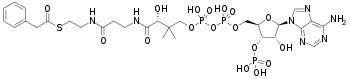
 Chemical structure of phenylacetyl-CoA | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3′-O-Phosphonoadenosine 5′-[(3R)-3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4-{[3-oxo-3-({2-[(phenylacetyl)sulfanyl]ethyl}amino)propyl]amino}-4-oxobutyl dihydrogen diphosphate] | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
O1-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)oxolan-2-yl]methyl} O3-[(3R)-3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4-{[3-oxo-3-({2-[(phenylacetyl)sulfanyl]ethyl}amino)propyl]amino}-4-oxobutyl] dihydrogen diphosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 3DMet | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C29H42N7O17P3S | |
| Molar mass | 885.67 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Phenylacetyl-CoA (C29H42N7O17P3S) is a form of acetyl-CoA formed from the condensation of the thiol group from coenzyme A with the carboxyl group of phenylacetic acid.[1][2]
Its molecular-weight is 885.7 g/mol. and IUPAC name is S-[2-[3-[[(2R)-4-[[[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-phosphonooxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanoyl]amino]propanoylamino]ethyl] 2-phenylethanethioate. It is formed via the actions of Phenylacetate—CoA ligase.[3]
Phenylacetyl-CoA is often produced via the reduction of ATP to AMP and the conversion of phenylacetate and CoA to diphosphate and Phenylacetyl-CoA.
- ATP + phenylacetate + CoA → AMP + diphosphate + phenylacetyl-CoA
This reaction is catalyzed by phenylacetate-CoA ligase.
Phenylacetyl-CoA combines with water and quinone to produce phenylglyoxylyl-CoA and quinol via a phenylacetyl-CoA dehydrogenase reaction acting as an oxidoreductase.
Phenylacetyl-CoA inhibits choline acetyltransferase acting as a neurotoxin. It competes with acetyl-CoA.[4]
References
- ↑ PubChem. "Phenylacetyl-CoA". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ↑ García, Belén; Olivera, Elías R.; Miñambres, Baltasar; Carnicero, David; Muñiz, Carmen; Naharro, Germán; Luengo, José M. (October 2000). "Phenylacetyl-Coenzyme A Is the True Inducer of the Phenylacetic Acid Catabolism Pathway in Pseudomonas putida U". Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 66 (10): 4575–4578. Bibcode:2000ApEnM..66.4575G. doi:10.1128/aem.66.10.4575-4578.2000. PMC 92347. PMID 11010921.
- ↑ Rhee, Sung-Keun; Fuchs, Georg (1999). "Phenylacetyl-CoA:acceptor oxidoreductase, a membrane-bound molybdenum–iron–sulfur enzyme involved in anaerobic metabolism of phenylalanine in the denitrifying bacterium Thauera aromatica". European Journal of Biochemistry. 262 (2): 507–515. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00399.x. ISSN 1432-1033. PMID 10336636.
- ↑ "Human Metabolome Database: Showing metabocard for Phenylacetyl-CoA (HMDB0006503)". www.hmdb.ca. Retrieved 2019-11-06.