Wales has traditionally been divided into a number of ambiguous and ill-defined areas described as regions, reflecting historical, geographical, administrative, cultural and electoral boundaries within the country. Presently, the most common form of division of Wales into "regions" has been using cardinal and intercardinal references: north or south-west for example.[1] None of the variously described "regions" have official status or defined boundaries; neither is there a fixed number of regions. Various organisations use different regions and combinations of regions for their individual purposes. This includes devolved institutions, such as Visit Wales,[2] Natural Resources Wales,[3] and the Welsh Government itself,[4][5][6] using different sets of Wales' regions. Wales is most commonly sub-divided into between two and four regions, with a North–South divide, and North, Mid, South East and South West division being common. This article lists the various terms applied to be the "regions of Wales" and the regions used by various organisations.
_p1.028_MAP_OF_NORTH_AND_SOUTH_WALES.jpg.webp)
Status
The regions of Wales have little administrative status, as of 2022, nor are they officially defined. Local government is primarily managed by the twenty-two principal areas.
Some argue that Wales should stop using terms to describe regions of Wales, as they lack both strict definitions and boundaries, and instead consider Wales as a single entity. However, others campaign for more recognition of Wales' various regions, such as the north and west.[1][7]
Historical usage
North-South divide
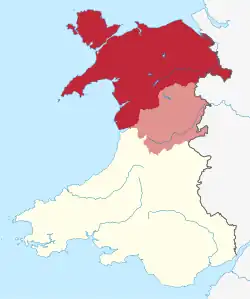
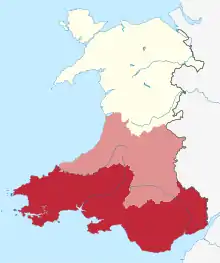
There may be a north-south divide, between North Wales and South Wales.[8] The Cambrian Mountains form a mountainous interior of Wales, limiting the connection between North and South with few transport links between them.[9] Most of the population of Wales is concentrated on opposing sides of Wales. Transport links between North and South Wales are significantly weak,[10] with major north–south links passing through England, and both the North and South, having closer transport links with North West England, and South West England respectively.[11][12] Liverpool is sometimes described as the "Capital of North Wales", as its the largest city closest to North Wales.[13] Historical maps divide North and South Wales using the boundaries between Montgomeryshire and Radnorshire, and between Cardiganshire and Merionethshire, but the modern-day divide is described as ambiguous or arbitrary.[14]
Modern usage
Since devolution, the Welsh Government is making efforts to increase connection between north and south.[8][15] However in 2013 there were reports that the Welsh Government may have short-changed the north by £131.53 million, which critics describe as proof of a modern north–south divide. The government responded that the figures are "highly misleading", as they ignore funding through Wales-wide programmes, and that the government has spent more on health and transport in the north than in the south-east, and more on education than the national average. The then First Minister of Wales, Carwyn Jones, disagreed that there was a north–south divide in Wales, but stated that there would "never be a time" that people will no longer see a north–south divide.[16]
There is a part-ministerial post in the Welsh Cabinet for "North Wales",[17] and a North Wales office of the Senedd.[18] Plaid Cymru has called for a trans-Wales railway as a solution to bridge the cultural divide between north and south.[19]
There is a north–south divide in language, not only between more and less Welsh-speaking areas, but also in terms of accents (both relating to English and Welsh) and dialects of Welsh.[20] There is also a cultural divide between "gogs" in the north and "hwntws" in the south.
