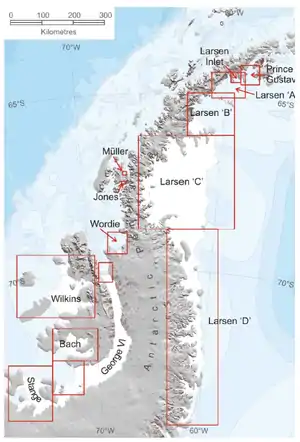
Prince Gustav Ice Shelf (64°15′S 58°30′W / 64.250°S 58.500°W) was an ice shelf of more than 15 nautical miles (28 km) extent occupying the south part of Prince Gustav Channel, including Rohss Bay, James Ross Island. Named by United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1990 in association with the channel. The ice shelf has since retreated and collapsed; in 1995 Prince Gustav Channel was open throughout its length, and only a remnant in Rohss Bay remained.[2]
Prince Gustav ice shelf also retreated in the mid-Holocene period 5000 to 2000 years before present, [this] "corresponds to regional climate warming deduced from other paleoenvironmental records."[3] This resulted in seasonally open water in the Prince Gustav Channel, as today.
References
- ↑ A. J. Cook; D. G. Vaughan (2009). "Ice shelf changes on the Antarctic Peninsula" (PDF). The Cryosphere Discussions. 3: 579–630. doi:10.5194/tcd-3-579-2009.
- ↑ Cooper, Alexander Paul Robin (1997). "Historical observations of Prince Gustav Ice Shelf". Polar Record. 33 (187): 285–294. doi:10.1017/s0032247400025389. S2CID 129126205. Retrieved 10 December 2012.
- ↑ Carol J. Pudsey, Jeffrey Evans; First survey of Antarctic sub–ice shelf sediments reveals mid-Holocene ice shelf retreat. Geology ; 29 (9): 787–790. doi: https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0787:FSOASI>2.0.CO;2
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Prince Gustav Ice Shelf". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Prince Gustav Ice Shelf". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey.