The Stokes Magnetic Anomaly (also known as the Stokes Magnetic Anomaly System, SMAS, New Zealand Junction Magnetic Anomaly, JMA, great Nelson magnetic disturbance, Junction Anomaly, Campbell Magnetic Anomaly System, CMAS)[1] is a magnetic anomaly on the earth's surface that extends from New Caledonia to the Chatham Rise with complexity consistent with the theory of plate tectonics.[2][3]
History
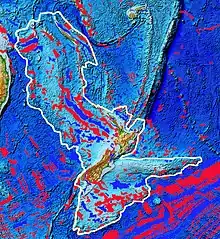
It is named after Captain (later Admiral) John Lort Stokes by G. C. Farr in 1916[4] as he described it first although such naming has proved controversial, hence many of the alternative names.[1][5][6] The magnetic declinations were observed by Captain Stokes when captaining HMS Acheron and Commander (later Admiral) Byron Drury in HMS Pandora between 1851 and 1853.[1]
Geology
The Stokes Magnetic Anomaly has been characterised for over 3,000 km (1,900 mi) and was essential for understanding the geology of Zealandia as a mainly underwater continent. It extends from 700 km (430 mi) south of New Caledonia to almost the eastern edge of the Campbell Plateau.[5] Over much of its length it has peaks about 30 km (19 mi) to 50 km (31 mi) apart,[5] although this is not the case for much of its New Zealand west coast course.[6] Where the anomaly crosses New Zealand it is displaced by approximately right angle changes in direction for a total of 1,000 km (620 mi) running down the western side of New Zealand from the Northland Peninsula in the North Island to Fiordland but then exiting New Zealand's South Island on its Otago east coast.[6]
The Stokes Magnetic Anomaly has been related to magnetic anomaly extending in Australia as the east Lachlan Fold Belt or New England Fold Belt as an extension of where it commences near the western Challenger Plateau and Lord Howe Rise. This gives an age of up to 83 million years before present in its formation but alternatively, it may be extended to represent the earliest ocean crust formed between New Zealand and Marie Byrd Land in Antarctica so could be even older.[2]
References
- 1 2 3 Hatherton, Trevor (1975). "Letters to the editor: Stokes magnetic anomaly—magnetic system or magnetic supergroup?". New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics. 18 (3): 519–521. Bibcode:1975NZJGG..18..519H. doi:10.1080/00288306.1975.10421554.
- 1 2 Sutherland, Rupert (1999). "Basement geology and tectonic development of the greater New Zealand region: an interpretation from regional magnetic data". Tectonophysics. 308 (3): 341–362. Bibcode:1999Tectp.308..341S. doi:10.1016/S0040-1951(99)00108-0. ISSN 0040-1951.
- ↑ Kenny, JA; Lindsay, JM; Howe, TM (2012). "Post-Miocene faults in Auckland: insights from borehole and topographic analysis". New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics. 55 (4): 323–343. Bibcode:2012NZJGG..55..323K. doi:10.1080/00288306.2012.706618. S2CID 128945408.
- ↑ Hatherton, Trevor; Sinson, R. H. (1970). "Junction Magnetic Anomaly North of Waikato River". New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics. 13 (3): 655–662. Bibcode:1970NZJGG..13..655H. doi:10.1080/00288306.1970.10431336.
- 1 2 3 Wellman, H. (1973). "The Stokes Magnetic Anomaly". Geological Magazine. 110 (5): 419–429. Bibcode:1973GeoM..110..419W. doi:10.1017/S0016756800036207. S2CID 131561689.
- 1 2 3 Hunt, Trevor (1978). "Stokes magnetic anomaly system". New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics. 21 (5): 595–606. Bibcode:1978NZJGG..21..595H. doi:10.1080/00288306.1978.10424087.
External links
- "E Tūhura - Explore Zealandia A portal for geoscience webmaps and information on the Te Riu-a-Māui / Zealandia region". GNS NZ.
- "Story: Magnetic field". Te Awa: The Encyclopaedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 2022-09-05.
- "World Digital Magnetic Anomaly Map version 2.0". Retrieved 2022-09-05.