There may be a tourism divide between north and south Wales due to geographic and existing transport capabilities, with tourism in the north aimed at nearby tourists from the rest of the UK and closer airports in Liverpool and Manchester, for day trips and staycations; whereas strategies for the south by the devolved administrations aim for more international and longer-term tourism through Cardiff Airport in the south. Strategies based on drawing tourists through Cardiff Airport may not have a big impact on the north due to a lack of connectivity with Cardiff Airport and the north of Wales.[21]
Capitalisation
There is a debate whether to spell the regions of Wales with a capitalised letter or a lowercase letter, for example either a lower case 'n' for north Wales or a capitalised 'N' for North Wales (see North Wales#Capitalisation). The debate has been coined as the "to cap or not to cap" debate in media.[22] Usage varies, BBC News[23] and the Welsh Government[24] for example use lowercase, whereas Visit Wales uses capitalised, with the latter having their own version of Wales' regions.[25] David Williams, chairman of the North Wales Business Club, announced his support for capping the term "North" in "North Wales" stating that the region should be "very recognisable [...] in our own right".[22]
List of regions
| This article is part of a series within the Politics of the United Kingdom on the |
| Politics of Wales |
|---|
 |
|
Geographical regions and sub-regions
Regions using the cardinal and intercardinal points of a compass, e.g. north and south-west for nomenclature, and are based mainly on physical and environmental geographic factors due to their lack of definition.
For many administrative purposes, most of the regions follow the boundaries of the twenty-two principal areas of Wales. Those listed below are based on the usage by organisations further down.
- North Wales
- North East Wales
- North West Wales
- North Central Wales (sometimes used)
- Mid Wales or Central Wales
- Mid and South West Wales
- Mid and West Wales
- South Wales
- South West Wales
- South East Wales
- South Central Wales (sometimes used)
- East Wales
- West Wales
- West Wales and the Valleys


By organisation

Note: names in-between inverted commas ("), implies there are other definitions of the region that may be more common.
Visit Wales
Visit Wales uses four regions:[2][26]
- North Wales — northern six principal areas (i.e. excluding Powys)
- Mid Wales — Ceredigion and Powys
- "West Wales" — with the common definition of South West Wales
- "South Wales" — with the common definition of South East Wales
Business Wales
Business Wales uses four regions:[4]
- North Wales — northern six principal areas (i.e. excluding Powys)
- "Mid Wales" — Carmarthenshire, Ceredigion, Pembrokeshire and Powys
- "South East Wales" — Blaenau Gwent, Caerphilly, Cardiff, Monmouthshire, Newport, Torfaen, Vale of Glamorgan
- "South West Wales" — Bridgend, Merthyr Tydfil, Neath Port Talbot, Rhondda Cynon Taf, Swansea
Welsh Government Economic Action Plan
Either a three economic region model or a four economic region model:[5][27]
Three region model
Four region model
Future Wales: The National Plan 2040 (Welsh Government)
- North (North Wales)[6]
- Mid Wales
- South West (South West Wales)
- South East (South East Wales)
Natural Resources Wales
Described as the six "areas" (with an additional "marine area") by Natural Resources Wales[3]
- North East Wales — Denbighshire, Flintshire, and Wrexham[28]
- North West Wales — Conwy, Gwynedd and Isle of Anglesey[29]
- Mid Wales — Ceredigion and Powys[30]
- South Central Wales — Bridgend, the Vale of Glamorgan, Merthyr Tydfil, Rhondda Cynon Taf and Cardiff[31]
- "South East Wales" — Blaenau Gwent, Caerphilly, Monmouthshire, Newport and Torfaen[32]
- "South West Wales" — Swansea, Neath Port Talbot, Pembrokeshire and Carmarthenshire[33]
Wales Spatial Plan
Note: no clear boundaries shown, merely labels on a blank map.
- North West Wales[34]
- North East Wales — Border and Coast
- Central Wales
- South East — the Capital Network
- Swansea Bay — Waterfront & Western Valleys
- Pembrokeshire — The Haven
Former organisations
Welsh Development Agency and the Development Board for Rural Wales
Pre-mid-1990s regions
- "North East Wales" — Clwyd with boundaries between 1974 and 1996[35]
- "North West Wales" — Gwynedd with boundaries between 1974 and 1996 (excluding Meirionnydd); (Modern Isle of Anglesey, half of Gwynedd and half of Conwy County Borough)
- Development Board for Rural Wales — Mid Wales (Powys and Ceredigion) and Meirionnydd of Gwynedd.
- "West Wales" — Pembrokeshire and Carmarthenshire (excluding Llanelli).
