| Siege of Plei Me | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Vietnam War | |||||||
 Special Forces camp at Plei Me in 1965 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Vĩnh Lộc (II Corps) William A. McKean (5th Special Forces Group) Charles Beckwith (Project DELTA) Nguyễn Trọng Luật (Armored TF) |
Chu Huy Man (B3 Front) Tô Đình Khẩn (32nd Rgmt) Vũ Sắc (33rd Rgmt) | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
| 33rd and 320th PAVN Regiments (~4,200) | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
|
U.S. body count: 326 killed during siege [2] U.S. estimate: 850 killed during siege and pursuit[3] | ||||||
The siege of Plei Me (Vietnamese: Bao vây Plei Me; 19–25 October 1965) was the beginning phase of the first major confrontation between soldiers of the North Vietnamese People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) and the U.S. Army during the Vietnam War. The lifting of the siege by South Vietnamese forces and American air power was followed by the pursuit of the retreating North Vietnamese from 28 October until 12 November, setting the stage for the Battle of Ia Drang.
Background
Plei Me camp was established in October 1963 by the United States Army Special Forces 40 kilometres (25 mi) south of Pleiku city and less than 20 miles (32 km) from the Cambodian border in the Central Highlands of South Vietnam. Plei Me was one of many Special Forces camps scattered around the Central Highlands and charged with gaining and maintaining the support of the Montagnards for the South Vietnamese war effort and gathering intelligence about the infiltration into South Vietnam of North Vietnamese soldiers along the Ho Chi Minh trail.[4]
In 1965 the camp was manned by more than 400 Civilian Irregular Defense Group program (CIDG) soldiers — local Montagnard irregulars, mostly members of the Jarai ethnic group, many of which had families living just outside the camp. 12 American soldiers from the 5th Special Forces Group and 14 Army of the Republic of Vietnam Special Forces assisted and advised the Montagnards. At the time of the attack on Plei Me, about 300 Montagnards, the 14 South Vietnamese and 10 Americans were inside the camp, the others were on patrol or stationed at nearby listening posts.[5]: 99 The camp itself was under the control and command of II Corps Command.
Brigadier General Chu Huy Man of the PAVN was tasked with destroying special forces outposts as a prelude to capturing Pleiku city, the headquarters of the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) in the II Corps region, and gaining control of Highway 19, which led from Pleiku to the coast of South Vietnam. The ARVN had nine battalions (about 4,500 soldiers) of combat troops stationed in Pleiku. Anticipating a PAVN offensive to capture Pleiku and Highway 19, the United States had stationed the 1st Cavalry Division at Camp Radcliff near the town of An Khe in September 1965. The 1st Cavalry Division was composed of three brigades with a total complement of eight battalions. The 1st Cavalry utilized the new tactic of relying on helicopters to transport soldiers and supplies, for medical evacuations and aerial rocket artillery.[5]: 95–6 [6]
General Man had under his command the 32nd (or 320th) and 33rd Regiments, comprising about 4,200 men,[7]: 122 with another regiment, the 66th, becoming available by early November. The 32nd Regiment had been operating in II Corps since January 1965; the 33rd Regiment had arrived in September;[7]: 45 and the 66th Regiment was expected to arrive by November 1965. General Man's offensive was to be launched by December 1965 with all the three regiments. The staging areas were located in the Chu Pong massif on the Vietnam-Cambodian border.
II Corps Command, in coordination with Military Assistance Command, Vietnam, planned to use B-52 airstrikes to destroy the three PAVN Regiments once they concentrated at the assembly areas: "The Chu Pong base was known to exist well prior to the Plei Me attack and J2 MACV had taken this area under study in September 1965 as a possible B-52 target."[8]
However, General Man decided to launch the attack earlier on October 19, 1965, with only two Regiments (the 32nd and the 33rd), apparently before the 1st Cavalry troops became combat ready. His battle "plan consisted of three phases: 1) The 33rd Regiment would surround Plei Me and harass the defenders, exerting enough pressure to force II Corps to send a reaction force; 2) The 32nd Regiment would ambush the relief column and destroy it; 3) Both Regiments would combine force to overrun and destroy the Camp itself."[7]: 47
II Corps Command had to hold off the use of B-52 airstrikes, and came up with a revised plan which consisted of repulsing without destroying the two attacking Regiments, then looking for the chance to use the airstrikes against all the three regiments as initially planned.
