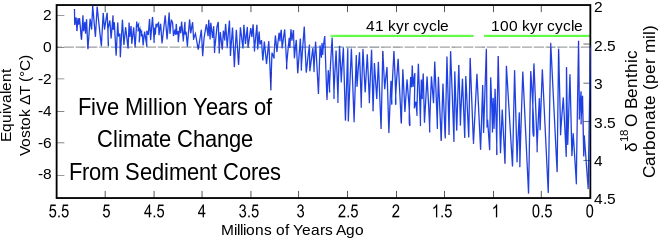
Marine Isotope Stage 9 (MIS 9) was an interglacial period that consisted of two interstadial and one stadial period.[1][2] It is the final period of the Lower Paleolithic and lasted from 337,000 to 300,000 years ago according to Lisiecki and Raymo's LR04 Benthic Stack.[3] It corresponds to the Purfleet Interglacial in Britain,[4] the Holstein Interglacial in continental Europe,[5] and the Pre-Illinoian in North America.
Climate
Both interstadial phases (a, c) comprised approximately 20,000 years.[6] The stadial or warmer period (b) divided these climates by 4000 years between 316 and 320 ka. During the MIS9c interstadial, temperatures were above −4.0°C for the first 16,000 years and the following 4000 years had temperatures of approximately 3.5°C above those of modern climate. MIS9b stadial followed this period reaching glacial temperatures. The MIS 9a interstadial period is what drove conditions to the MIS 8. The temperatures during this period reached a maximum of −2.5°C.[1]
MIS Drivers
Marine Isotope Stages are glacial and interglacial periods throughout time.[7] One of the processes that drive this major change are the Milankovitch Cycles, which control the insolation received from the Sun. [8] The data is retrieved from deep sea core samples. The manner by which the data is obtained through core samples is mainly due to the sedimentation in the region which can be very indicative of an interglacial or glacial phases.
Marine Oxygen Isotopes
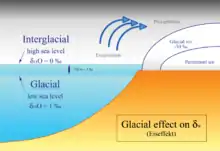
MIS are obtained through oxygen isotope analysis within the core samples to understand paleoclimate changes. [7] This includes glacial and interglacial periods. The data is retrieved from proxies, such as foraminifera and pollen that have diverse oxygen-18 to oxygen-16 ratios depending on the temperature in the ocean during said events. When the isotopic analysis results in high isotopic ratio values, it is representative of colder glacial environments, while isotopic values with low ratios are indicative of warmer temperatures.[9]
Interglacial Impacts on Living Organisms
European culture impacts
During this interglacial stage, Europe was occupied by Homo heidelbergensis, who had retreated from Britain during the preceding glacial period. Populations returned as the climate warmed and sea levels rose around 330,000 years ago. The evidence of their return is found along terraces of the Thames and former Solent rivers of Europe. Within the area, thousands of hand axes and other artefacts have been found indicating their return after the increasing warmer temperatures. In Southern England, the summers were similar to or slightly warmer than today, and the winters slightly cooler.[4] The period saw a transition to Clactonian culture for manufacture of stone tools.[10]
References
- 1 2 Webb, Steve (2013-01-01), Webb, Steve (ed.), "6 - Australia and the Quaternary Ice Ages", Corridors to Extinction and the Australian Megafauna, Oxford: Elsevier, pp. 127–148, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-407790-4.00006-9, ISBN 978-0-12-407790-4, retrieved 2023-02-13
- ↑ Webb, Steve (2013), "Australia's Megafauna Extinction Drivers", Corridors to Extinction and the Australian Megafauna, Elsevier, pp. 217–242, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-407790-4.00009-4, ISBN 9780124077904, retrieved 2023-02-05
- ↑ Lisiecki, Lorraine E.; Raymo, Maureen E. (2005-01-18). "A Pliocene-Pleistocene stack of 57 globally distributed benthic δ18O records". Paleoceanography. 20 (1): n/a. Bibcode:2005PalOc..20.1003L. doi:10.1029/2004pa001071. ISSN 0883-8305. S2CID 12788441.
- 1 2 Ashton, Nick (2017). Early humans. London. ISBN 978-0-00-815035-8. OCLC 959648563.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ↑ Moncel, Marie-Hélène; Arzarello, Marta; Peretto, Carlo (2016-07-21). "The Hoslteinian period in Europe (MIS 11-9)". Quaternary International. Special Issue: The Hoslteinian period in Europe (MIS 11-9). 409: 1–8. Bibcode:2016QuInt.409....1M. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2016.06.006. ISSN 1040-6182.
- ↑ Turner, C. (1998-03-01). "Volcanic Maars, Long Quaternary Sequences and the Work of the Inqua Subcommission on European Quaternary Stratigraphy". Quaternary International. 47–48 (1): 41–49. Bibcode:1998QuInt..47...41T. doi:10.1016/S1040-6182(97)00069-4. ISSN 1040-6182.
- 1 2 M., Cronin, Thomas (2010). Paleoclimates understanding climate change past and present. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-51636-5. OCLC 1303291501.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Stirling, C. H.; Esat, T. M.; Lambeck, K.; McCulloch, M. T.; Blake, S. G.; Lee, D.-C.; Halliday, A. N. (2001-01-12). "Orbital Forcing of the Marine Isotope Stage 9 Interglacial". Science. 291 (5502): 290–293. Bibcode:2001Sci...291..290S. doi:10.1126/science.291.5502.290. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 11209076.
- ↑ Polar Libraries Colloquy (23rd : 2010 : Bremerhaven, Germany) (2010). Cool libraries in a melting world : proceedings of the 23rd Polar Libraries Colloquy 2010, June 13-18, 2010, Bremerhaven, Germany. AWI, Alfred-Wegener-Institut für Polar- und Meeresforschung. OCLC 1064296475.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ↑ McNabb, John (2011-03-17). The British Lower Palaeolithic: Stones in Contention. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-09055-6.