| Shirvanshah's palace mausoleum | |
|---|---|
Azerbaijani: Şirvanşahlar sarayı türbəsi | |
 | |
 Location within Azerbaijan | |
| General information | |
| Type | Mausoleum |
| Architectural style | Architectural school of Shirvan-Absheron |
| Location | Old City |
| Address | Gala turn, 76 |
| Town or city | |
| Country | Azerbaijan |
| Coordinates | 40°21′59″N 49°50′00″E / 40.366258°N 49.833469°E |
| Completed | 1435–1436 |
| Client | Khalilullah I |
| Design and construction | |
| Architect(s) | Muhammad Ali |
Shirvanshah's palace mausoleum (Azerbaijani: Şirvanşahlar sarayı türbəsi) or tomb of Shirvanshahs’ family (Azerbaijani: Şirvanşahların ailə türbəsi) is a historical monument of the XV century. Locating in Old City, it is a part of Palace of the Shirvanshahs complex. The mausoleum is one of the three buildings located in courtyard of the complex, the others being Shirvanshah's palace mosque and Shirvanshah's palace bath house.[1]
The monument was also registered as a national architectural monument by the decision of the Cabinet of Ministers of the Republic of Azerbaijan dated August 2, 2001, No. 132.[2]
History

The inscription on the entrance gives information about the history and architecture of the building. It says: "The defender of the religion, the man of the prophet, the great Sultan, Shirvanshah Khalilullah, God save his kingdom and reign, he ordered this magnificent tomb for his mother and his seven-year-old son, May Allah have mercy on them, he ordered to build in 839."[3][1]
In 1954, orientalist A.A. Alesgerzade read these writings on the portal.[1] The other writings are taken from the Koran. On medallion, which decorates the portal, there's an inscription, which can be only red with a mirror. It indicates the architect of the monument: "Allah, architect Muhammad Ali". As it is forbidden for architects to write their names on buildings, they encoded their name with this method.[3][1]
The use of the mausoleum later as a madrasa resulted worsening condition of the graves.[4] During the archeological excavations carried out in 1947, six tombs were discovered deeper than the floor surface.[4]
Burials

.JPG.webp)
According to the inscriptions on the entrance, it is clear that the mausoleum was built for the mother and son of Shirvanshah Khalilullah. Nevertheless, there were buried other members of the Shirvanshahs’ family. Stone plaques were discovered under the dismantled floor during the excavations. These plaques were used to cover 7 graves. Only in five graves bone remains were found, although the other two were empty.[5][1]
The historian Khwandamir of XV century wrote in his work, Habib al-Siyar that Ismail I, the ruler of Safavids promised to burn bones of Shirvanshahs family to ash as an insult and to take vengeance of his father and grandfather. During capture of Baku by Safavids in 1501, two graves were opened and the bones inside were removed. The other five graves weren't touched.[5]
In praises, qasidas, ghazals of the palace poet of Shirvanshahs, Badr Shirvani, the persons buried in the tombs were distinguished and specified. He was one of the most famous poets of Shirvan in late 14th-early 15th centuries. In his collection of works, Badr indicated names and birth dates of the persons who were buried in the mausoleum.[5]
In the first tomb the son of Shirvanshah Farrukh Yamin of 6–7 years old, was buried.[1] There remains hair on the skull and chest of the corpse. During cleaning of the bones remnants of the shroud were determined. According one of the praises, the son of the Shirvanshah (1435–1442) died at the age of seven.[5]
Thinness of the teeth and the bones are the indicators that the second grave belongs to an old woman. In one of the praises, the name of the mother of the Shirvanshah were shown as Bika and it was noted that she was an influential woman who died in 1435–1436 (Hijri 839).[5][1]
In the third grave Khanika khanim, wife of Shirvanshah Shahrukh was buried.[1] Badr Shirvani used to note her name in his works.[6]
Sheikh Salah, two years old son of the Shirvanshah was buried in the fourth tomb.[1] He lived in 1443–1445 (Hijri 847–849). Inside the grave, glazed ceramics and candelabrum parts.[6]
The fifth tomb belongs to Ibrahim II (1432), who died at the age of 19.[1] Silk remnants, blue beads, and a golden pin with a needle with length of 36 cm were found in the grave. On the pin there was a turquoise and six sapphire gems.[6]
On the opposite side of the entrance a large skeleton with a height of 2.10 meters was discoreved. It is that is the grave of Khalilullah I. A comb and a gold earring was found in the site.[6]
Architectural features
General planning and construction
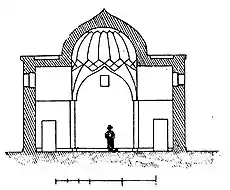
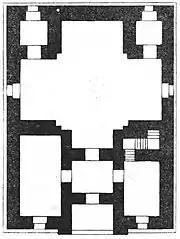
The only entrance to the tomb is the portal on the main facade. On the right and left sides of the corridor there are two small rooms. A door is opened to the corridor from each of these rooms. It is supposed that these rooms used to belong to religious figures. Visitors enters the main hall – the crypt from the corridor. The hall is cruciform in the plan. The middle part of it is covered with a stone dome. The dome is fixed to the roof and stone walls.[7]
On the opposite side of the door, between the branches of the cross there are two small rooms inside the thick stone walls. It is supposed to be used as a cell or warehouse where the tomb items were stored.[8] The external side of the dome covering upper part of the middle of the hall were decorated with glazed tiles. However, those tiles do not currently exist.[7]
On the upper part of tympanum ornament on the stalactite dome there is a zone consisting of inscriptions with religious characters, and on the tympanums there are medallions on both sides, which is written internally. To reduce differences with other surrounding ornaments, the letters of the writings were specially scaled and styled. The inscription on the entrance door of the portal shows that the mausoleum was built by Shirvanshah Khalilullah I for his mother and son in Hijri 839 (1435–1436).
Tectonics of architectural volumes dominate the interior. Here appears artistic style of architectural techniques that was implemented by architect Ali.[9]