- South Wales (West) — Llanelli, Swansea, Neath Port Talbot and parts of Bridgend County Borough
- South Wales (Valleys) — Blaenau Gwent, Caerphilly County Borough, Merthyr Tydfil County Borough, Rhondda Cynon Taf, Torfaen, and parts of Bridgend County Borough.
- South Wales (East) — City and County of Cardiff, Newport, Monmouthshire, and the Vale of Glamorgan.
Post-mid-1990s regions
- "North Wales" — Clwyd and Gwynedd with boundaries between 1974 and 1996 (excluding Meirionnydd)[35]
- Development Board for Rural Wales — Mid Wales (Powys and Ceredigion) and Meirionnydd of Gwynedd.
- "West Wales" — Pembrokeshire, Carmarthenshire, City and County of Swansea, Neath Port Talbot and Bridgend County Borough
- "South Wales" — Blaenau Gwent, Caerphilly County Borough, City and County of Cardiff, Merthyr Tydfil County Borough, Monmouthshire, Newport, Rhondda Cynon Taf, Torfaen, and Vale of Glamorgan
Other organisations
- Royal Society of Architects in Wales: Branches in North, Mid, West and South Wales (latter described as the "Design Circle" (RSAW South)).
- The Wildlife Trusts: Gwent, Montgomeryshire, North Wales, Radnorshire, and South and West Wales.
- For the National Forest for Wales Welsh Government programme, Wales was divided into three "areas", North, Mid, South based on the use of lettering ("N", "M", "S").[36]
Statistical regions
StatsWales
StatsWales divides Wales into "Economic regions", of either a three economic region model or a four economic region model:
Three region model
Four region model
International Territorial Level 2 regions
Cultural regions
- South Wales Valleys ("The Valleys")
- North Wales
- South Wales
- Little England beyond Wales
Denis Balsom's three-Wales model (1985)
- Welsh Wales — Areas with majority of those identifying as 'Welsh'
- British Wales — Areas with majority of those identifying as 'British'
- Y Fro Gymraeg — Areas with majority Welsh-speakers
Linguistic regions
Welsh speakers
Dialect regions
Two dialect model:[20]
- Northern Welsh — North Wales
- Southern Welsh — South Wales
Four dialect model:[38]
- Gwyndodeg — North West Wales
- Powyseg — Northern Mid Wales and North East Wales
- Dyfedseg — South West Wales (includes subdialect Iaith Sir Benfro — "Pembrokeshire language")
- Gwenhwyseg — South East Wales
City regions
- North Wales Economic Ambition Board — consisting the principal areas of: Conwy County Borough, Denbighshire, Flintshire, Gwynedd, Isle of Anglesey, and Wrexham County Borough, in the north of Wales. (A common definition of North Wales).
- Growing Mid Wales Partnership — consisting the principal areas of: Ceredigion, and Powys
- Swansea Bay City Region — consisting the principal areas of: Carmarthenshire, Neath Port Talbot, Pembrokeshire, and Swansea, around Swansea Bay in south-west Wales. (Similar definition to South West Wales).
- Cardiff Capital Region — consisting the principal areas of: Blaenau Gwent, Bridgend County Borough, Caerphilly County Borough, Cardiff, Merthyr Tydfil County Borough, Monmouthshire, Newport, Rhondda Cynon Taf, Torfaen, and Vale of Glamorgan, in south-east Wales. (Similar definition to South East Wales).
