| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 225 seats to the Parliament of Sri Lanka 113 seats were needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 61.26% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
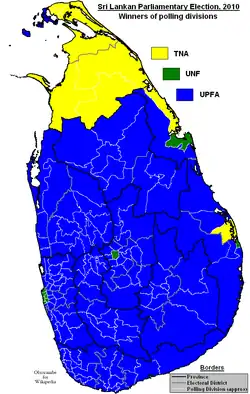 Winners of polling divisions. UPFA in blue, UNF in green and TNA in yellow. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Parliamentary elections were held in Sri Lanka on 8 and 20 April 2010, to elect 225 members to Sri Lanka's 14th Parliament.[1] 14,088,500 Sri Lankans were eligible to vote in the election at 11,102 polling stations. It was the first general election to be held in Sri Lanka following the conclusion of the civil war which lasted 26 years.
The main parties contesting in the election were the ruling United People's Freedom Alliance (UPFA), the main opposition United National Front (UNF) and the Democratic National Alliance (DNA) led by former commander of the Sri Lankan Army Sarath Fonseka. President Mahinda Rajapaksa had previously been reelected as president in January 2010.
As expected, the UPFA secured a landslide victory in the elections, buoyed by its achievement of ending the 30 year Sri Lankan Civil War and defeating the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam in May 2009. The UPFA won a large majority in the parliament, obtaining 144 seats, an increase of 39 since the 2004 election. The main opposition UNF won 60 seats, a decline of 22. The minority Tamil party Tamil National Alliance (TNA) won 14 seats, down from the 22 they won in 2004, and the DNA, contesting for the first time, won 7 seats.[2][3] The UPFA however fell short of its goal of obtaining a two-thirds supermajority in the house, which it would have needed to change the constitution on its own.[4] The election had the lowest voter turnout in Sri Lanka since independence.[5]
While the elections were initially scheduled to be concluded on 8 April, irregularities in two districts led the Commissioner of Elections to hold re-polls on 20 April. Final results were announced the following day, a day before the new parliament was scheduled to meet for the first time.
Background
General elections are usually held every six years in Sri Lanka, to elect 225 members to the Parliament of Sri Lanka. The country is divided into 22 electoral districts, and each district is assigned a specific number of seats depending on the districts population, with 196 seats distributed among the districts. At the election, parties contesting in a given district are awarded a certain number of seats available from the district based on the number of votes obtained in the whole district. The remaining 29 seats are distributed amongst the contesting political parties based on the percentage of the national vote received by each party.[6]
The previous parliamentary election was held on April 2, 2004. The newly formed UPFA alliance became the largest group in Parliament by winning 105 of the 225 seats, allowing it to form a minority government with the support of the sole Eelam People's Democratic Party MP.[7][8] On April 6, 2004, President Chandrika Kumaratunga appointed Mahinda Rajapaksa, the leader of the UPFA, as the new Prime Minister.[9] The rest of the government were sworn in on April 10, 2004.[10][11] The new parliament was sworn in on April 22, 2004.[12]
Since then a number of defections and counter-defections from the opposition have increased the number of government MPs to 129, most of whom have been rewarded with ministerial posts:[13]
- 9 August 2004: Three Sri Lanka Muslim Congress (SLMC) MPs join UPFA.[14]
- 3 September 2004: Ceylon Workers' Congress (eight MPs) joins UPFA, giving it a majority in parliament.[15][16]
- 16 June 2005: Janatha Vimukthi Peramuna (JVP) (39 MPs) quits UPFA.[17][18]
- 25 January 2006: Four United National Party MPs join UPFA.[19][20]
- 28 January 2007: 18 UNP MPs and 6 SLMC MPs join UPFA.[21][22][23]
- 30 January 2007: Jathika Hela Urumaya (eight MPs) joins UPFA.[24][25][26][27]
- 12 December 2007: Four SLMC MPs quit the UPFA.[28][29]
- 28 December 2008: 12 MPs, who had left the JVP in May 2008 to form the National Freedom Front, join the UPFA.[30][31]
This has allowed the UPFA form a stable government for six years.
Following the expiration of the second term of President Kumaratunge, Prime Minister Mahinda Rajapakse defeated the leader of the United National Party and former Prime Minister Ranil Wickremasinghe in the 2005 Presidential election. He was succeeded as Prime Minister by Ratnasiri Wickremanayake. Under Rajapakse, the Sri Lankan military defeated the militant Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam group in May 2009, ending the 30 year Sri Lankan Civil War and significantly increasing Rajapaksa's popularity in the country. Rajapaksa rode this wave of popularity to win the 2010 Presidential election, defeating opposition candidate Sarath Fonseka by a large margin.
