 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
sodium metagermanate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.535 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Na2GeO3 | |
| Molar mass | 166.62 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 3.31 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 1,060 °C (1,940 °F; 1,330 K) |
| 14.4 g/100 mL (0 °C) 23.8 g/100 mL (25 °C) | |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.59 |
| Structure | |
| orthorhombic | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Sodium silicate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Sodium germanate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Na2GeO3. It exists as a colorless solid. Sodium germanate is primarily used for the synthesis of other germanium compounds.
Preparation and reactions
Sodium germanate can be prepared by the fusion of germanium oxide with sodium hydroxide at high temperatures:
- 2 NaOH + GeO2 → Na2GeO3 + H2O
An intermediate in this reaction is the protonated derivative NaHGeO3, which is a water-soluble salt.
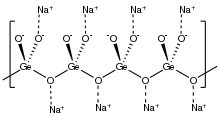
Structure

Structure of solid sodium germanate. (color scheme: red = O) Si resides at the center of the blue tetrahedra.
it is structurally analogous to sodium metasilicate, Na2SiO3, consisting of polymeric GeO32− anions made up of vertex sharing {GeO4} tetrahedra.[1][2]
See also
References
- ↑ Cruickshank, D. W. J.; Kálmán, A.; Stephens, J. S. (1978). "A Reinvestigation of Sodium Metagermanate". Acta Crystallographica Section B: Structural Crystallography and Crystal Chemistry. 34 (4): 1333–1334. doi:10.1107/S0567740878005488.
- ↑ C. C. Addison, Inorganic Chemistry of the Main-Group Elements, vol 1, 1973, The chemical Society, ISBN 9780851867526
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.