| History of Estonia |
|---|
 |
| Chronology |
|
|
The Phosphorite War (Estonian: Fosforiidisõda) is the name given to a late-1980s environmental campaign in the then-Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic, against the opening of large phosphorite mines in the Virumaa region. The movement, peaking in 1987, was successful in achieving its immediate goals, but also in encouraging and strengthening the nationalist movement which led to the restoration of Estonian independence in 1991.[1][2] In Estonia it is regarded as a catalyst that led to the destabilization and dissolution of the Soviet government in Estonia.[3]
The campaign focused on two major issues. The large-scale environmental degradation that the new mines would cause was the most common subject in the public discussion. The other, more covert issue was the fear that the new mines' need for a workforce would start a wave of migration, bringing tens of thousands of workers from other parts of the Soviet Union to Estonia. In the view of Estonians this would have greatly worsened the already fragile demographic balance[2] (the share of Estonians in Estonia dropped from about 97% immediately after World War II to 61.5% in 1989[4]).
Background and early developments
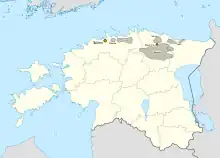
Phosphorite deposits (Obolus sandstone at the Upper Cambrian/Lower Ordovician boundary) are found in several places in Northern Estonia.[5] The Rakvere deposit, lying mostly in Lääne-Viru County, is the largest phosphorite deposit in Europe.[5] Phosphorite mining in Estonia started in 1924 near Maardu. In 1940 a new larger mine was opened, which together with a factory producing low-grade phosphorus fertilizers operated until late 1991, causing several environmental problems in the area.[5] Currently no phosphorite is mined in Estonia as it is not considered economically viable.
The central government of the Soviet Union in Moscow took interest in exploiting the phosphorite deposits in Lääne-Viru County in the early 1970s.[6] The first proposals suggested mining the Toolse deposit (north of Rakvere), but in the early 1980s, plans for the Toolse mine were cast aside and instead mining the Rakvere deposit was seen as more favourable. The plans were not made public, but among Estonian scientists and environmentalists involved in the decision-making there was considerable opposition to the plan. Notably, there were people in the Estonian Academy of Sciences, like Endel Lippmaa, who were aware of and opposed to the plan.[3]
Major events
The phosphorite issue became known to the general public on 25 February 1987, which is often used to mark the start of the Phosphorite War.[3] On this day Moscow’s plans to expand phosphorite mining in Northern Estonia were revealed on Estonian TV.[2] Although the Estonian Communist Party publicly held a position that the decision about mining had to be made by Estonians, it appeared that the central government had already finalized the plans.[3]

Numerous protests broke out and petitions were signed against the new mines.[1] The question came to a head in spring 1987 in an unprecedented public debate.[7] In April students from Tartu University held a meeting in the main hall of the university and unanimously condemned the actions of the leadership of the Estonian SSR.[1] At traditional May Day demonstrations, students carried slogans against phosphorite mining and wore yellow T-shirts with the text "Phosphorite – no thanks", which became extremely popular.[1]
On May 8 a cartoon by Priit Pärn was published in the newspaper Sirp ja Vasar (Hammer and Sickle). Entitled Just shit (Estonian: Sitta kah!), the cartoon showed a peasant shoveling on his field a piece of manure shaped like Estonia. The cartoon was widely discussed and is probably the most famous cartoon ever published in Estonia.[8][9] Following these and other events and faced with general opposition to the mines, on 18 September 1987 the Soviet authorities had to back down from their plans.[6] The end of the Phosphorite War is hard to define, but the movement mostly calmed down during 1988.[10]
Aftermath
Regarding the Estonian independence movement, the unintended consequences of the campaign were of similar importance to the immediate outcome.[3] The Phosphorite War activated the Estonian masses,[7] gave people faith in the power of collective action[3] and was an important factor in the disappearance of fear of the regime.[2] Overall, it acted as a catalyst that led to the destabilization of the Soviet government in Estonia.[3]
References
- 1 2 3 4 Subrenat, Jean-Jacques, ed. (2004). Estonia: identity and independence. New York: Rodopi. ISBN 90-420-0890-3.
- 1 2 3 4 Vogt, Henri (2005). Between Utopia and disillusionment : a narrative of the political transformation in Eastern Europe. New York; Oxford: Berghahn Books. p. 333. ISBN 1-57181-895-2.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Miljan, Toivo (2004). Historical dictionary of Estonia. Oxford: Scarecrow Press. p. 558. ISBN 9780810865716.
- ↑ Eesti rahvastik rahvaloenduste andmetel (Population of Estonia by population censuses) (in Estonian and English). Vol. 2. Eesti Statistikaamet (Statistical Office of Estonia). 1996. ISBN 9985-826-44-2. Retrieved 2009-10-22.
- 1 2 3 Raukas, Anto; Teedumäe, Aada, eds. (1997). Geology and Mineral Resources of Estonia. Tallinn: Estonian Academy Publishers. p. 436. ISBN 9985-50-185-3. Archived from the original on 2007-12-11.
- 1 2 Laurisaar, Riho (2007-05-26). "Fosforiidisõda päästis Kirde-Eesti looduse pöördumatust hävingust". Eesti Päevaleht (in Estonian). Archived from the original on 2008-04-26. Retrieved 2009-10-22.
- 1 2 Raun, Toivo U. (2001). Estonia and the Estonians. Stanford: Hoover Institution Press, Stanford University. ISBN 0-8179-2852-9.
- ↑ Kolk, Tiina (2007-04-27). "Priit Pärn - Botaanik kunstimaailmas". Äripäev (in Estonian).
- ↑ Lõhmus, Maarja (2004). "An effect of meaning-breaker: Analysis of the cartoon 'Just shit'". Semiotica. 150 (1): 257–282. Archived from the original on 2012-02-19. Retrieved 2009-10-22.
- ↑ Raudsep, Rein (1997). "Kümme aastat fosforiidisõjast". Eesti Loodus (in Estonian) (7). Archived from the original on 2012-02-24. Retrieved 2009-10-22.