Details
With the term of the 13th Parliament (also known as the 6th Parliament) scheduled to end in April 2010, Rajapaksa dissolved parliament on February 9, 2010, paving the way for fresh elections.[1] Nominations took place between February 19 and February 26, and the date of the election was set for April 8, 2010.[1] 14,088,500 Sri Lankans were eligible to vote in the election, for which 11,102 polling stations were set up. Of this, 415,432 people were eligible to cast their vote via postal voting. Final votes were counted at 1,387 counting centers around the country.[32]
Since the 2004 election, there were four changes to number of seats allocated to each electoral district. Anuradhapura and Gampaha gained one seat each while Colombo and Kurunegala lost a seat each.[33]
Contesting parties
All the constituent parties of the ruling UPFA contested under its banner. The parliamentary opposition parties (UNF, Janatha Vimukthi Peramuna (JVP) and (TNA), who had come together to support common opposition candidate Sarath Fonseka at the presidential election, were unable to form a common alliance to contest in the election. Therefore, the UNF and the TNA contested alone, while Fonseka and the JVP allied to form a new alliance called the Democratic National Alliance (DNA). Fonseka was the DNA's chief candidate in Colombo district.[34]
The UPFA, UNF and DNA contested in all 22 electoral districts while the TNA contested in the 5 districts in the north and east.[35] The UNF contested under the name and symbol of the United National Party, as it had done in the previous two parliamentary elections.[35] The TNA contested under the name and symbol of the Illankai Tamil Arasu Kachchi, as it did in the last parliamentary election.[35]
A record 7,680 candidates contested for the 196 district seats.[35]
Violence and violations of election laws
Sri Lankan elections have a history of violence, misuse of state resources, and other violations of election laws. 274 incidents had been reported to the police up to 5 April.[36] The Centre for Monitoring Election Violence (CMEV) recorded 413 incidents up to 7 April.[37] The CMEV has stated that it is impossible to say if the election had been "free and fair".[38] People's Action for Free and Fair Elections (PAFFREL) recorded 270 incidents up to 7 April.[39] The Campaign for Free and Fair Elections (CaFFE) has stated that the election was not free and fair.[40] CaFFE condemned the police and election commissioner for not enforcing electoral law.[41] The Asian Network for Free Elections (ANFREL) also recorded a number of violations.[42] A significant feature of the violence was intra-party clashes between UPFA candidates.
On the day of the election, there were a number of elections violations reported around the country. The violations in the Nawalapitiya electorate of the Kandy District were serious enough for the Elections Commissioner to nullify the voting in some areas of the electorate and order a re-poll.[43] Results from the Trincomalee District were also suspended as some ballot papers had been stolen.[44] Re-polling for the effected polling areas took place on April 20.[45]
Results
 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | |||||
| District | National | Total | ||||||
| United People's Freedom Alliance[lower-roman 1] | 4,846,388 | 60.33 | 127 | 17 | 144 | |||
| United National Front[lower-roman 2] | 2,357,057 | 29.34 | 51 | 9 | 60 | |||
| Democratic National Alliance[lower-roman 3] | 441,251 | 5.49 | 5 | 2 | 7 | |||
| Tamil National Alliance[lower-roman 4] | 233,190 | 2.90 | 13 | 1 | 14 | |||
| Up-Country People's Front | 24,670 | 0.31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Tamil Makkal Viduthalai Pulikal | 20,284 | 0.25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Sinhalaye Mahasammatha Bhoomiputra Pakshaya | 12,170 | 0.15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Tamil United Liberation Front | 9,223 | 0.11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Tamil National People's Front[lower-roman 5] | 7,544 | 0.09 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Democratic People's Liberation Front[lower-roman 6] | 6,036 | 0.08 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Sri Lanka National Front | 5,313 | 0.07 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Eelavar Democratic Front | 3,709 | 0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Jathika Sangwardhena Peramuna | 3,358 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Eelam People's Democratic Party | 2,867 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Our National Front | 2,647 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| United National Alternative Front | 2,454 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Eksath Lanka Podujana Pakshaya | 2,387 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Left Liberation Front | 2,386 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| United Socialist Party | 2,192 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Pathmanabha Eelam Revolutionary Liberation Front | 2,100 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Jana Setha Peramuna | 1,501 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| United Democratic Front | 1,497 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Democratic Unity Alliance | 1,270 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Eksath Lanka Maha Sabha | 673 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Patriotic National Front | 558 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Okkoma Wasiyo Okkoma Rajawaru Sanvidanaya | 476 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Socialist Equality Party | 371 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Sri Lanka Labour Party | 338 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| National Peoples Party | 164 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Muslim National Alliance | 147 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| The Liberal Party | 131 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Muslim Liberation Front | 130 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Ruhunu Janatha Party | 109 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Akila Ilankai Tamil United Front | 85 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Ceylon Democratic Unity Alliance | 75 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| New Sinhala Heritage | 19 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Independents | 38,947 | 0.48 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Total | 8,033,717 | 100.00 | 196 | 29 | 225 | |||
| Valid votes | 8,033,717 | 93.08 | ||||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 596,972 | 6.92 | ||||||
| Total votes | 8,630,689 | 100.00 | ||||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 14,088,500 | 61.26 | ||||||
| Source: Election Commission, Election Commission | ||||||||
- ↑ Consisting of the All Ceylon Muslim Congress, the Ceylon Workers' Congress, the Eelam People's Democratic Party (which contested separately in Vanni), Jathika Hela Urumaya, Mahajana Eksath Peramuna, the National Congress, the National Freedom Front, the Socialist Alliance (the Communist Party of Sri Lanka, the Democratic Left Front, Lanka Sama Samaja Party, the National Liberation People's Party and the Sri Lanka People's Party), the Sri Lanka Freedom Party and the Up-Country People's Front (which contested separately in Badulla and Nuwara Eliya).
- ↑ Contested under the name and symbol of United National Party. It also included the Citizen's Front, the Democratic People's Front, the National Union of Workers and the Sri Lanka Muslim Congress).
- ↑ Including Janatha Vimukthi Peramuna.
- ↑ Contested under the name and symbol of Illankai Tamil Arasu Kachchi. It also consisted of the Eelam People's Revolutionary Liberation Front and the Tamil Eelam Liberation Organization.
- ↑ Contested under the name and symbol of All Ceylon Tamil Congress.
- ↑ Including the People's Liberation Organisation of Tamil Eelam.
By district
| District | Province | UPFA | UNF | DNA | TNA | Others | Total seats | Turnout | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | Seats | +/- | Votes | Seats | +/- | Votes | Seats | +/- | Votes | Seats | +/- | Seats | ||||
| Colombo | Western | 480,896 | 10 | +2 | 339,750 | 7 | −2 | 110,683 | 2 | +2 | DNC | 0 | 19 | 65% | ||
| Gampaha | 589,476 | 12 | +3 | 266,523 | 5 | −1 | 69,747 | 1 | +1 | DNC | 0 | 18 | 67% | |||
| Kalutara | 313,836 | 7 | +1 | 139,596 | 2 | −1 | 36,722 | 1 | +1 | DNC | 0 | 10 | 67% | |||
| Mahanuwara | Central | 339,819 | 8 | +3 | 192,798 | 4 | −2 | 23,728 | 0 | - | DNC | 0 | 12 | 64% | ||