Regional Tourism Partnerships
- Tourism Partnership North Wales
- South West Wales Tourism Partnership
- Tourism Partnership Mid Wales
- Capital Region Tourism
- Forgotten Landscapes Project (Blaenavon)
Regional Corporate Joint Committees
Regional Skills Partnerships
Transport-related
- M4 Corridor in England and Wales
- Trunk road agents:
- Regional Metros:
- Former regional transport consortia:
- South East Wales Transport Alliance
- South West Wales Integrated Transport Consortium
- Taith Joint Board (North Wales excluding Meirionydd in Gwynedd)
- TraCC (Mid Wales including Meirionydd in Gwynedd)
Cross-border regions
- Welsh Marches
- Welsh Lost Lands
- The Mersey Dee Alliance, composed of Cheshire West and Chester, Flintshire, Wirral and Wrexham councils, describes an "economic sub-region" known as the Mersey Dee.[41] Sometimes expanded to also include the rest of North Wales as "North Wales (and) Mersey Dee".[42]
- Severnside
- Western Gateway[43]
Electoral regions
- North Wales (Senedd electoral region) & North Wales (European Parliament constituency)
- Mid and West Wales (Senedd electoral region) & Mid and West Wales (European Parliament constituency)
- South Wales Central (Senedd electoral region) & South Wales Central (European Parliament constituency)
- South Wales East (Senedd electoral region) & South Wales East (European Parliament constituency)
- South Wales West (Senedd electoral region) & South Wales West (European Parliament constituency)
Historic regions

Natural regions
Tourism names
- Welsh Lake District – for Elan Valley
- Waterfall Country – for Vale of Neath
Coal mining regions
Fire and Rescue
Rugby league
- North Wales Crusaders
- South Wales Ironmen, later renamed as West Wales Raiders
Rugby union
- Welsh regional rugby, which divides Wales into regions represented by four clubs: Scarlets, based in Llanelli; Ospreys, based in Swansea; Cardiff Rugby; and Dragons RFC, based in Newport
- RGC 1404, named Rygbi Gogledd Cymru (North Wales Rugby), based in Colwyn Bay
Others
- Local health boards — some health boards are described to be "regional" health boards due to the size of their coverage.
- Betsi Cadwaladr University Health Board — locally described as the "North Wales health board"
- Hywel Dda University Health Board — locally described as the "West Wales health board"
- South Wales Police
- North Wales Police
See also
References
- 1 2 "Why it's time to dump North Wales and South Wales and come together as a nation". Nation.Cymru. 2017-11-09. Retrieved 2021-12-11.
- 1 2 "Introduction to Wales". VisitWales. Retrieved 2021-12-06.
- 1 2 "Natural Resources Wales / Area Statements". naturalresources.wales. Retrieved 2021-12-05.
- 1 2 "Regions of Wales". Business Wales - Wales Screen. Retrieved 2021-12-05.
- 1 2 "Prosperity for All: economic action plan" (PDF). gov.wales. Welsh Government. 13 December 2017.
- 1 2 Future Wales - The National Plan 2040 (PDF). gov.wales: Welsh Government. p. 100.
- ↑ "Give us back our real places: why north Wales shouldn't be North". The National Wales. Retrieved 2021-12-11.
- 1 2 "20 years of Welsh Devolution: Is there still a North / South divide in Wales?". The Leader. Retrieved 2021-12-16.
- ↑ Minnis, Andrew (2013). East-west or north-south? Strategic priorities for a Welsh transport infrastructure (PDF). senedd.wales: National Assembly for Wales.
- ↑ "Driving in Wales: Why the north-south road is so slow". BBC News. 2019-10-18. Retrieved 2021-12-11.
- ↑ "20 years of Welsh Devolution: Is there still a North / South divide in Wales?". The Leader. Retrieved 2021-12-11.
- ↑ "Connecting North and South Wales". Transport For Wales News. Retrieved 2021-12-16.
- ↑ Weston, Alan (2021-03-01). "Liverpool's deep rooted connection with 'North Wales'". Liverpool Echo. Retrieved 2021-12-11.
- ↑ Pyke, Chris (2016-06-17). "Where is the dividing line between North and South Wales?". WalesOnline. Retrieved 2021-12-11.
- ↑ "Connecting North and South Wales". Transport For Wales News. Retrieved 2021-12-11.
- ↑ Flint-NW, Rachel (2015-11-24). "Has North Wales been shortchanged by millions due to the north-south divide?". North Wales Live. Retrieved 2021-12-16.
- ↑ "Cabinet members and ministers". GOV.WALES. Retrieved 2022-11-13.
- ↑ "Senedd North Wales Office". senedd.wales. Retrieved 2022-11-13.
- ↑ "Plaid Cymru calls for trans-Wales railway to boost economy". the Guardian. 2019-12-07. Retrieved 2021-12-16.
