| Hungary | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operation | |||||
| National railway | Magyar Államvasutak | ||||
| Statistics | |||||
| Ridership | 110 million (2017)[1] | ||||
| System length | |||||
| Total | 8,057 kilometres (5,006 mi) | ||||
| Double track | 1,335 kilometres (830 mi) | ||||
| Electrified | 3,060 kilometres (1,900 mi) | ||||
| High-speed | 0 kilometres (0 mi) | ||||
| Track gauge | |||||
| Main | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) | ||||
| Features | |||||
| No. tunnels | 21 | ||||
| Longest tunnel | Kopár-hágó tunnel 780 metres (2,560 ft) | ||||
| Longest bridge | Nagyrákos viadukt 1,399 metres (4,590 ft) | ||||
| |||||
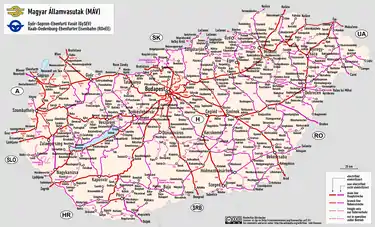
Rail transport in Hungary is mainly owned by the national rail company MÁV, with a significant portion of the network owned and operated by GySEV.
The railway network consists of 7,893 km, its gauge is 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge and 3,060 km are electrified.
Hungary is a member of the International Union of Railways (UIC). The UIC country code for Hungary is 55.
Statistics
- Railway lines total: 7,606 km (4,726 mi)
- Standard gauge: 7,394 km (4,594 mi)
- Broad gauge: 36 km (22 mi) of 1,520 mm (4 ft 11+27⁄32 in)
- Narrow gauge: 176 km (109 mi)
Note: The standard and broad gauge railways are operated by the State Railways and also the following narrow gauge railways: Nyíregyháza–Balsai Tisza part/Dombrád; Balatonfenyves–Somogyszentpál; Kecskemét–Kiskunmajsa/Kiskőrös and the Children's Railway in Budapest. All the other narrow gauge railways are run by State Forest companies or local non-profit organisations. See also Narrow gauge railways in Hungary.
Financial performance and corporate statistics
- Revenue = 372,549 million Ft (2014)[2]
- Net income = 22,851 million Ft (2014)[2]
- Number of employees = 38,456 (2009)
- Owner = Hungarian state (100% state ownership)
Rail links to adjacent countries
Same gauge:
- Austria — voltage change 25 kV AC / 15 kV AC
- Slovenia — voltage change 25 kV AC / 3 kV DC
- Croatia — same voltage 25 kV AC
- Serbia — same voltage 25 kV AC
- Romania — same voltage 25 kV AC
- Slovakia — same voltage 25 kV AC (west) and 3 kV DC (east)
Break-of-gauge (1,520 mm (4 ft 11+27⁄32 in):
- Ukraine — no electrified rail link
Modern and historical railway maps
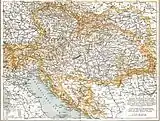 1898 railway map of Austria-Hungary
1898 railway map of Austria-Hungary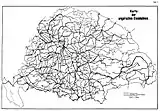 1912 railway map of Kingdom of Hungary
1912 railway map of Kingdom of Hungary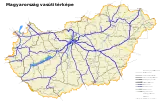 Electrified railways in Hungary
Electrified railways in Hungary
Urban rail
Commuter
The largest agglomeration of Hungary has a suburban rail system:
| City | System | Operator | Electrification | Conductor system | Gauge | Bidirectional traffic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Budapest | BHÉV | MÁV–HÉV | 1000 V DC | Overhead line | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge | Right-hand traffic (with the exception of lines H8 and H9) |
Metro
The largest city in Hungary has a Metro system:
| City | System | Electrification | Conductor system | Gauge | Bidirectional traffic | Opened |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Budapest | Budapest Metro | 550 V DC (M1) 750 V DC (M4) 825 V DC (M2, M3) |
Overhead line (M1) Third rail (M2, M3, M4) |
1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge | Right-hand traffic | 3 May 1896 |
Tram
There are also tram systems in the following cities:
| City | System | Electrification | Operator | Gauge | Bidirectional traffic | Opened |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Budapest | Budapest Tram | 600 V DC | BKV | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge | Right-hand traffic | 30 July 1866 |
| Debrecen | Debrecen Tram | 600 V DC | DKV | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge | Right-hand traffic | 16 March 1911 |
| Miskolc | Miskolc Tram | 600 V DC | MVK | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge | Right-hand traffic | 10 July 1897 |
| Szeged | Szeged Tram | 600 V DC | SZKT | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge | Right-hand traffic | 1 July 1884 |
| Hódmezővásárhely | Szeged-Hódmezővásárhely Tram-train | 600 V DC | MÁV-Start | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge | Right-hand traffic | 29 November 2021 |
See also
References
- ↑ "Railway Statistics – 2017 Synopsis" (PDF). International Union of Railways, IUC. 2017. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 April 2019. Retrieved 11 June 2019.
- 1 2 "Consolidated Annual Report 2014" (PDF) (in Hungarian). Budapest: MÁV Magyar Államvasutak Zrt. 4 June 2015. Retrieved 30 July 2015.