State of E 鄂 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c. 12th century BCE–863 BCE | |||||||||||||
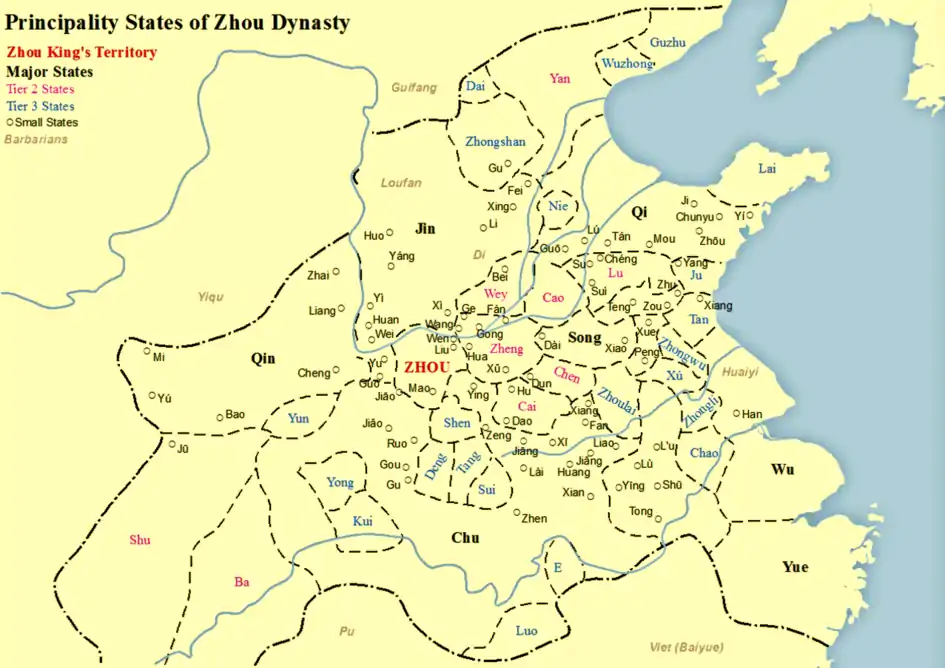 State of E as a territory of the Zhou Dynasty, near the South | |||||||||||||
| Status | Monarchy | ||||||||||||
| Capital | Xiangning County Nanyang, Henan Province Ezhou, Hubei Province | ||||||||||||
| Religion | Chinese folk religion, Ancestor worship | ||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||
• Established | c. 12th century BCE | ||||||||||||
• Disestablished | 863 BCE | ||||||||||||
| Currency | Spade money | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| E | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese | 鄂 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The State of E (IPA: /ɤ̂/), whose Middle and Old Chinese name has been reconstructed as Ngak (IPA: /ŋˤak/),[1] was an ancient Chinese state in the area of present-day Henan and Hubei in China from around the 12th century BCE until its overthrow in 863 BCE. It was a vassal of the Shang state and its ruler was one of the Three Ducal Ministers appointed by Dixin of Shang, who is known pejoratively as King Zhou of Shang.[2]
E was originally located in the southern part of the modern province of Henan[3] but later moved to Hubei. Its name is now used as the provincial abbreviation for Hubei.
History
There are a number of different theories about the origins of E, including that its original rulers were descended from the Baiyue[4] or the Daxi culture.[5] Another theory claims that during the Shang dynasty, descendants of the Yellow Emperor surnamed Jí (姞) were granted land by Dixin around modern-day Xiangning County in Shanxi and that it became the original nucleus of E.
In Chinese historical records, Dixin was said to have wanted to make the daughter of the Marquess of Jiu an imperial concubine but she was a dignified woman who regarded such a role as beneath her. In a fit of anger, Dixin murdered both the Marquess and his daughter and turned the marquess's body into mincemeat. The Marquess of E, protesting this injustice, renounced his vassalage but was also then murdered.
Following the c. 1046 BCE establishment of the Western Zhou, the state of Jin moved into E's territory and forced its people to flee southward into the northern part of modern-day Nanyang, Henan. The relocation exposed them to the powerful southern state of Chu. By the middle of the Western Zhou, E had fled once again, settling east of present-day Ezhou in Hubei.
E led a confederation of Southern Huaiyi tribes in a rebellion during the seventh year of the reign of King Yi of Zhou (863 BCE) and was destroyed by Zhou forces, permitting Chu to finally absorb the smaller state. Chu's ruler Xiong Qu conferred its former lands upon his son Xiong Zhi. The destruction of E was inscribed upon a bronze tripod cauldron, the Yu Ding.[6]
Xiong Zhi continued to live in E's capital after the death of his father, making it the de facto capital of Chu. Subsequent rulers remained there until Xiong E (r. 799-791 BCE) decided to reduce it to the status of an alternative capital.
After Chu became an independent state in the Spring and Autumn period, King Gong of Chu (楚共王, r. 590–560 BCE) made his third son Lord of E. In the sixth year of the reign of King Huai of Chu (323 BCE), the king made his younger brother Xiong Qu the Lord of E. Following the destruction of Chu by Qin in 223, E became a county under the Qin and Han dynasties.
Xi'e was a county in the Nanyang Commandery during the Qin and Han dynasties and the Three Kingdoms period which took its name from the State of E.
See also
References
- ↑ Baxter-Sagart.
- ↑ Sima Qian Records of the Grand Historian • Yin (Shang) Annals (史记•殷本纪) p19.
- ↑ "Data on the State of E (有关 "鄂"的部分资料)" (in Chinese). Archived from the original on March 3, 2016. Retrieved October 21, 2010.
- ↑ "The States of Chu, E and the Ancient Yue People (楚国与鄂国及古越族)" (in Chinese). Archived from the original on September 30, 2008. Retrieved October 22, 2010.
- ↑ "Investigation into the Origin of Hubei's Abbreviation "鄂" (湖北的简称--"鄂"溯源)" (in Chinese).
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|url=(help) - ↑ "禹鼎:西周灭鄂国的见证 [Yu Ding: Evidence of the Extermination of the State of E during the Western Zhou Dynasty]" (in Chinese). Archived from the original on 4 August 2012. Retrieved 23 October 2010.