 | |
| Location | Mackinac Island, Mackinac County, US |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 45°50′36″N 84°36′54″W / 45.8433°N 84.615°W |
| Tower | |
| Constructed | 1947 |
| Construction | reinforced concrete (tower), box crib (foundation) |
| Automated | 1973 |
| Height | 18 m (59 ft) |
| Shape | octagon |
| Markings | white (tower) |
| Heritage | National Register of Historic Places listed place |
| Fog signal | Horn: On request - 1 every 30s |
| Racon | X |
| Light | |
| First lit | 1948 |
| Focal height | 22 m (72 ft) |
| Lens | Sealed beam (original), 7.5-inch (190 mm) (current) |
| Range | 14 nmi (26 km; 16 mi) |
| Characteristic | Fl R 4s |
Round Island Passage Light | |
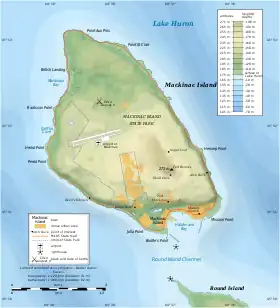 Round Island Passage Light is SW of the southern end of the west breakwater guarding Haldimand Bay. | |
| MPS | Light Stations of the United States MPS |
| NRHP reference No. | 13000583[1] |
| Added to NRHP | August 7, 2013[2] |
Round Island Passage Light is an automated, unmanned lighthouse located in the Round Island Channel in the Straits of Mackinac, Michigan.[3][4][5] The channel is a branch of Lake Huron.[6]
History
The Round Island Lighthouse was constructed in 1895 to mark the southern side of the Round Island Channel. In 1936, the United States Coast Guard developed plans to construct another lighthouse, 1000 feet south of Mackinac Island, to mark the northern side of the navigable channel. However, World War II intervened, and construction was delayed. In the interim, a buoy with a radio beacon was moored near the site. The Coast Guard began construction on the Round Island Passage Light in 1947, and finished in 1948.[7] Construction included building a control house at the southern tip on Mackinac Island, and running power cables underwater to the light. The lighthouse was equipped with a beacon light, fog signal, and radiobeacon. The light flashed a green signal from an array of sealed beam lamps mounted at the top of the light tower.[8]
The Passage Light was one of the last lights to be constructed on the Great Lakes. The light was built at the same time that the 1895 lighthouse was deactivated. In 1959, the lighthouse's beacon characteristic was changed from green to a flashing red light, and the radiobeacon distance-finding system was deactivated in 1962. In 1968 the formerly all-white light was given a red-painted base on a white pier. In 1973 the light was automated, and the steel antenna tower was removed in the early 2000s.[8]
In 1996, the Round Island Light was relighted as a private aid to navigation, and as of 2017 both lights currently mark the channel.[9] On August 7, 2013, the light was listed on the National Register of Historic Places.[2] In the same year, the General Services Administration announced that Round Island Passage Lighthouse was not needed by the Coast Guard. The light was sold at auction in 2014 for $65,500.[7]
Description
The Round Island Passage Light is constructed on a timber crib foundation which is 56 feet square. The timber crib has perimeter cells filled with concrete, and internal cells filled with rock. Atop the crib is a concrete superstructure with a 41-foot square reinforced concrete deck. The superstructure is octagonal, with four vertical and four sloping sides.[7]
Atop the tower's concrete deck is a red-painted 20 foot square enclosure, eleven feet high, constructed of steel plates. The enclosure can be entered through a nine-foot wide door on one side.[8] Above the enclosure is a five-story octagonal steel tower, 41-1/2 feet high and 12 feet across. Each side of the tower contains a four-foot bronze relief Indian head, commemorating the fact that Mackinac Island was a sacred spot for Native American tribes. On the interior, ladders reach from each story to higher ones. The light originally had a 47-foot steel antenna atop the tower, but it was removed in the early 2000s.[7]
See also
References
- ↑ "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. March 13, 2009.
- 1 2 "Weekly List of Actions Taken on Properties: 8/05/13 Through 8/09/13". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. Retrieved August 17, 2013.
- ↑ Light List, Volume VII, Great Lakes (PDF). Light List. United States Coast Guard. 2009. p. 126.
- ↑ "Historic Light Station Information and Photography: Michigan". United States Coast Guard Historian's Office. Archived from the original on 2017-05-01.
- ↑ Rowlett, Russ (2010-03-12). "Lighthouses of the United States: Michigan's Eastern Upper Peninsula". The Lighthouse Directory. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
- ↑ "Chart 14881:Lake Huron: Straits of Mackinac: De Tour Pass to Waugoshance Point (1/80,000)". NOAA. 2005.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - 1 2 3 4 Round Island Passage, MI, www.LighthouseFriends, retrieved February 28, 2016
- 1 2 3 Daniel Koski-Karell (April 11, 2013), National Register of Historic Places Registration Form: Round Island Passage Light (PDF)
- ↑ "Chart 14881:Inset: Mackinac Island (1/10,000)". NOAA. 2005.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)
Further reading
- "A Tour of the Lights of the Straits." Michigan History 70 (Sep/Oct 1986), pp. 17–29.
- Brisson, Steven C. (Mackinac State Historic Parks chief curator). Old Mackinac Point Lighthouse: A History & Pictorial Souvenir (1/29/2008).
- "Round Island Passage Light Station." Proceedings of the Merchant Marine Council 5 (Sep 1948), p. 145.
- "Round Island Passage Light Station Established." Coast Guard Engineers Digest No. 51 (Jul-Aug, 1948), pp. 28–29; No. 52 (Sep-Oct 1948), pp. 10–12.
External links
![]() Media related to Round Island Passage Light at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Round Island Passage Light at Wikimedia Commons
