| Polyvinyl esters: General formula |
|---|
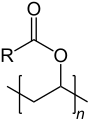 (R = CH3; CH2Cl; C2H5 etc.) |
Polyvinyl esters are a group of thermoplastic vinyl polymers. The most important examples of this group are polyvinyl acetate (PVAC) and polyvinyl propionate.[1]
Production
The radical polymerization of vinyl ester 1 (e.g. in case of vinyl acetate; R = CH3) yields polyvinyl ester 2:
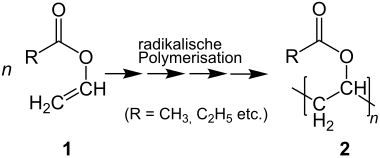
Synthese der Polyvinylester
Use
The transparent polymers are used for the production of lacquers and as adhesives.[1] The hydrolytic cleavage of the ester bonds of vinyl acetate is of industrial significance.[2]
References
- 1 2 Hans-Dieter Jakubke, Ruth Karcher (1999), Lexikon der Chemie in drei Bänden (in German), Heidelberg: Spektrum Verlag, p. 93, ISBN 3827403812
- ↑ Sebastian Kotzenburg, Michael Maskus, Oskar Nuyken (2014), Polymere: Synthese, Eigenschaften und Anwendungen (in German), Berlin: Springer Spektrum, pp. 429–430, ISBN 978-3-642-34772-6
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.