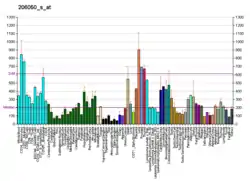
| RNH1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | RNH1, RAI, RNH, ribonuclease/angiogenin inhibitor 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 173320 MGI: 1195456 HomoloGene: 2204 GeneCards: RNH1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ribonuclease inhibitor is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RNH1 gene.[5]
References
- 1 2 3 ENSG00000023191 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000276230, ENSG00000023191 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000038650 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: RNH1 ribonuclease/angiogenin inhibitor 1".
Further reading
- Zneimer SM, Crawford D, Schneider NR, Beutler B (1991). "Mapping of the human ribonuclease inhibitor gene (RNH) to chromosome 11p15 by in situ hybridization". Genomics. 8 (1): 175–8. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(90)90242-M. PMID 2081593.
- Weremowicz S, Fox EA, Morton CC, Vallee BL (1991). "The placental ribonuclease inhibitor (RNH) gene is located on chromosome subband 11p15.5". Genomics. 8 (4): 717–21. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(90)90260-2. PMID 2276743.
- Lee FS, Vallee BL (1989). "Binding of placental ribonuclease inhibitor to the active site of angiogenin". Biochemistry. 28 (8): 3556–61. doi:10.1021/bi00434a061. PMID 2742853.
- Bond MD, Vallee BL (1989). "Isolation of bovine angiogenin using a placental ribonuclease inhibitor binding assay". Biochemistry. 27 (17): 6282–7. doi:10.1021/bi00417a013. PMID 3064806.
- Hofsteenge J, Kieffer B, Matthies R, et al. (1989). "Amino acid sequence of the ribonuclease inhibitor from porcine liver reveals the presence of leucine-rich repeats". Biochemistry. 27 (23): 8537–44. doi:10.1021/bi00423a006. PMID 3219361.
- Lee FS, Fox EA, Zhou HM, et al. (1989). "Primary structure of human placental ribonuclease inhibitor". Biochemistry. 27 (23): 8545–53. doi:10.1021/bi00423a007. PMID 3219362.
- Schneider R, Schneider-Scherzer E, Thurnher M, et al. (1989). "The primary structure of human ribonuclease/angiogenin inhibitor (RAI) discloses a novel highly diversified protein superfamily with a common repetitive module". EMBO J. 7 (13): 4151–6. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03310.x. PMC 455125. PMID 3243277.
- Shapiro R, Vallee BL (1987). "Human placental ribonuclease inhibitor abolishes both angiogenic and ribonucleolytic activities of angiogenin". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84 (8): 2238–41. Bibcode:1987PNAS...84.2238S. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.8.2238. PMC 304624. PMID 3470787.
- Kiyohara H, Menjo M (1984). "Ribonuclease and ribonuclease inhibitor in the human pancreas". Gastroenterol. Jpn. 18 (5): 468–73. doi:10.1007/BF02776587. PMID 6653993. S2CID 10963236.
- Nadano D, Yasuda T, Takeshita H, et al. (1994). "Purification and characterization of human brain ribonuclease inhibitor". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 312 (2): 421–8. doi:10.1006/abbi.1994.1328. PMID 8037455.
- Kobe B, Deisenhofer J (1994). "Crystal structure of porcine ribonuclease inhibitor, a protein with leucine-rich repeats". Nature. 366 (6457): 751–6. doi:10.1038/366751a0. PMID 8264799. S2CID 34579479.
- Papageorgiou AC, Shapiro R, Acharya KR (1997). "Molecular recognition of human angiogenin by placental ribonuclease inhibitor--an X-ray crystallographic study at 2.0 A resolution". EMBO J. 16 (17): 5162–77. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.17.5162. PMC 1170149. PMID 9311977.
- Gaur D, Swaminathan S, Batra JK (2001). "Interaction of human pancreatic ribonuclease with human ribonuclease inhibitor. Generation of inhibitor-resistant cytotoxic variants". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (27): 24978–84. doi:10.1074/jbc.M102440200. PMID 11342552.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Fu P, Chen J, Tian Y, et al. (2005). "Anti-tumor effect of hematopoietic cells carrying the gene of ribonuclease inhibitor". Cancer Gene Ther. 12 (3): 268–75. doi:10.1038/sj.cgt.7700742. PMID 15592448.
- Iyer S, Holloway DE, Kumar K, et al. (2005). "Molecular recognition of human eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (RNase 2) by placental ribonuclease inhibitor". J. Mol. Biol. 347 (3): 637–55. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.01.035. PMID 15755456.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1173R. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- Johnson RJ, McCoy JG, Bingman CA, et al. (2007). "Inhibition of Human Pancreatic Ribonuclease by the Human Ribonuclease Inhibitor Protein". J. Mol. Biol. 368 (2): 434–49. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.02.005. PMC 1993901. PMID 17350650.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.