| Matale | 131,069 | 4 | +1 | 55,737 | 1 | −1 | 7,636 | 0 | - | DNC | 0 | 5 | 60% | |||
| Nuwara Eliya | 149,111 | 5 | +3 | 96,885 | 2 | − 2 | 3,984 | 0 | - | DNC | 0 | 7 | 66% | |||
| Galle | Southern | 305,307 | 7 | +1 | 120,101 | 2 | −2 | 33,663 | 1 | +1 | DNC | 0 | 10 | 64% | ||
| Matara | 213,937 | 6 | +1 | 91,114 | 2 | −1 | 20,465 | 0 | - | DNC | 0 | 8 | 59% | |||
| Hambantota | 174,808 | 5 | - | 83,027 | 2 | - | 19,186 | 0 | - | DNC | 0 | 7 | 69% | |||
| Jaffna | Northern | 47,622 | 3 | +3 | 12,624 | 1 | +1 | 201 | 0 | - | 65,119 | 5 | −3 | 0 | 9 | 23% |
| Vanni | 37,522 | 2 | +2 | 12,783 | 1 | - | 301 | 0 | - | 41,673 | 3 | −2 | 0 | 6 | 44% | |
| Batticaloa | Eastern | 62,009 | 1 | +1 | 22,935 | 1 | +1 | 324 | 0 | - | 66,235 | 3 | −1 | 0 | 5 | 59% |
| Digamadulla | 132,096 | 4 | +1 | 90,757 | 2 | +1 | 2,917 | 0 | - | 26,895 | 1 | - | 0 | 7 | 74% | |
| Trincomalee | 59,784 | 2 | +1 | 39,691 | 1 | +1 | 2,519 | 0 | - | 33,268 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 4 | 62% | |
| Kurunegala | North Western | 429,316 | 10 | +1 | 213,713 | 5 | −2 | 26,440 | 0 | - | DNC | 0 | 15 | 61% | ||
| Puttalam | 167,769 | 6 | +1 | 81,152 | 2 | −1 | 8,792 | 0 | - | DNC | 0 | 8 | 57% | |||
| Anuradhapura | North Central | 221,204 | 7 | +2 | 80,360 | 2 | −1 | 18,129 | 0 | - | DNC | 0 | 9 | 61% | ||
| Polonnauwa | 118,694 | 4 | +1 | 45,732 | 1 | −1 | 6,457 | 0 | - | DNC | 0 | 5 | 66% | |||
| Badulla | Uva | 203,689 | 6 | +3 | 112,886 | 2 | −3 | 15,768 | 0 | - | DNC | 0 | 8 | 65% | ||
| Monaragala | 120,634 | 4 | +1 | 28,892 | 1 | −1 | 9,018 | 0 | - | DNC | 0 | 5 | 56% | |||
| Ratnapura | Sabaragamuwa | 305,327 | 7 | +1 | 125,076 | 3 | −1 | 11,053 | 0 | - | DNC | 0 | 10 | 65% | ||
| Kegalle | 242,463 | 7 | +2 | 104,925 | 2 | −2 | 13,518 | 0 | - | DNC | 0 | 9 | 63% | |||
| National List | 17 | +4 | 9 | −2 | 2 | +2 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 29 | - | |||||
| Total | 4,846,388 | 144 | +39 | 2,357,057 | 60 | −22 | 441,251 | 7 | +7 | 233,190 | 14 | −8 | 0 | 225 | 61% | |
| Source: Sri Lanka Department of Elections Archived 2010-04-14 at the Wayback Machine | ||||||||||||||||
Elected members
See also
Notes
References
- 1 2 3 "6th Parliament Dissolved". News and Events. Parliament of Sri Lanka. 10 February 2010. Archived from the original on 4 March 2010. Retrieved 13 February 2010.
- ↑ Sirilal, Ranga. "Sri Lanka ruling party records landslide win at polls". Montrealgazette.com. Archived from the original on 2010-04-24. Retrieved 2010-04-21.
- ↑ "Department of Election". Slelections.gov.lk. Archived from the original on 2010-04-21. Retrieved 2010-04-21.
- ↑ "Sri Lanka ruling party wins majority in parliament", BBC News, 9 April 2010
- ↑ Haviland, Charles (21 April 2010). "Final Sri Lanka vote count confirms Rajapaksa triumph". BBC News. Retrieved 21 April 2010.
- ↑ "Department of Election". Slelections.gov.lk. Archived from the original on 2013-01-21. Retrieved 2010-04-21.
- ↑ "The 7th Parliamentary Election Today". The Daily Mirror (Sri Lanka). 8 April 2010. Archived from the original on 13 April 2010. Retrieved 8 April 2010.
- ↑ Gnanadass, Wilson (11 April 2004). "Shorter life span for minority govt.'s". The Sunday Leader. Archived from the original on June 17, 2011. Retrieved 8 April 2010.
- ↑ "Sri Lanka's 14th Prime Minister Mr. Mahinda Rajapakse". TamilNet. 6 April 2004. Retrieved 28 November 2009.
- ↑ Vidanage, Harinda (11 April 2004). "Cabinet in crisis – JVP keeps out By Harinda Vidanage". Sunday Times, Sri Lanka. Retrieved 28 November 2009.
- ↑ "JVP boycotts UPFA cabinet swearing in ceremony". TamilNet. 10 April 2004. Retrieved 28 November 2009.
- ↑ "Opening of 13th Parliament today". Daily News, Sri Lanka. 22 April 2004. Archived from the original on 5 June 2011. Retrieved 28 November 2009.
- ↑ de Silva, Lakshmi (25 November 2009). "UPFA gained huge ground after 2005". Daily News, Sri Lanka. Archived from the original on 28 November 2009. Retrieved 28 November 2009.
- ↑ "SLMC dissident to be made Minister in UPFA government". TamilNet. 9 August 2004. Retrieved 28 November 2009.
- ↑ "CWC will support Kumaratunga's government – Thondaman". TamilNet. 3 September 2004. Retrieved 28 November 2009.
- ↑ P. Krishnaswamy (4 September 2004). "CWC announces unconditional support to UPFA Government". Daily News, Sri Lanka. Archived from the original on 5 June 2011. Retrieved 28 November 2009.
