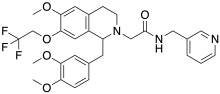
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C29H32F3N3O5 |
| Molar mass | 559.586 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
RTIOX-276 is an orexin antagonist. RTIOX-276 binds selectively to the orexin 1 receptor (KE = 8.5nM) and lacks significant affinity for the orexin 2 receptor (KE = > 10,000nM). RTIOX-276 may have therapeutic utility for the treatment of cocaine addiction. In conditioned place preference studies, RTIOX-276 attenuated the development of place preference in mice exposed to cocaine.[1][2][3]
References
- ↑ Perrey DA, German NA, Gilmour BP, Li JX, Harris DL, Thomas BF, Zhang Y (September 2013). "Substituted tetrahydroisoquinolines as selective antagonists for the orexin 1 receptor". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 56 (17): 6901–16. doi:10.1021/jm400720h. PMC 3849818. PMID 23941044.
- ↑ Perrey DA, Decker AM, Li JX, Gilmour BP, Thomas BF, Harris DL, et al. (September 2015). "The importance of the 6- and 7-positions of tetrahydroisoquinolines as selective antagonists for the orexin 1 receptor". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 23 (17): 5709–24. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2015.07.013. PMC 4554834. PMID 26216017.
- ↑ Perrey DA, German NA, Decker AM, Thorn D, Li JX, Gilmour BP, et al. (April 2015). "Effect of 1-substitution on tetrahydroisoquinolines as selective antagonists for the orexin-1 receptor". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 6 (4): 599–614. doi:10.1021/cn500330v. PMC 4400266. PMID 25643283.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.