| Sharon Conglomerate | |
|---|---|
| Stratigraphic range: Pennsylvanian | |
 Outcrop of the Sharon Conglomerate at the Ledges, Cuyahoga Valley National Park | |
| Type | Sedimentary |
| Unit of | Pottsville Formation |
| Overlies | Meadville Shale |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | conglomerate |
| Location | |
| Region | Pennsylvania |
| Country | United States |
| Extent | Pennsylvania, Ohio, Maryland |
| Type section | |
| Named for | Sharon, Pennsylvania |
The Sharon Conglomerate is a geologic formation of early Pennsylvanian age in Pennsylvania, Ohio, and Maryland, in the United States. It is dominantly conglomerate and quartzarenite sandstone. In places it is abundantly crossbedded.
The Sharon Conglomerate is generally considered a Member of the Pottsville Formation in Pennsylvania and Maryland,[1] but it is a Formation in Ohio.
Exposures
The Sharon conglomerate has no formal type section,[2] although it is named after the town of Sharon, Pennsylvania.
One excellent exposure is located in Cuyahoga Valley National Park at "the Ledges," located southeast of the town of Peninsula, Ohio. Another exposure is at Mary Campbell Cave near Cuyahoga Falls.
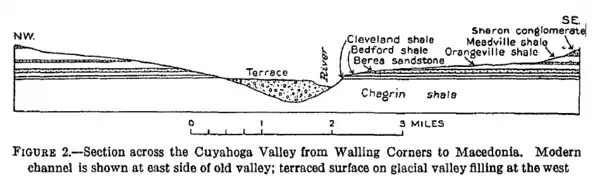
Geologic cross section at Cuyahoga Valley National Park showing the Sharon Conglomerate at upper right (stratigraphic top).[3]

_66_(23891106818).jpg.webp) Mudshale clasts in one of the roadcuts near Jackson. Rock hammer for scale.
Mudshale clasts in one of the roadcuts near Jackson. Rock hammer for scale._1_(44411342545).jpg.webp) Exposure at Mary Campbell Cave
Exposure at Mary Campbell Cave
References
- ↑ Lyons, P.C., Jacobsen, E.F., and Scott, B.K., 1985. Coal geology of the Castleman coal field, Garrett County, Maryland, U.S. Geological Survey, Coal Investigations Map C-98. Scale: 1:24,000. link.
- ↑ Sharon, National Geologic Map Database, Geologic Unit: Sharon
- ↑ Cushing, H.P.; Leverett, Frank; Van Horn, Frank (1931). Geology and Mineral Resources of the Cleveland District, Ohio, USGS Bulletin 818. Washington: US Government Printing Office.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.