| Pythium debaryanum | |
|---|---|
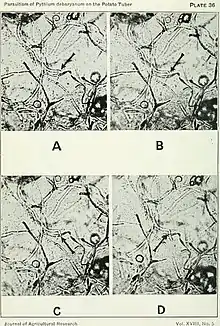 | |
| Photographs enlarged from portions of a motion photomicrograph, showing the method of cell wall penetration by Pythium hyphae. A. — Shows hypha growing toward the potato cell wall. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Clade: | Diaphoretickes |
| Clade: | SAR |
| Clade: | Stramenopiles |
| Phylum: | Oomycota |
| Order: | Peronosporales |
| Family: | Pythiaceae |
| Genus: | Pythium |
| Species: | P. debaryanum |
| Binomial name | |
| Pythium debaryanum R. Hesse (1874) | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Eupythium debaryanum (R. Hesse) Nieuwl., (1916) | |
Pythium debaryanum is a species of water mould in the family Pythiaceae. It is known as a plant pathogen on many kinds of wild and cultivated plants, including peanut, beet, eucalyptus, tobacco, and pine trees. The plants develop damping off, a disease state.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ Pythium debaryanum. Plantwise.
External links

Photographs enlarged from portions of a motion photomicrograph, showing the method of cell wall penetration by Pythium hyphae.
A. — Shows the hypha growing against the potato cell wall. Sufficient pressure has already been applied to cause the hypha to bend. Notice that this bending increases in later photographs.
B. — A little later stage than A.
C. — The tip has broken through as a small tube
D. — Penetration is complete. Notice the constriction of the hypha at the point where it penetrates the potato cell wall.
A. — Shows the hypha growing against the potato cell wall. Sufficient pressure has already been applied to cause the hypha to bend. Notice that this bending increases in later photographs.
B. — A little later stage than A.
C. — The tip has broken through as a small tube
D. — Penetration is complete. Notice the constriction of the hypha at the point where it penetrates the potato cell wall.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.