 Viking Orbiter 1 mosaic | |
| Planet | Mars |
|---|---|
| Region | Noachis Terra |
| Coordinates | 48°00′S 330°30′W / 48°S 330.5°W |
| Quadrangle | Noachis |
| Eponym | Richard A. Proctor |
Proctor is a large crater in the Noachis quadrangle of Mars. It measures 168.2 kilometres (104.5 miles) in diameter and was named after Richard A. Proctor, a British astronomer (1837–1888).[1]
Dune fields
The crater contains a 35 x 65 km dark dune field.[2][3] It was one of the first sand dune fields ever recognized on Mars based on Mariner 9 images.[4] The crater's dunes are being monitored by HiRISE to identify changes over time.[5]
 Topographical map showing location of Proctor crater and other nearby craters
Topographical map showing location of Proctor crater and other nearby craters Another Viking image of the dunes in Proctor and in nearby craters
Another Viking image of the dunes in Proctor and in nearby craters Proctor crater transverse aeolian ridges and Dunes, as seen by HiRISE
Proctor crater transverse aeolian ridges and Dunes, as seen by HiRISE HiRISE image of the crater with transverse aeolian ridges surrounding a large dune
HiRISE image of the crater with transverse aeolian ridges surrounding a large dune The edge of a dark dune field on the floor of Proctor crater
The edge of a dark dune field on the floor of Proctor crater Dune field on floor of Proctor crater, as seen by CTX camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
Dune field on floor of Proctor crater, as seen by CTX camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.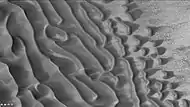 Close-up of dunes on floor of Proctor crater, as seen by CTX camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. This is an enlargement of part of previous image.
Close-up of dunes on floor of Proctor crater, as seen by CTX camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. This is an enlargement of part of previous image.
See also
References
- ↑ "Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature | Proctor". usgs.gov. International Astronomical Union. Retrieved 4 March 2015.
- ↑ Fenton, L. K. (2005). "Seasonal Movement of Material on Dunes in Proctor Crater, Mars: Possible Present-Day Sand Saltation" (PDF). Lunar and Planetary Science XXXVI (2005).
- ↑ Mary Chapman, ed. (2007). The Geology of Mars: Evidence from Earth-Based Analogs. Cambridge University Press. p. 250. ISBN 978-0-521-83292-2.
- ↑ "Dune Activity in Proctor Crater". Mars Global Surveyor - Mars Orbiter Camera - MGS MOC Release No. MOC2-170. Malin Space Science Systems. 10 August 1999.
- ↑ Bridges, Nathan (9 March 2009). "Sand Dunes and Ripples in Proctor Crater". HiRISE Operations Center.
External links
 Media related to Proctor (Martian crater) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Proctor (Martian crater) at Wikimedia Commons- Nemiroff, Robert; Bonnell, Jerry (February 26, 2002). "Sand Dunes on Mars". Astronomy Photo of the Day (APOD).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.