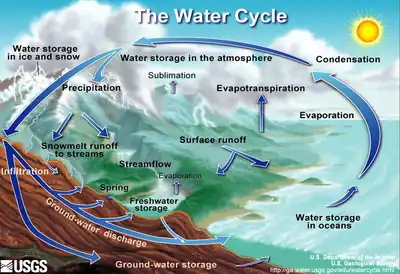
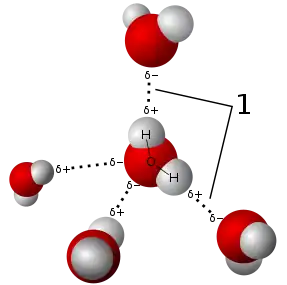
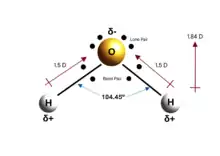
The Water Portal The multiple arches of the Pont du Gard in Roman Gaul (modern-day southern France). The upper tier encloses an aqueduct that carried water to Nimes in Roman times; its lower tier was expanded in the 1740s to carry a wide road across the river.  Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula H2O. It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, and it is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, H2O, indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. "Water" is also the name of the liquid state of H2O at standard temperature and pressure. Because Earth's environment is relatively close to water's triple point, water exists on Earth as a solid, a liquid, and a gas. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice may precipitate in the form of snow. The gaseous state of water is steam or water vapor. Water covers about 71% of the Earth's surface, with seas and oceans making up most of the water volume (about 96.5%). Small portions of water occur as groundwater (1.7%), in the glaciers and the ice caps of Antarctica and Greenland (1.7%), and in the air as vapor, clouds (consisting of ice and liquid water suspended in air), and precipitation (0.001%). Water moves continually through the water cycle of evaporation, transpiration (evapotranspiration), condensation, precipitation, and runoff, usually reaching the sea. (Full article...) Selected article -Ice is water that is frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 °C, 32 °F, or 273.15 K. As a naturally occurring crystalline inorganic solid with an ordered structure, ice is considered to be a mineral. Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaque bluish-white color. In the Solar System, ice is abundant and occurs naturally from as close to the Sun as Mercury to as far away as the Oort cloud objects. Beyond the Solar System, it occurs as interstellar ice. It is abundant on Earth's surface – particularly in the polar regions and above the snow line – and, as a common form of precipitation and deposition, plays a key role in Earth's water cycle and climate. It falls as snowflakes and hail or occurs as frost, icicles or ice spikes and aggregates from snow as glaciers and ice sheets. (Full article...)Did you know (auto-generated) -
More did you know - DYK Question Mark
Water NewsNote: this section was updated in February 2020
Selected pictureCategoriesCategory puzzle Select [►] to view subcategories
Water Water by city Water by continent Water by country Water by dependent territory Water by region Forms of water Anoxic waters Aquatic ecology Aquatic organisms Aquatic therapy Bodies of water Body water Water castles Water chemistry Water clocks Water in culture Desiccation Drinking water Water and the environment Extraterrestrial water Flood Fluvial landforms Fresh water Hydraulic rams Hydraulophones Hydropower Ice Lacustrine landforms Water management Moisture protection Water organizations Water physics Water and politics Water power Saline water Water scarcity Water and society Spa waters Water technology Water torture Water transport Underwater Waterborne diseases Watermills Waterproofing Photo gallery links(updated in February 2020)
TopicsGeneral imagesThe following are images from various water-related articles on Wikipedia.
Related portalsWikiprojects
 Lake Nyos – WikiProject Lakes
Things you can do
Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
More portalsDiscover Wikipedia using portals
|
.jpg.webp)







%252C_Port_Campbell_National_Park%252C_Worm_Bay_--_2019_--_0863.jpg.webp)



.jpg.webp)









%252C_OWID.svg.png.webp)




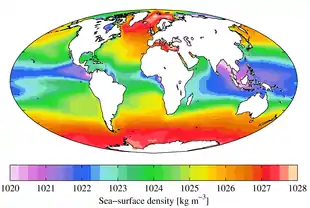
.jpg.webp)

.svg.png.webp)
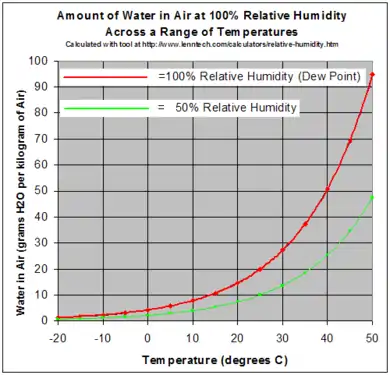



.svg.png.webp)