talung puppets are made of dried cattle hide, cut beautifully into the characters of each shadow play. The puppets are usually painted black and each of them is held firmly between split bamboo slats called "mai tap". A puppet's mouth and hands will move in accordance with the narration. A Talung ensemble comprises the puppet masters (who are also the vocalists) and a band, totalling no more than eight persons. The musical instruments include pipes, drums, phon (a special kind of drum), and a gong.
References
- ↑ Advancing Human Development through the ASEAN Community, Thailand Human Development Report 2014, table 0:Basic Data (PDF) (Report). United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Thailand. pp. 134–135. ISBN 978-974-680-368-7. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-08-01. Retrieved 17 January 2016, Data has been supplied by Land Development Department, Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives, at Wayback Machine.
{{cite report}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - 1 2 "รายงานสถิติจำนวนประชากรและบ้านประจำปี พ.ศ.2561" [Statistics, population and house statistics for the year 2018]. Registration Office Department of the Interior, Ministry of the Interior (in Thai). 31 December 2018. Retrieved 20 June 2019.
- 1 2 Human achievement index 2017 by National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB), pages 1-40, maps 1-9, retrieved 14 September 2019, ISBN 978-974-9769-33-1
- ↑ "Gross Regional and Provincial Product, 2019 Edition". <>. Office of the National Economic and Social Development Council (NESDC). July 2019. ISSN 1686-0799. Retrieved 22 January 2020.
- ↑ "About Phatthalung". Tourism Authority of Thailand (TAT). Retrieved 23 May 2015.
- ↑ http://www.siewlianlim.com/uploads/7/1/1/3/7113499/the_role_of_shadow_puppetry_in_the_development_of__phatthalung.pdf
- ↑ "Khao Pu-Khao Ya National Park". Department of National Parks (DNP) Thailand. Archived from the original on 17 November 2015. Retrieved 23 May 2015.
- ↑ "ตารางที่ 2 พี้นที่ป่าไม้ แยกรายจังหวัด พ.ศ.2562" [Table 2 Forest area Separate province year 2019]. Royal Forest Department (in Thai). 2019. Retrieved 6 April 2021, information, Forest statistics Year 2019
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ↑ C. Skinner (1985). The Battle for Junk Ceylon: The Syair Sultan Maulana. Foris Publications. p. 272. ISBN 90-6765-066-8.
- ↑ William Chambers (publisher), Robert Chambers (1898). Chambers's Journal. W. & R. Chambers. p. 539.
- ↑ "Number of local government organizations by province". dla.go.th. Department of Local Administration (DLA). 26 November 2019. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
34 Phatthalung: 1 PAO, 1 Town mun., 48 Subdistrict mun., 24 SAO.
- ↑ "Phraya Thukkharat (Chuai) Monument". Tourism Authority of Thailand (TAT). Retrieved 2019-02-05.
External links
 Phatthalung travel guide from Wikivoyage
Phatthalung travel guide from Wikivoyage- Website of the province (Thai only)
- Phattalung provincial map, coat of arms and postal stamp Archived October 6, 2010, at the Wayback Machine