| SLC10A3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | SLC10A3, DXS253E, P3, solute carrier family 10 member 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 312090 MGI: 95048 HomoloGene: 10525 GeneCards: SLC10A3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
P3 protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC10A3 gene.[5][6]
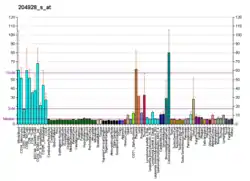
This gene maps to a GC-rich region of the X chromosome and was identified by its proximity to a CpG island. It is thought to be a housekeeping gene.[6]
See also
- SLC10A3+protein,+human at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000126903 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000032806 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Chen EY, Zollo M, Mazzarella R, Ciccodicola A, Chen CN, Zuo L, Heiner C, Burough F, Repetto M, Schlessinger D, D'Urso M (Jun 1997). "Long-range sequence analysis in Xq28: thirteen known and six candidate genes in 219.4 kb of high GC DNA between the RCP/GCP and G6PD loci". Hum Mol Genet. 5 (5): 659–68. doi:10.1093/hmg/5.5.659. PMID 8733135.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: SLC10A3 solute carrier family 10 (sodium/bile acid cotransporter family), member 3".
Further reading
- Mehrle A, Rosenfelder H, Schupp I, et al. (2006). "The LIFEdb database in 2006". Nucleic Acids Res. 34 (Database issue): D415–8. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj139. PMC 1347501. PMID 16381901.
- Wiemann S, Arlt D, Huber W, et al. (2004). "From ORFeome to biology: a functional genomics pipeline". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2136–44. doi:10.1101/gr.2576704. PMC 528930. PMID 15489336.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Simpson JC, Wellenreuther R, Poustka A, et al. (2001). "Systematic subcellular localization of novel proteins identified by large-scale cDNA sequencing". EMBO Rep. 1 (3): 287–92. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kvd058. PMC 1083732. PMID 11256614.
- Hartley JL, Temple GF, Brasch MA (2001). "DNA cloning using in vitro site-specific recombination". Genome Res. 10 (11): 1788–95. doi:10.1101/gr.143000. PMC 310948. PMID 11076863.
- Alcalay M, Toniolo D (1988). "CpG islands of the X chromosome are gene associated". Nucleic Acids Res. 16 (20): 9527–43. doi:10.1093/nar/16.20.9527. PMC 338761. PMID 3186440.
- Faust CJ, Levinson B, Gitschier J, Herman GE (1992). "Extension of the physical map in the region of the mouse X chromosome homologous to human Xq28 and identification of an exception to conserved linkage". Genomics. 13 (4): 1289–95. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(92)90048-W. PMID 1354645.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.