PAVN attacks Plei Me
The first indication of an impending attack was about 19:00 hours on October 19 when a Montagnard patrol was attacked near Plei Me. At 22:00, one PAVN Company overran an outpost southwest of the camp and shortly after midnight the PAVN attacked from the north, west, and east with small arms, mortars and recoilless rifles with some attackers reaching the defensive perimeter of the camp. The American commander at Plei Me, Captain Harold M. Moore, called in airstrikes which arrived about 04:00 on October 20 and continued throughout the day and the next night.[5]: 99–100
US and ARVN commanders in Pleiku agreed that reinforcement of the besieged garrison was necessary and decided, while preparing an overland relief convoy, to airlift 175 men, mostly ARVN Rangers, into Plei Me commanded by Major Charles A. Beckwith. The relief group, transported by helicopter, landed about 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) northeast of Plei Me on the morning of October 21 and made its way to the camp the next morning. Beckwith took command of Plei Me and was ordered to rally outside the camp to confront the besiegers, but his force of two companies of Rangers quickly suffered 14 dead and retreated to Plei Me again.[5]: 100–3
Plei Me was resupplied with airdrops from CV-2 Caribous of the 92nd Aviation Company, CV-7 Buffalos of the U.S. Army Aviation Test Board and a number of night drops of munitions, medical supplies, and rations by C-123s from the 310th Air Commando Squadron from Nha Trang Air Base. Some of the air drops landed outside the camp, while two defenders were killed when a pallet of supplies fell on them.[3] Plei Me became, up until then, the largest air support operation of the war with 696 sorties and more than 1.5 million pounds of bombs, napalm, and rockets dropped on the attackers. Several U.S. planes and helicopters were damaged or shot down by intense ground fire.[6]
At Plei Me, the PAVN plan was not to overrun the camp, only to lure out II Corps' main force from Pleiku to destroy it.[7]: 53 Air strikes were called in to hit the attackers only a few meters outside the defensive perimeter of the camp.[2] This was the "grab them by the belt buckle" tactic that would be commonly employed by the communist forces throughout the Vietnam War.
The ambush
General Vĩnh Lộc, II Corps Commander, decided to accept the PAVN's challenge.[7]: 55 A relief task force was established in the afternoon of October 20. In order to allow the 22nd Ranger Battalion that defended Pleiku to participate in the rescue column, General Vĩnh Lộc requested the help of the U.S. Task Force Ingram to secure Pleiku and Pleiku Air Base to meet all contingencies.[7]: 55
The 1,400 man armored Task Force, led by Lieutenant Colonel Nguyễn Trọng Luật, moved out to Phú Mỹ, 20 kilometers south of Pleiku on October 21. LTC Luật was expressly given orders by II Corps Command to simulate the imminent approach of a relief column to the Plei Me camp by lingering around Phú Mỹ to counter the enemy's mobile ambush tactics.[7]: 55 On October 22, the armored task force continued to patrol around Phú Mỹ while 91st Ranger Battalion continued to advance to the camp.[7]: 61 Early on the morning of October 23, when all was clear, the armored task force received orders to advance to the camp.[7]: 63 At 13:00 on the same day, Task Force Ingram closed in on Pleiku city.[9] Vĩnh Lộc also sent a battalion of troops west of the suspected ambush site to engage the PAVN from the rear.