- 1 2 Robinson, Jonnie (24 April 2019). "Accents and dialects of Wales". www.bl.uk. British Library. Retrieved 2021-12-16.
- ↑ Russell, Matt (2018-08-20). "The north-south divide of Welsh tourism". Coinslot International. Retrieved 2021-12-16.
- 1 2 Hughes, Owen (2017-09-24). "Why North Wales should ALWAYS be in capital letters...business leader makes case for 'capping up'". North Wales Live. Retrieved 2021-12-11.
- ↑ "A-Z complete guide". www.bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 2022-11-13.
Also lower case for south Wales, north Wales, mid-Wales etc.
- ↑ "GOV.WALES style guide". GOV.WALES. Retrieved 2021-12-11.
- ↑ "Guidance on house style and use of language mechanics". Wales. 2019-11-13. Retrieved 2021-12-11.
- ↑ "Destinations". VisitWales. Retrieved 2021-12-05.
- ↑ "OECD case study: Considerations for economic regions in Mid Wales and South West Wales". www.oecd-ilibrary.org. Retrieved 2021-12-05.
- ↑ "Natural Resources Wales / North East Wales Area Statement". naturalresources.wales. Retrieved 2021-12-05.
- ↑ "Natural Resources Wales / North West Wales Area Statement". naturalresources.wales. Retrieved 2021-12-05.
- ↑ "Natural Resources Wales / Mid Wales Area Statement". naturalresources.wales. Retrieved 2021-12-05.
- ↑ "Natural Resources Wales / South Central Wales Area Statement". naturalresources.wales. Retrieved 2021-12-05.
- ↑ "Natural Resources Wales / South East Wales Area Statement". naturalresources.wales. Retrieved 2021-12-05.
- ↑ "Natural Resources Wales / South West Wales Area Statement". naturalresources.wales. Retrieved 2021-12-05.
- ↑ Winter, Graham (September 2008). Members' Research Service: Topic Brief — Wales Spatial Plan (PDF). National Assembly for Wales.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - 1 2 Phelps, Nick; Morgan, Kevin; Fuller, Crispian (2000), Hood, Neil; Young, Stephen (eds.), "Regions, Governance and FDI: The Case of Wales", The Globalization of Multinational Enterprise Activity and Economic Development, London: Palgrave Macmillan UK, pp. 366–389, doi:10.1057/9780230599161_15, ISBN 978-0-230-59916-1, retrieved 2021-12-17
- ↑ "National Forest for Wales: woodland sites". GOV.WALES. Retrieved 2022-11-13.
- 1 2 3 Irvine, Fiona E.; Roberts, Gwerfyl W.; Jones, Peter; Spencer, Llinos H.; Baker, Colin R.; Williams, Cen (March 2006). "Communicative sensitivity in the bilingual healthcare setting: A qualitative study of language awareness". Journal of Advanced Nursing. 53 (4): 422–434. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2648.2006.03733.x. ISSN 0309-2402. PMID 16448485.
- ↑ Harries, Robert (2018-09-30). "Why we use different words for the same thing based on where in Wales we live". WalesOnline. Retrieved 2021-12-05.
- 1 2 3 4 "Consultation on the Corporate Joint Committees (General) (No.2) (Wales) Regulations 2021 [HTML]". GOV.WALES. Retrieved 2022-01-08.
- 1 2 3 George, Russell; Asghar, Mohammad; David, Hefin; Howells, Vikki; Sayed, Bethan; Watson, Joyce; Reckless, Mark; Rowlands, David J; Sargeant, Jack (October 2019). "Regional Skills Partnerships" (PDF). Senedd.wales. National Assembly for Wales Economy, Infrastructure and Skills Committee. p. 12. Retrieved 13 January 2022.
- ↑ "Mersey Dee Alliance – Connecting people". Retrieved 2022-11-13.
- ↑ "World-class sectors driving growth across North Wales & Mersey Dee region | TheBusinessDesk.com". North West. 2018-10-29. Retrieved 2022-11-13.
- ↑ "About the Western Gateway". Western Gateway. Retrieved 2022-11-13.