 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Silver(I) permanganate | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Silver(I) manganate(VII) | |
| Other names
Argentous permanganate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.127 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
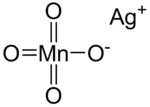
| AgMnO4 | |
| Molar mass | 226.804 g/mol |
| Appearance | purple crystals or gray powder |
| Density | 4.27 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 160 °C (320 °F; 433 K) (decomposes) |
| 0.55 g/100 mL (0 °C) 1.69 g/100 mL (30 °C) | |
| −63.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
| monoclinic | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Eye irritant |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Warning | |
| H272, H312, H319, H332 | |
| P210, P220, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P310, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P311, P321, P330, P337+P313, P362+P364, P370+P378, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Silver permanganate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula AgMnO4. This salt is a purple crystal adopting a monoclinic crystal system.[1] It decomposes when heated or mixed with water, and heating to high temperature may lead to explosion. The compound is used in gas masks.
Production
It can be produced through the reaction of silver nitrate and potassium permanganate:[2]
- AgNO
3 + KMnO
4 → AgMnO
4 + KNO
3
References
- ↑ Boonstra, E. G. (14 August 1968). "The crystal structure of silver permanganate". Acta Crystallographica Section B. 24 (8): 1053–1062. doi:10.1107/S0567740868003699.
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.