 | |
| Developer(s) | Juliusz Chroboczek |
|---|---|
| Final release | 1.1.1
/ 15 May 2014 |
| Repository | |
| Written in | C |
| Operating system | Windows, OS X, Linux, OpenWrt, FreeBSD, OpenBSD[1] |
| Type | web cache, proxy server |
| License | MIT License (free software)[2] |
| Website | www.pps.univ-paris-diderot.fr/~jch/software/polipo/ |

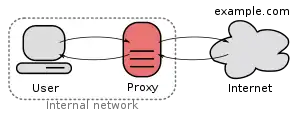
Polipo is a discontinued lightweight caching and forwarding web proxy server. It has a wide variety of uses, from aiding security by filtering traffic; to caching web, DNS and other computer network lookups for a group of people sharing network resources; to speeding up a web server by caching repeated requests. It can be configured to use on-disk cache and serve cached content when offline and perform various forms of content filtering.
To minimize latency, Polipo both pipelines multiple resource requests and multiplexes multiple transactions onto the same TCP/IP connection.[3] Polipo is HTTP 1.1-compliant, supports IPv4, IPv6, traffic filtering and privacy-enhancement.
Polipo is free software[4] released under the MIT License.[5]
Polipo ceased to be maintained on 6 November 2016[6] due to the increasingly widespread use of encryption (i.e. HTTPS) making caching proxies obsolete.[7]
Design
Polipo is designed to be used as a personal web cache or a web cache shared among a few users to boost internet access.[8][9] Designed to be fast, lightweight and small, it is useful when the system resources for a larger proxy are unavailable. Because of this, it has been put to uses such as a tether on the OpenWrt.
GUI wrappers
Natively, polipo comes as a highly specialized command-line interface (CLI) software application, which requires commands to be typed on the keyboard and parameters stored in configuration text files. Alternatively, polipo allows users to run the program automated and non-interactively, such as in a shell script. By starting a GUI wrapper application users can intuitively interact with polipo, start and stop it and change its working parameters, through graphical icons and visual indicators.
Some independent GUI wrapper projects are:
Features
The fast, lightweight and small memory footprint proxy server polipo uses a variety of techniques:[4]
- Polipo will upgrade client requests to HTTP/1.1 even if they come in as old HTTP/1.0.
- Polipo does HTTP 1.1 pipelining well, so it can enhance internet communication latency.
- Polipo will make web browsing faster or at least appear to have less latency.
- Polipo will cache the initial segment of a download and can complete it later using Range requests, in case of interrupts.
- Polipo can, to some extent, substitute for filtering and privacy-enhancing proxies such as Privoxy or WWWOFFLE, it provides capabilities to block or redirect requests, censor HTTP request headers and referrer information.[13]
- Polipo has complete support for IPv6.
- Since Polipo can speak both IPv4 and IPv6, Polipo can be used as a bridge between the IPv4 and IPv6 Internets.
- Polipo can speak the SOCKS 4 and SOCKS 5 protocols.
- Polipo serves as a web cache.
Limitations
Polipo is limited to 2G or 4G file sizes on 32 bit systems which will cause errors when serving large requests.
See also
- Web accelerator which discusses host-based HTTP acceleration
- Reverse proxy which discusses origin-side proxies
- Comparison of web servers
- Internet Cache Protocol
- List of TCP and UDP port numbers
References
- ↑ "polipo-1.1.1 – HTTP caching proxy". OpenBSD ports. 20 August 2014. Retrieved 10 November 2015.
- ↑ "The Polipo Manual". Retrieved 23 September 2010.
- ↑ Fielding, R.; Gettys, J.; Mogul, J.; Frystyk, H.; Berners-Lee, T. (1997). "rfc2068 - HTTP/1.1". doi:10.17487/RFC2068. Retrieved 23 September 2010.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - 1 2 "Polipo — a caching web proxy". Retrieved 5 February 2010.
- ↑ "Polipo distribution conditions". Retrieved 23 September 2010.
- ↑ polipo commits: rephrase README (6 November 2016)
- ↑ "Polipo — a caching web proxy". Retrieved 5 December 2016.
- ↑ "Boost your Internet browsing - Install Polipo". Retrieved 5 February 2010.
- ↑ "The Polipo Manual". Retrieved 23 September 2010.
- ↑ "Solipo". Retrieved 23 September 2010.
- ↑ "Dolipo". Retrieved 23 September 2010.
- ↑ "Polipoid". Retrieved 21 April 2014.
- ↑ "Censoring headers - The Polipo Manual". Retrieved 30 April 2013.