| Radzyń Chełmiński Castle | |
|---|---|
 Radzyń Chełmiński Castle | |
| Location | Radzyń Chełmiński, Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, in Poland |
| Coordinates | 53°23′18″N 18°56′08″E / 53.38833°N 18.93556°E |
| Built | 1310-1330 |
| Architectural style(s) | Gothic |
 Location of the Radzyń Chełmiński Castle in Poland  Radzyń Chełmiński Castle (Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship) | |
Radzyń Chełmiński Castle is a Brick Gothic monastery-castle completed in 1330 as the seat of the Teutonic Knights' Commandry. It lies near Castle Lake (Polish: Jezioro Zamkowe) to the north of the town of Radzyń Chełmiński. Three of the four walls and most of the internal buildings of the keep are ruined.[1]
History
The square keep (52 x 51 metres) is a relic of one of the oldest castles built by the Teutonic Knights. Originally known as “Rehden”, it was started in 1234 on the orders of Hermann von Balk.[2] In 1251, in the wake of the Prussian Uprising, the original wooden fort was remade in brick in 1270–1285, destroyed, then rebuilt in its current form in 1310–1330.[2]
In September 1410, after the Battle of Grunwald, it was captured by Polish forces, but soon returned to the Knights with the first Peace of Thorn (1411). In 1454, it was captured by rebels in the Thirteen Years' War (1454–1466).
Under the Second Peace of Thorn (1466), it again went into Polish control. In 1628, during the wars with the Swedes, the castle was devastated during a siege, slowly turning into a ruin.
It remained largely unusable until annexed by the Kingdom of Prussia in the First Partition of Poland in 1772. In 1780, authorities ordered the deconstruction of the castle. Bricks from the castle's outer structures and the inner keep's walls and buildings were repurposed to build houses for the nearby town. The castle's deconstruction was eventually stopped in 1837.
The site survived both World War I and World War II and was twice transferred to Poland after it regained independence in both 1918 and 1945.
Preservation
Only parts of the inner keep remain extant alongside the base of the western outer wall and the western and southern walls of the southern extension. The southern buildings, eastern extension, moat, and nearby small lake no longer exist.
A restoration was undertaken in 1961-1968[2] and the inner walls, courtyard, and cellars were cleared of debris. The main wall was restored to its original height and the chapel roof replaced.
The ruins were opened for visits at the end of the twentieth century.[3][4] Currently visitors are still able to see the restored southern facade,[2] and enter the courtyard, towers, cellars, and the chapel.
 Main building plan (black indicates surviving elements)
Main building plan (black indicates surviving elements)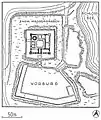 Site plan of the 1330 castle.
Site plan of the 1330 castle. Model
Model_(cropped).jpg.webp) 1880 lithograph.
1880 lithograph. Rear view (2010)
Rear view (2010) Interior (2020)
Interior (2020)
See also
References
- ↑ "Radzyń Castle". Zamki. Retrieved 6 May 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 "Radzyń Chełmiński - Teutonic Castle". Ancient and medieval architecture. Retrieved 2021-09-26.
- ↑ "Radzyń Chełmiński Castle". Zamki Polskie. Retrieved 6 May 2015.
- ↑ "Zamek Radzyń Chełmiński". Zamek Radzyń Chełmiński. Retrieved 6 May 2015.
External links
- Radzyń Chełmiński Castle (Wikimedia)
- Radzyń Chełmiński
- Zamek Radzyń Chełmiński (YouTube)