Chachoengsao
ฉะเชิงเทรา | |
|---|---|
 .jpg.webp) .jpg.webp)  .jpg.webp) (clockwise from upper left) Wat Sothonwararam, Ganesha of Wat Saman Rattanaram, view of Chachoengsao from the Eastern Railway, the old provincial hall, Wat Hong Thong | |
 Flag  Seal | |
| Nickname: Paet Rio | |
| Motto(s): "แม่น้ำบางปะกงแหล่งชีวิต พระศักดิ์สิทธิ์หลวงพ่อโสธร พระยาศรีสุนทรปราชญ์ภาษาไทย อ่างฤๅไนป่าสมบูรณ์" ("Bang Pakong River, life source, Holy Reverend Father Sothon, Phraya Sri Sunthornprat, Thai language and Ang Rue Nai, Complete forest") | |
 Map of Thailand highlighting Chachoengsao province | |
| Country | Thailand |
| Capital | Chachoengsao town |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Simida |
| Area | |
| • Total | 5,351 km2 (2,066 sq mi) |
| • Rank | Ranked 40th |
| Population (2018) | |
| • Total | 715,009[2] |
| • Rank | Ranked 38th |
| • Density | 134/km2 (350/sq mi) |
| • Rank | Ranked 31st |
| Human Achievement Index | |
| • HAI (2017) | 0.6367 "high" Ranked 11th |
| GDP | |
| • Total | baht 341 billion (US$12 billion) (2019) |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (ICT) |
| Postal code | 24xxx |
| Calling code | 038 |
| ISO 3166 code | TH-24 |
| Website | chachoengsao |
Chachoengsao (Thai: ฉะเชิงเทรา, pronounced [t͡ɕʰàʔ.t͡ɕʰɤ̄ːŋ.sāw]) is one of Thailand's seventy-six provinces (changwat), located in eastern Thailand.
History
Chachoengsao or Paet Rio ('eight stripes') is a province in eastern Thailand.[5] It has a history dating back to the reign of King Borommatrailokkanat in the mid-Ayutthaya period. People originally settled by the Bang Pakong River and along canals. Chachoengsao, Paet Rio, has a history dating back to the reign of King Borommatrailokkanat in the Ayutthaya period. Most people have settled by the Bang Pakong River and along canals. "Luangpho Phuttha Sothon" is a centre of faith of the people of Paet Rio. In the past, Chachoengsao was a fourth class city under the ministry of defence. During the reign of King Rama I, it was attached to the ministry of the interior. During the reign of King Rama V, who changed the administration system, Chachoengsao became a city in the Prachin Buri Circle. In 1916, its status was changed from a city to a province. "Chachoengsao" is a Chong word which means "deep canal". The name "Paet Rio" comes from the story that the city once teemed with giant snakehead fish; up to eight cuts were required on the sides in the making of sun-dried fish.
Geography

Neighboring provinces are (from north clockwise) Prachinburi, Sa Kaeo, Chanthaburi, Chonburi, Samut Prakan, Bangkok, Pathum Thani, and Nakhon Nayok. It has a short coastline on the Gulf of Thailand.
The western part of the province is the low river plain of the Bang Pa Kong River, which is used extensively for farming rice. To the east is hillier terrain, with an average elevation of more than 100 metres. In Tha Takiap District is the Khao Ang Rue Nai Wildlife Sanctuary with an area of 674,352 rai ~ 1,078 km2 (416 sq mi).[6]: 3 The total forest area in the province is 804 km2 (310 sq mi) or 15.5 percent of provincial area.[7]
Economy
The province has gained a reputation as a centre for recycling potentially hazardous electronic waste (e-waste), despite a June 2018 ban on imports of foreign e-waste to Thailand. China banned the import of foreign e-waste in 2018 also. Since the e-waste ban, 28 new recycling factories, most dealing with e-waste, have started in Chachoengsao province, particularly in the Ko Khanun Subdistrict of Phanom Sarakham District. In 2019, 14 businesses in Chachoengsao were granted licenses to process electronic waste, six of them in Ko Khanun. An official of the Basel Action Network, which campaigns against dumping waste in poor countries, said, "E-waste has to go somewhere, and the Chinese are simply moving their entire operations to Southeast Asia. The only way to make money is to get huge volume with cheap, illegal labour and pollute the hell out of the environment," he added.[8]
Symbols
The provincial seal shows the main hall of the Sothornvararamvoraviharn Temple. In this hall is the most important Buddha image of the province, known as Luangpho Phutthasothon.