Decoration of the portal and facade
The portal repeats composition of Divankhane, which is a part of Palace of the Shirvanshahs complex but in comparison, it is simply solved. The stalactite dome consists of four stalactites, the side walls are smooth, only tympanums of the arches on the entrance door are with ornaments, and on its upper parts two lines of inscriptions are etched.[8]
An hexagonal figure is included in ornaments of the tympanums on the entrance door. Inside of them, the word "Ali" is repeated six times vividly.[1] The portal is about half a meter from the wall. In front of this ledge there is a pavement which plays the role of a bench for people, extending all over the main facade and which is inside the portal. This structure is characteristic for the most of the buildings constructed during that era.[8]
On the top part of the portal, 92nd ayah of XII surah of Koran is etched with method of carving: “Allah, the greatest, said: "Today Allah will forgive you, for he is the most merciful of all.” [3]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 "Şirvаnşаhlаr türbəsi" (in Azerbaijani). icherisheher.gov.az. Archived from the original on November 15, 2009. Retrieved April 5, 2018.
- ↑ "Azərbaycan Respublikası ərazisində dövlət mühafizəsinə götürülmüş daşınmaz tarix və mədəniyyət abidələrinin əhəmiyyət dərəcələrinə görə bölgüsünün təsdiq edilməsi haqqında Azərbaycan Respublikasi Nazirlər Kabinetinin qərarı". e-qanun.az. Retrieved April 4, 2018.
- 1 2 3 Fərhadoğlu 2006, p. 126
- 1 2 Dadaşov, Useynov 1955, p. 21
- 1 2 3 4 5 Fərhadoğlu 2006, p. 127
- 1 2 3 4 Fərhadoğlu 2006, p. 128
- 1 2 Dadaşov, Useynov 1955, p. 20
- 1 2 3 Dadaşov, Useynov 1955, p. 19
- ↑ Fətullayev 2013, p. 105
Literature
- Fərhadoğlu, Kamil (2006). İçərişəhər. Bakı: Şərq-Qərb nəşriyyatı, AMEA Arxeologiya və Etnoqrafiya İnstitutu. p. 256.
- Fətullayev-Fiqarov, Şamil (2013). Bakının memarlıq ensiklopediyası. Bakı: Şərq-Qərb, Azərbaycan Respubliksı Memarlar İttifaqı. p. 528.
- S. Dadaşov, M. Useynov (1955). Bakının memarlıq abidələri. Bakı: Azərbaycan SSR Elmlər Akademiyası Nəşriyyatı. p. 42.
