| Line B | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 | |||
.jpg.webp) A CAF MB/400 train in Termini Station | |||
| Overview | |||
| Status | In use | ||
| Owner | ATAC | ||
| Locale | Rome, Italy | ||
| Termini |
| ||
| Stations | 26 | ||
| Service | |||
| Type | Rapid transit | ||
| System | Rome Metro | ||
| Operator(s) | ATAC | ||
| Daily ridership | 345,000[1] | ||
| History | |||
| Opened | 9 February 1955 | ||
| Technical | |||
| Line length | 18.151 km (11.279 mi) plus B1 branch of 5,5 km[2] | ||
| Character | Underground and Elevated | ||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) | ||
| Electrification | Overhead lines | ||
| |||
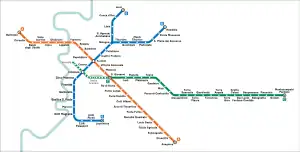
Line B is a metro line serving Rome, Italy, and part of the Rome Metro. Despite its name, Line B was the first line to be built in the city. It crosses Rome diagonally from north-east, starting at Rebibbia and at Jonio stations, to south, terminating at Laurentina, in the EUR district. It crosses Line A at Termini station. The line has 26 stations and is shown in blue on Metro maps.
Overview
Its first service runs at 05:30 and its last at 23:30. From 18 January 2008, the last Friday and Saturday service runs at 1:30. It carries 345,000 passengers a day and runs 377 trains a day, with a peak time frequency of one train every 3 minutes in the shared section and 4,5 minutes in the branches. Every 6 minutes at other times, at a maximum frequency of 9 minutes at the most off-peak times.[3]
History
Despite its name, Line B was the first metro line in Rome. The line was planned during the 1930s by the Fascist government in search of a rapid connection between the main train station, Termini, and a new district to the south-east of the city, E42, the planned location of the Universal Exposition (or Expo), which was to be held in Rome in 1942. The exposition never took place due to Italy's entrance into World War II in 1940. When work was interrupted some of the tunnels on the city-centre side of the metro (between Termini and Piramide) had been completed and were used as air raid shelters during the war.
Work on the metro began again in 1948, in concert with turning the space, formerly designated for the Expo, into a commercial district under the name Esposizione Universale Roma (EUR). The line was officially opened on 9 February 1955 by the President of the Republic Luigi Einaudi. Regular services began on the following day.[4]
When the new east–west line began service in 1980 from Anagnina to Ottaviano, it was named Line A, while the existing Termini-Laurentina line was renamed Line B.
In 1990, Line B was extended from Termini to Rebibbia to the east of the city, and the entire line was modernised. A spur called B1 opened on 13 June 2012.[5] It is a branch of Line B from Bologna to Jonio with 4 stations: Sant'Agnese/Annibaliano, Libia, Conca d'Oro, and the branch's new terminus at Jonio, opened on 21 April 2015).
Line B has 26 stations with terminuses at Rebibbia, Jonio and Laurentina (just east of EUR).
Opening dates
- 9 February 1955: Termini – Laurentina
- 8 December 1990: Termini – Rebibbia
- 13 June 2012: Bologna – Conca d'Oro (B1)
- 21 April 2015: Conca d'Oro – Jonio (B1)
Extensions
After the recently opened B1 line, there have been plans for an extension beyond Jonio (and then to Bufalotta).[6] Another future extension has been planned beyond Rebibbia with two stations: San Basilio and Torraccia/Casal Monastero.[7]
 Logo of the B1 extension
Logo of the B1 extension

_-_Entry.jpg.webp)

Rolling stock
When the B line opened in 1955, MR100 and MR200 trains (also collectively known as Automotrice Stanga-TIBB) were used, and were transferred to the Rome-Lido railway in 1987, replaced by Series MB100 trains introduced in the same year, not only to replace the ageing MR100 and MR200 trains but also to cope with an increase in passengers following the opening of the eastward extension to Rebibbia.
A fleet of trains identical to the MB100 trains were also built for the Lima Metro in Peru.
Since 2010, Line B has also uses the newer CAF MA300 and from 2014, MB400 Series trains similar to those on the Line A.
 Entrance of Cavour Station, Feb 2017
Entrance of Cavour Station, Feb 2017 Interior of Line B train, Feb 2017
Interior of Line B train, Feb 2017 Ticket gates of Colosseo Station, Feb 2017
Ticket gates of Colosseo Station, Feb 2017 MR200 train at Piramide, 1984
MR200 train at Piramide, 1984 MB100 train at Colosseo
MB100 train at Colosseo A side view of the 1990 built MB100 cars on a Laurentina bound train stopping at EUR Magliana covered with graffiti.
A side view of the 1990 built MB100 cars on a Laurentina bound train stopping at EUR Magliana covered with graffiti. Interior of an MB100 series car.
Interior of an MB100 series car.
Notes
- ↑ http://www.agenzia.roma.it/documenti/carta_servizi/40.pdf
- ↑ "Caratteristiche principali". romametropolitane.it. Retrieved 12 May 2018.
- ↑ http://www.agenzia.roma.it/documenti/carta_servizi/40.pdf
- ↑ Rome Underground Railway Opened The Railway Magazine issue 649 May 1955 page 361
- ↑ Online, Redazione Roma. "Ore 5.30, taglio del nastro: inaugura la metro B1 Si viaggia da Piazza Bologna a Conca d'Oro". Retrieved 12 May 2018.
- ↑ "Metro B1, ok alla tratta Ionio-Bufalotta", La Repubblica Roma.it, 18 February 2012.
- ↑ "Prolungamento Linea B". romametropolitane.it. Retrieved 12 May 2018.
External links
![]() Media related to Line B (Rome metro) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Line B (Rome metro) at Wikimedia Commons
.png.webp)