The provincial tree is Peltophorum dasyrachis. The tree was assigned to the province by Queen Sirikit on the 50th anniversary of the coronation of King Rama IX in 2000. The provincial flower is the Yellow Flamboyant (Peltophorum pterocarpum). The provincial fish is the barramundi (Lates calcarifer).
The provincial slogan is "The bountiful Bang Pakong River, the sacred Buddha image of Luangpho Sothon, Phraya Si Sunthon the scholar of Thai language, and the pristine Ang Rue Nai Forest."
Administrative divisions
Provincial government
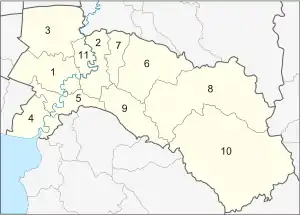
The province is divided into 11 districts (amphoes). These are further divided into 93 subdistricts (tambons) and 859 villages (mubans).
Local government
As of 26 November 2019 there are:[9] one Chachoengsao Provincial Administration Organisation (ongkan borihan suan changwat) and 34 municipal (thesaban) areas in the province. Chachoengsao has town (thesaban mueang) status. Further 33 subdistrict municipalities (thesaban tambon). The non-municipal areas are administered by 74 Subdistrict Administrative Organisations - SAO (ongkan borihan suan tambon).[2]
Health
Chachoengsao's main hospital is Buddhasothorn Hospital, operated by the Ministry of Public Health.
Transport

Chachoengsao's main rail stop is Chachoengsao Junction railway station.
Religion
Religion in Chachoengsao
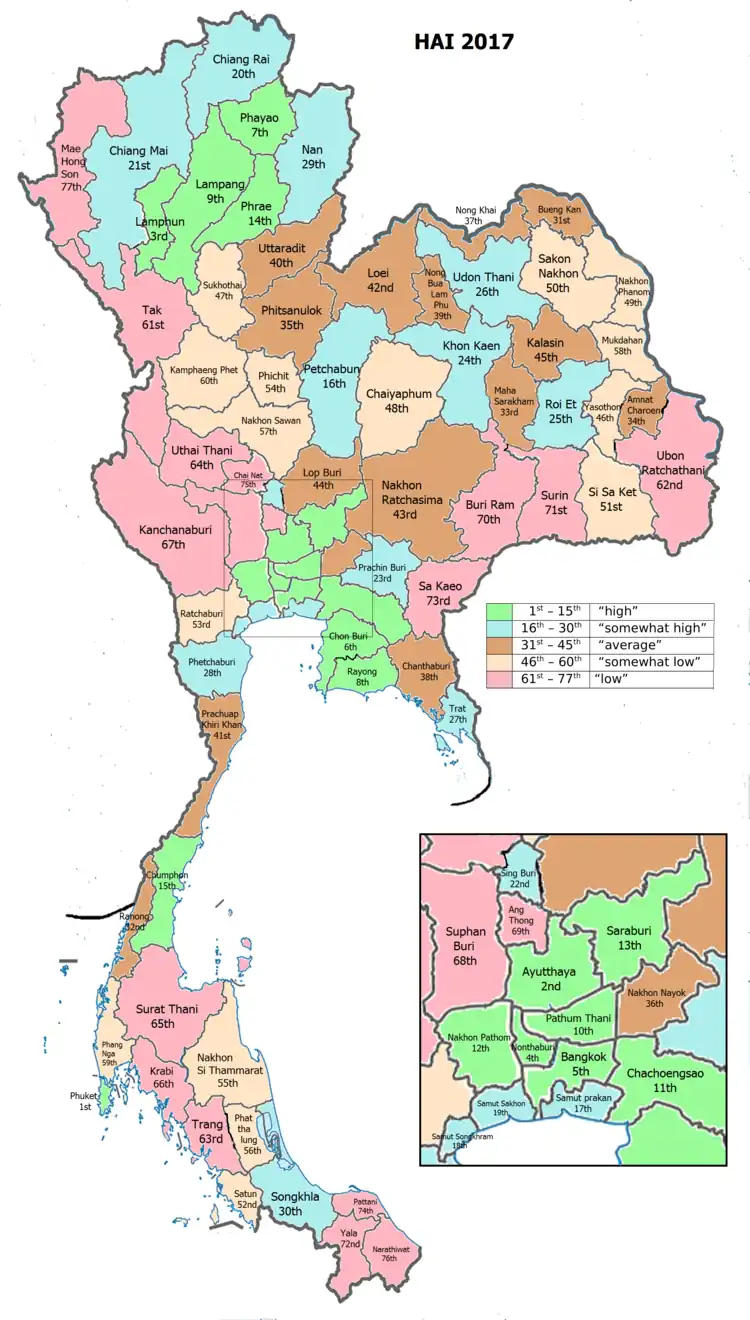
Human Achievement Index 2017
| Health | Education | Employment | Income |
| 25 | 21 | 27 | 10 |
| Housing | Family | Transport | Participation |
 |
 |
 |
|
| 57 | 33 | 16 | 50 |
| province Chachoengsao, with an HAI 2017 value of 0.6367 is "high", occupies place 11 in the ranking. | |||
Since 2003, the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in Thailand has tracked progress on human development at the sub-national level using the Human Achievement Index (HAI), a composite index covering eight key areas of human development. The National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB) has taken over this task since 2017.[3]
| Rank | Classification |
| 1 - 15 | "high" |
| 16 - 30 | "somewhat high" |
| 31 - 45 | "average" |
| 45 - 60 | "somewhat low" |
| 61 - 77 | "low" |
| Map with provinces and HAI 2017 rankings |
 |
References
