| SITVA | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Train near Berrío Park station | |||
| Overview | |||
| Owner | Department of Antioquia, Medellín City | ||
| Area served | Aburrá Valley | ||
| Locale | Medellín Metropolitan Area, Antioquia, Colombia | ||
| Transit type |
| ||
| Number of lines | 12[1] | ||
| Line number |
| ||
| Number of stations |
| ||
| Daily ridership | 0.53 million (weekday 2020)[3] | ||
| Annual ridership | 328 million (2021)[4] | ||
| Website | SITVA | ||
| Operation | |||
| Number of vehicles |
| ||
| Technical | |||
| System length | 85.12 km (52.9 mi)[2] | ||
| |||
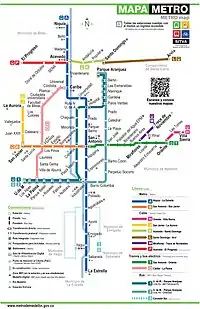
SITVA (Sistema Integrado de Transporte del Valle de Aburrá in Spanish or Aburrá Valley Integrated Transport System) is the public transportation system of Medellín and its metropolitan area. It allows people from the Metropolitan Area of Medellín to move across the ten Aburrá Valley municipalities using different transport modes. It uses integrated fares and a single payment card (Cívica card).
Components
SITVA includes the Medellín Metro, currently comprising two lines: Line A, which is 25.8 kilometres (16.0 mi) long and serves 21 stations, and Line B, which is 5.5 kilometres (3.4 mi) long and serves 6 stations (plus San Antonio station, the transfer station with Line A). There is also a tram line: Line T (Ayacucho Tram).[2][1]
Additionally, the aerial cable car system, Metrocable, which supplements the metro system, comprises six lines: Line J with 3 stations (plus one transfer station with Metro Line B),[1][2] Line K with 3 stations (plus one transfer station with Metro Line A and one with Line L),[2][1] Line L with one station (plus one transfer station with Line K), Line H with two stations (plus one transfer station with Line T), Line M with two stations (plus one transfer station with Line T) and Line P with 3 stations (plus one transfer station with Metro Line A).[1] SITVA also integrates a bus rapid transit system (Metroplús), a minibus network called Sistema Integrado de Transporte (SIT) in Spanish and a bicycle-sharing system (EnCicla).
As of 2022, there are 27 metro stations, 15 Metrocable stations, 3 tramway stations (+ 6 tram stops), 20 BRT stations (+ 42 feeding bus stops) in the SITVA network, all listed in the following table; for a total of 65 stations and 48 stops. Transfer stations are in bold, and the transfer station between metro lines A and B is shown in bold-italic:
| Name | Stations | Date of opening | Fleet | Commercial speed | Capacity (per vehicle) | Capacity (passengers/h-direction) | Travel time one journey | Top frequency (rush hour) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metro services | ||||||||
.svg.png.webp) Line A |
30 November 1995 | 80 three-car trains; for a total of 240 cars | 40 km/h (25 mph); max. speed 80 km/h (50 mph) | 300 users per car | 41,480 | 42 minutes | 3 minutes | |
.svg.png.webp)
|
29 February 1996 | 16,231 | 10.5 minutes | 3:50 minutes | ||||
| Metrocable services | ||||||||
.svg.png.webp)
|
7 August 2004 | 93 gondolas | 18 km/h (11 mph) | 8 users sitting, 2 standing; for a total of 10 users per gondola | 3,000 | 9 minutes | 0:12 minutes | |
.svg.png.webp)
|
3 March 2008 | 119 gondolas | 12 minutes | |||||
.svg.png.webp)
Line L |
9 February 2010 | 55 gondolas | 1,200 | 15 minutes | 0:14 minutes | |||
.svg.png.webp)
|
|
17 December 2016 | 44 gondolas | 1,800 | 5 minutes | 0:13 minutes | ||
.svg.png.webp)
|
|
28 February 2019 | 49 gondolas | 2,500 | 4 minutes | 0:09 minutes | ||
.svg.png.webp)
Line P West to Northwest 2.7 km (1.7 mi)[2] 3 stations[1] |
|
10 June 2021 | 138 gondolas | 19 km/h (12 mph) | 10 users sitting, 2 standing; for a total of 12 users per gondola | 4,000 | 10 minutes | 0:11 minutes |
| BRT services | ||||||||
.png.webp)
|
|
22 December 2011 | 30 gas working buses, 1 fully electric bus; for a total of 31 articulated buses | 16 km/h (9.9 mph); max. speed 60 km/h (37 mph) | 154 users per bus | 3,270 | 45 minutes | 2:45 minutes |
.png.webp)
Line 3 Southwest/Southeast |
South Corridor | Under development | ||||||
| Feeding bus services | ||||||||
.png.webp)
Line 2 |
|
22 April 2013 | 47 gas feeding buses | 13 km/h (8.1 mph); max. speed 60 km/h (37 mph) | 90 users per bus | 1,417 | 52 minutes | 4:17 minutes |