- ↑ "JVP leaves coalition Government". TamilNet. 16 June 2005. Retrieved 28 November 2009.
- ↑ Weerasinghe, Chamikara (17 June 2005). "VP leaves Govt with regret". Daily News, Sri Lanka. Archived from the original on 5 June 2011. Retrieved 28 November 2009.
- ↑ "Two UNP parliamentarians cross over". TamilNet. 25 January 2006. Retrieved 28 November 2009.
- ↑ "Four senior UNPers join Sri Lanka govt". MahindaRajapaska.com. 25 January 2006. Archived from the original on 27 May 2006. Retrieved 28 November 2009.
- ↑ "UNP dissidents, SLMC join UPFA government, appointed ministers". TamilNet. 28 January 2007. Retrieved 28 November 2009.
- ↑ "18 jumbos cross over". Daily News, Sri Lanka. 29 January 2007. Archived from the original on 5 June 2011. Retrieved 28 November 2009.
- ↑ "Sri Lankan ruling party boosts parliamentary strength". People's Daily, China. 28 January 2007. Retrieved 28 November 2009.
- ↑ "Monks' party to join UPFA government". TamilNet. 30 January 2007. Retrieved 8 April 2010.
- ↑ Kirinde, Chandani (4 February 2007). "Parliament: Old faces in new places". The Sunday Times (Sri Lanka). Retrieved 8 April 2010.
- ↑ "JHU decides to accept portfolio to support the President". The Nation, Sri Lanka. 4 February 2007. Retrieved 8 April 2010.
- ↑ Mandana Ismail Abeywickrema (7 March 2010). "The Best Among Equals". The Sunday Leader. Archived from the original on 17 June 2011. Retrieved 8 April 2010.
- ↑ "SLMC resigns from Rajapaksa government". TamilNet. 12 December 2007. Retrieved 28 November 2009.
- ↑ "Why the SLMC quit the Rajapaska government". Nation, Sri Lanka. 16 December 2007. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 28 November 2009.
- ↑ "JVP dissidents form JNP". TamilNet. 12 May 2008. Retrieved 28 November 2009.
- ↑ "UPFA looks for strength in alliance with JVP as election fever hots up". The Nation, Sri Lanka. 28 December 2008. Archived from the original on 14 March 2010. Retrieved 28 November 2009.
- ↑ "Department of Election". Slelections.gov.lk. Archived from the original on 2009-12-09. Retrieved 2010-04-21.
- ↑ "Parliamentary Elections – 2010". News. Department of Elections, Sri Lanka. Archived from the original on 9 December 2009. Retrieved 28 February 2010.
- ↑ "Nominations for Parliamentary elections close". Sunday Times (Sri Lanka). 26 February 2010. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011. Retrieved 28 February 2010.
- 1 2 3 4 Wellaboda, Ishtartha (28 February 2010). "Battle of Titans in Colombo". News. The Nation, Sri Lanka. Archived from the original on 18 April 2010. Retrieved 28 February 2010.
- ↑ "Violence rages in Ampara, officials threaten boycott". Daily Mirror (Sri Lanka). 6 April 2010. Retrieved 21 April 2010.
- ↑ "Monitoring election violence in Sri Lanka Parliamentary Election April 2010: Summary of incidents to date". Centre for Monitoring Election Violence. 7 April 2010. Retrieved 21 April 2010.
- ↑ Burke, Jason (9 April 2010). "Sri Lanka's President Rajapaska's party looks set for election victory". The Guardian. Retrieved 21 April 2010.
- ↑ "Parliamentary General Elections –2010 Third interim report – 7th April 2010" (PDF). People's Action for Free and Fair Elections. 7 April 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 July 2011. Retrieved 21 April 2010.
- ↑ "Sri Lanka ruling party wins majority in parliament". BBC News. 9 April 2010. Retrieved 21 April 2010.
- ↑ "CaFFE Election Day Press Release". Campaign for Free and Fair Elections. 8 April 2010. Archived from the original on 17 April 2010. Retrieved 21 April 2010.
- ↑ Kelum Bandara and Yohan Perera (9 April 2010). "Some candidates violated the law – Asian monitors". Daily Mirror (Sri Lanka). Archived from the original on 11 April 2010. Retrieved 21 April 2010.
- ↑ "N'pitiya repoll to be Gazetted". Dailymirror.lk. 2010-04-09. Retrieved 2010-04-21.
- ↑ "Trinco results suspended". Dailymirror.lk. 2010-04-09. Retrieved 2010-04-21.
- ↑ Elections to the National Assembly Sri Lanka government election website

.jpg.webp)