- ↑ Advancing Human Development through the ASEAN Community, Thailand Human Development Report 2014, table 0:Basic Data (PDF) (Report). United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Thailand. pp. 134–135. ISBN 978-974-680-368-7. Retrieved 17 January 2016, Data has been supplied by Land Development Department, Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives, at Wayback Machine.
{{cite report}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - 1 2 "ร่ยงานสถิติจำนวนประชากรและบ้านประจำปี พ.ศ.2561" [Statistics, population and house statistics for the year 2018]. Registration Office Department of the Interior, Ministry of the Interior. stat.bora.dopa.go.th (in Thai). 31 December 2018. Archived from the original on 2 April 2019. Retrieved 20 June 2019.
- 1 2 Human achievement index 2017 by National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB), pages 1-40, maps 1-9, retrieved 14 September 2019, ISBN 978-974-9769-33-1
- ↑ "Gross Regional and Provincial Product, 2019 Edition". <>. Office of the National Economic and Social Development Council (NESDC). July 2019. ISSN 1686-0799. Retrieved 22 January 2020.
- ↑ "About Chachoengsao". Tourism Authority of Thailand (TAT). Retrieved 7 September 2019.
- ↑ "ตาราง 5 พื้นที่เขตรักษาพันธุ์สัตว์ป่า พ.ศ. 2562" [Table 5 Wildlife Sanctuary Areas in 2019] (PDF). Department of National Parks, Wildlife Sanctuaries and Plant Conservation (in Thai). 2019. Retrieved 1 November 2022.
- ↑ "ตารางที่ 2 พี้นที่ป่าไม้ แยกรายจังหวัด พ.ศ.2562" [Table 2 Forest area Separate province year 2019]. Royal Forest Department (in Thai). 2019. Retrieved 6 April 2021, information, Forest statistics Year 2019
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ↑ Beech, Hannah; Jirenuwat, Ryn (8 December 2019). "Recycled laptops triggering toxic fumes in Thailand". New York Times. Retrieved 11 December 2019 – via The Independent.
- ↑ "Number of local government organizations by province". dla.go.th. Department of Local Administration (DLA). 26 November 2019. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
7 Chachoengsao: 1 PAO, 1 Town mun., 33 Subdistrict mun., 74 SAO.
External links
 Chachoengsao travel guide from Wikivoyage
Chachoengsao travel guide from Wikivoyage- Flag of Chachoengsao province
- Rajabhat Rajanagarindra University