The ARVN armored column proceeded down Provincial Road 6C toward Plei Me, and was ambushed at two places at 17:30 on 23 October. The leading elements of the convoy responded effectively to the PAVN assault, but the ARVN suffered heavy casualties in the second attack toward the rear of the convoy. Both attacks were repelled by U.S. airpower and by morning the PAVN had given up the attack and withdrawn westward. Fearing another attack, Vĩnh Lộc remained in place on October 24, but proceeded onward to Plei Me with only minor resistance on October 25. The PAVN withdrew westward that same evening after suffering heavy casualties from U.S. bombing and the siege of Plei Me was lifted.[5]: 102–4
Pursuing the PAVN
In the aftermath of the siege, elements of the 1st Cavalry were airlifted to Plei Me and the camp was visited by the U.S. Commander in South Vietnam, General William Westmoreland. At the request of II Corps Command,[7]: 73 :"On 26 October 1965, while the relief column and the garrison of Plei Me were conducting a sweep around the Camp, a conference was held at II Corps TOC with the presence of US advisors and unit commanders...The decision made by II Corps Command to exploit the results of the first phase and to pursue the enemy was fully concurred by the US military authorities and agreement was reached to establish a close cooperation in operational activities. The 1st Cavalry Division made the main effort with the Long Reach Operations and the ARVN Airborne Brigade acted as reserve, ready to participate on Corps order."on October 26, Westmoreland authorized the 1st Cavalry to take the offensive and pursue the withdrawing North Vietnamese. A division tactical Command Post was established, co-located with II Corps headquarters for the purpose of tactical coordination led by Brigadier General Richard T. Knowles, 1st Cavalry Division Deputy Commander.[10]
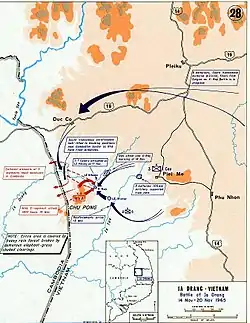
On October 26, with the Plei Me camp secured, ARVN II Corps Command requested that "1st Air Cavalry Tactical Area Of Responsibility (TAOR) be extended to include the Plei Me area except the camp itself,"[11] so that the camp remained vulnerable in the enemy's eyes: "Dan Thang 21 operation finished, Plei Me camp was back on its footing, but among the two VC Regiments that had joined in the attack, we only inflicted the enemy with more than 400 killed. The withdrawal was a rational and intelligent initiative taken by the VC Field Front Command. But the enemy would attempt to take revenge and furthermore, the remote Pleime camp remains an eye sore to them."[7]: 94 With the extension of the operational area, II Corps Command further assigned to the American division the Long Reach operation: "Therefore the decision to organize an enemy pursuit of II Corps Command, in which 1st Cavalry Division is the main effort and ARVN Airborne Group is the reserved force ready to intervene when necessary, was wholeheartedly accepted by the entire division, because rarely a unit got the chance to open its first history pages with a trường chinh (Long Reach) operation."[7]: 101 This operation was carried out in three stages: All the Way (1st Brigade, 27 Oct-9 Nov), Silver Bayonet I (3rd Brigade, 9 Nov-17 Nov) and Silver Bayonet II (2nd Brigade, 18 Nov- 26 Nov).[12]
The 1st Brigade, 1st Cavalry under Colonel Harlow Clark undertook the search and destroy operation over an area of 1,500 square miles (3,900 km2) north and west of Plei Me.[9] PAVN officers later described their forces as in "great disorder" following the siege. The 33rd Regiment had suffered heavy casualties; the 32nd remained mostly intact. In the pursuit, the 33rd would continue to be punished by the U.S. forces. Approximately 40 percent, or 600, of its 1,500 men were killed in the siege and its aftermath.[13]
On 1 November elements of the 1st Brigade, 1st Cavalry located a PAVN hospital area and killed 99 or more soldiers at a cost of 11 Americans dead and 47 wounded. On 3–4 November, the Americans ambushed (and were in turn counter-ambushed) an element of the newly arrived PAVN 66th Regiment, killing an estimated 72 PAVN at a cost of 4 American dead. This firefight was distinguished by the first use of helicopters to reinforce and supply an American unit at night. On 6 November, two American companies engaged in a lengthy firefight with PAVN elements with the US claiming to have killed 77 at a cost of 26 American dead and 73 wounded. Between 9 and 11 November the 1st Brigade was withdrawn to its base at An Khe and replaced with the 3rd Brigade.[14]: 186
On November 10, the 3rd Brigade was ordered to perform a diversionary maneuver by switching the operational direction to the east[15] to entice B3 Field Front to regroup its three regiments in assembly areas,[16] to stage a second attack on Plei Me camp set for November 16.[17]
On November 11, intelligence sources revealed the disposition of the three PAVN regiments: the 66th at vicinity YA9104, the 33rd at YA 940010, and the 32nd at YA 820070.[18] On November 12, the 3rd Brigade was given orders to prepare for "...an air assault near the foot of the Chu Pongs,"[14]: 196 at 14 miles (23 km) northwest of Plei Me. On November 13, Colonel Brown met with Lieutenant Colonel Moore and told Moore "...to conduct an air-mobile assault the following morning."[14]: 199 On November 14, the 1st Battalion, 7th Cavalry Regiment air assaulted into LZ X-Ray, starting the Battle of Ia Drang which lasted from 14 to 18 November 1965. The PAVN B3 Field Front Command decided to postpone the renewed attack on Plei Me camp and met the new threat with its 7th and 9th Battalions.[19]
Miscellaneous
During the battle, A-1E Skyraider (s/n 52-132442) pilot Captain Melvin C. Elliott was shot down while strafing the area around the camp. After evading the PAVN for 36 hours by covering himself with mud, Elliott was rescued by helicopter.[20]
During the siege, U.S. President Lyndon Johnson telephoned Beckwith to congratulate him on his defense of Plei Me.[21]
References
- ↑ 5th Special Forces Group, CIDG in Camp Defense (Plei Me), 31 December 1965.
