| RPG-22 | |
|---|---|
 RPG-22 launcher | |
| Type | Disposable Rocket-propelled grenade |
| Place of origin | Soviet Union |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1985–present |
| Used by | See Operators |
| Wars | Soviet–Afghan War[1] Russo-Georgian War Iraq War Syrian Civil War[2] Iraqi Civil War[3] Russo-Ukrainian War |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 2.8 kg (loaded) |
| Length | 785 mm (unarmed) 850 mm (ready to fire) |
| Shell | HEAT |
| Caliber | 72.5 mm |
| Action | 400 mm: RHA 1000 mm: Concrete 1200 mm: Brick |
| Muzzle velocity | 133 m/s |
| Effective firing range | 150–200 m |
| Maximum firing range | 250 m |
The Soviet RPG-22 Netto is a one-shot disposable anti-tank rocket launcher first deployed in 1985, based on the RPG-18 rocket launcher, but firing a larger 72.5 mm fin stabilised projectile. The weapon fires an unguided projectile, can be prepared to fire in around 10 seconds, and can penetrate 400 mm of armour, 1.2 metres of brick or 1 metre of reinforced concrete.[4]
Operation

The smoothbore container is made from two fibreglass parts; a main tube containing the rocket, and a telescoping forward extension, which slides over the barrel.
In transport mode, both ends of the barrel are closed by plastic covers, which open when the weapon is extended. The firing mechanism is manually cocked by raising the rear sight. Lowering the rear sight de-cocks the weapon if there is no target.
On firing, there is a backblast danger area behind the weapon, of at least 15 metres. The solid propellant motor completely burns out while the rocket is still in the barrel tube, accelerating it to about 133 metres per second. The weapon has simple pop-up sights graduated to ranges of 50, 150 and 250 metres.
To keep training costs down, a reusable RPG-22 is available that fires a 30 mm subcalibre projectile, weighing 350g, to operational ranges. Handling is identical to that of the full calibre version, with the exception of the discharge noise and backblast.
Real IRA use
On the evening of 20 September 2000, dissident Irish Republican group the Real IRA attacked the MI6 Building in London (the headquarters of the British Secret Intelligence Service) with a single RPG-22 round, causing superficial damage - see 2000 MI6 attack.[5][6] The rocket used in London was made in Russia; a rocket found in a Real IRA cache near Dungannon came from Bulgaria.[7] A weapons cache destined for the Real IRA, seized in Croatia in August 2000, contained a number of RPG-22s.[7] Prices range from £150 to £220 per launcher.[7]
Operators
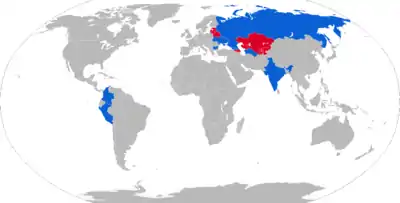
Current operators
 Russia – Russian Ground Forces
Russia – Russian Ground Forces Bulgaria – Bulgarian Land Forces, local production at VMZ Sopot.[8]
Bulgaria – Bulgarian Land Forces, local production at VMZ Sopot.[8] Colombia – Colombian National Army
Colombia – Colombian National Army Croatia – Croatian Army
Croatia – Croatian Army Georgia – Georgian Land Forces
Georgia – Georgian Land Forces India – Indian Army
India – Indian Army Iraq: Iraqi insurgents[3]
Iraq: Iraqi insurgents[3] Moldova – Moldovan Ground Forces
Moldova – Moldovan Ground Forces Peru – Peruvian Army
Peru – Peruvian Army Syria[9]
Syria[9].svg.png.webp) Transnistria
Transnistria Turkmenistan – Turkmenistan Ground Forces
Turkmenistan – Turkmenistan Ground Forces Ukraine – Ukrainian Ground Forces, Ukrainian National Guard.
Ukraine – Ukrainian Ground Forces, Ukrainian National Guard.
Former operators
 Soviet Union, passed on to successor states[10]
Soviet Union, passed on to successor states[10]
See also
References
- ↑ Campbell, David (30 November 2017). Soviet Paratrooper vs Mujahideen Fighter: Afghanistan 1979–89. Combat 29. Osprey Publishing. p. 62. ISBN 9781472817648.
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eRBNYDKoebU
- 1 2 Small Arms Survey (2012). "Surveying the Battlefield: Illicit Arms In Afghanistan, Iraq, and Somalia". Small Arms Survey 2012: Moving Targets. Cambridge University Press. p. 324. ISBN 978-0-521-19714-4. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 August 2018. Retrieved 30 August 2018.
- ↑ "RPG-22 Neto light anti-tank weapon (Russian Federation), Anti-tank weapons". Jane's Infantry Weapons. 11 December 2009. Archived from the original on 3 May 2012. Retrieved 20 September 2011.
- ↑ Cracknell, David (5 November 2000). "Found: Real IRA's rocket launcher that scored a hit on MI6". The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on 21 July 2014. Retrieved 26 May 2014.
- ↑ "'Rocket' theory over MI6 blast". BBC. 21 September 2000. Archived from the original on 17 December 2012. Retrieved 5 July 2009.
- 1 2 3 "Missile launcher in attack was new to UK". The Independent. 23 September 2000. Archived from the original on 29 October 2017. Retrieved 5 July 2009.
- ↑ "RPG-22 NETTO". VMZ Sopot Official Website. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 20 January 2012.
- ↑ Michael Weiss (25 February 2023). "Are Syrian rebels now armed with heavy weapons from Croatia?". Atlantic Council. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- ↑ "RPG-22 Single-Use Anti-Tank Rocket Launcher | Military-Today.com".
Reference in print
- Jones, Richard. Jane's Infantry Weapons 2005–06. Coulsdon: Jane's, 2005. ISBN 0-7106-2694-0.