|
2 December 2019 | 64 electric buses | 13 km/h (8.1 mph); max. speed 60 km/h (37 mph) | 80 users per bus | 800 | 45 minutes | 6:00 minutes | |
| Tram services | ||||||||
.svg.png.webp)
Line T |
|
31 March 2016 | 12 tramway vehicles | 16 km/h (9.9 mph); max. speed 70 km/h (43 mph) | 300 users per tram | 3,807 | 19 minutes | 4:44 minutes |
| Total | ||||||||
| 65 stations (48 stops) | Oldest: Newest: |
|
Fastest: Slowest: |
Most capacity: Least capacity: |
82,502 | Fastest journey: Slowest journey: |
Least wait time: Most wait time:
| |
Expansions
Metrocable

On 7 August 2004,[5] the city inaugurated a new line known as "Metro Cable" (Line K). The line starts in the Acevedo Station and goes to the up hill district of Santo Domingo Savio.[6] This important addition integrated new additions to the city that since the 1960s that previously were not considered part of the "real city".

On 3 March 2008,[5] a second "Metro Cable" line (Line J) was inaugurated. The line starts in the San Javier Station and goes through Juan XXIII and Vallejuelos to the La Aurora district.[6] This new line benefits approximately 150,000 new users.
A new Metrocable line (line L) was inaugurated in 2009[5] with a transfer station at Santo Domingo Savio Station. This line continues further uphill to El Tambo[6] in Arví park near Guarne. The reason for constructing this line is because the city wants to promote tourism in the rural area near Lake Guarne. It takes 14 minutes to ascend to El Tambo and there are no intermediate stations.
Line A extension
Line A was expanded from Itagüí to La Estrella, in the south of the metropolitan area. A new intermediate station, Sabaneta, built near 67th South Street, was opened on 5 August 2012[7] and the final station, La Estrella, was built near 77th South Street and opened on 17 September 2012.[8]
Train line
In February 2020 it was announced that Medellín will reactivate the train line between Bello and Caldas.[9]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 "Metro map" (pdf). Medellín Metro. Retrieved 16 May 2020.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 "Metro facts" (jpg). Medellín Metro. 16 Jun 2021.
- ↑ "Memoria de Sostenibilidad 2020". p. 28.
- ↑ "Boletín Técnico Encuesta de Transporte Urbano de Pasajeros (ETUP) IV trimestre de 2021". p. 14.
- 1 2 3 "Historia" [History] (in Spanish). Metro de Medellín. 4 January 2016. Retrieved 15 January 2016.
- 1 2 3 "Metrocable - Metrocable Lines". Metro de Medellín. 15 November 2013. Archived from the original on 2015-06-10. Retrieved 16 November 2013.
- ↑ "ESTE DOMINGO 5 DE AGOSTO INICIA LA OPERACIÓN COMERCIAL HASTA LA NUEVA ESTACIÓN SABANETA" (in Spanish). Retrieved 5 January 2013.
- ↑ "ESTE LUNES 17 DE SEPTIEMBRE EL METRO INAUGURARÁ LA EXTENSIÓN AL SUR" (in Spanish). Retrieved 5 January 2013.
- ↑ El Colombiano. "Antioquia definió el primer tramo para reactivar su ferrocarril". Retrieved 22 February 2020.