- 1 2 Project CHECO Southeast Asia Report #160 – Special Report: The Siege of Plei Me – 19–29 October 1965, 24 February 1966, Folder 0279, Box 0001, Vietnam Archive Collection, The Vietnam Center and Archive, Texas Tech University. Accessed 9 Apr. 2015.<http://www.vietnam.ttu.edu/virtualarchive/items.php?item=F031100010279>
- 1 2 "Seven Days of Zap". Time Magazine. 1965-11-05. Archived from the original on October 27, 2007. Retrieved 2007-11-14.
- ↑ Vietnam Studies: U.S. Army Special Forces, 1961–1971 (1989), CHM Publication 90-23, Department of the Army. http://www.history.army/milBOOKS/Vietnam/90-23/tab5.htm%5B%5D, accessed 8 April 2015
- 1 2 3 4 5 Carland, John (2000). Combat Operations Stemming the Tide, May 1965 to October 1966. Army Center of Military History.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - 1 2 1st Cavalry Division Association – Interim Report of Operations, First Cavalry Division, July 1965 to December 1966, ca. 1967, Folder 01, Box 01, Richard P. Carmody Collection, The Vietnam Center and Archive, Texas Tech University, pp. 15–19, accessed 8 Apr. 2015. <http://www.vietnam.ttu.edu/virtualarchive/items.php?item=22030101001>
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Vinh Loc (1966). Why Pleime. Viet Nam: Information Printing Office. Archived from the original on 2018-09-29. Retrieved 2015-05-05.
- ↑ McChristian, J.A. (1966). Intelligence Aspects of Pleime/Chupong Campaign, J2/MACV. Archived from the original on 2019-12-31. Retrieved 2015-05-06., p. 9
- 1 2 1st Cavalry Division Association – Interim Report of Operations, First Cavalry Division, July 1965 to December 1966, ca. 1967, Folder 01, Box 01, Richard P. Carmody Collection, The Vietnam Center and Archive, Texas Tech University, pp. 15–19, accessed 8 Apr. 2015.<http://www.vietnam.ttu.edu/virtualarchive/items.php?item=22030101001>
- ↑ Kinnard, William (1966). Pleiku Campaign, After Action Report. Archived from the original on 2017-07-03. Retrieved 2015-05-07., p.2
- ↑ G3Journal/I Field Force Vietnam
- ↑ Kinnard, page 1.
- ↑ Moore and Galloway, pp. 50–54
- 1 2 3 Coleman, J.D. (1988). Pleiku, The Dawn of Helicopter Warfare in Vietnam. New York: St.Martin's Press.
- ↑ Kinnard, page 67: By this time Field Force Vietnam had asked the Division to consider moving this operations east of Plei Me
- ↑ Kinnard, page 73: The movement and shift in emphasis from west to east was to further stimulate a forthcoming decision from the PAVN division headquarters.
- ↑ Kinnard, page 76: With American units seemingly withdrawing to the east of Plei Me, the decision was to attempt to regain its early advantage with an attack. The target once again was the Plei Me CIDG Camp. The division headquarters set the date for attack at 16 November, and issued orders to its three regiments.
- ↑ McChristian, J2/MACV, page 44.
- ↑ General Nguyen Huu An, Chien Truong Moi – Hoi Uc: Brother Chu Huy Man, Commander, brother Dang Vu Hiep, Political Commissar and I at the headquarters were making arrangements to prepare for a second phase of action against a target near Pleime. Upon receiving news from all directions reporting that the Americans had inserted troops, we issued an order to delay the attack of Chu Ho.
- ↑ "Pilot covers himself with mud to elude VC", http://www.skyraider.org/skyassn/warstor/pleime.htm, accessed 10 Apr 2015
- ↑ "Plei Me 9", http://www.lzxray.com/content/plei-me-9, accessed 15 Apr 2015
Further reading
- Beckwith, Charles (1983). Delta Force: The Army's Elite Counterterrorist Unit. Avon Books.
- Hay Jr., Lieutenant General John H (1989) [1974]. "Chapter II: Ia Drang (October–November 1965". Tactical and Material Innovations. Vietnam Studies. Washington, D.C.: United States Army Center of Military History. CMH Pub 90-21.
- "Plei Me – The 82nd Ranger". Vietnamese Rangers.
- "Plei Me Newspaper Articles".