 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Potassium O-pentyl carbonodithioate | |
| Other names
potassium pentylxanthogenate potassium-O-pentyl dithiocarbonate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.018.481 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
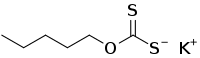
| C6H11KOS2 | |
| Molar mass | 202.37 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Pale yellow or yellow powder |
| Density | 1.073 g/cm3 |
| Soluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
   | |
| Warning | |
| H228, H302, H312, H315, H319, H335, H411 | |
| P210, P240, P241, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P363, P370+P378, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Potassium amyl xanthate (/pəˈtæsiəm ˌæmɪl ˈzænθeɪt/) is an organosulfur compound with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)4OCS2K. It is a pale yellow powder with a pungent odor that is soluble in water. It is widely used in the mining industry for the separation of ores using the flotation process.
Production and properties
As typical for xanthates, potassium amyl xanthate is prepared by reacting n-amyl alcohol with carbon disulfide and potassium hydroxide.[1]
- CH3(CH2)4OH + CS2 + KOH → CH3(CH2)4OCS2K + H2O
Potassium amyl xanthate is a pale yellow powder. Its solutions are relatively stable between pH 8 and 13 with a maximum of stability at pH 10.[2]
Related compounds
- Sodium amyl xanthate is used in the separation of nickel and copper from their ores.[3]
Safety
The LD50 is 90-148 mg/kg (oral, rat). [4]
It is a biodegradable compound.
References
- ↑ Charles C. Price and Gardner W. Stacy (1948). "p-nitrophenyl sulfide". Organic Syntheses. 28: 82.; Collective Volume, vol. 3, p. 667
- ↑ J. Dyer, L. H. Phifer, Macromolecules 2 (1969) 111. R. J. Millican, C. K. Sauers, J. Org. Chem. 44 (1979) 1964.
- ↑ Kerfoot, Derek G. E. (2005). "Nickel". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_157. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ↑ Kathrin-Maria Roy "Xanthates" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.