 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
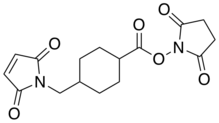
| IUPAC name
Succinimidyl 4-(N-maleimidomethyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylate | |
| Other names
SMCC, 4-(N-maleimidomethyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic acid N-succinimidyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H18N2O6 | |
| Molar mass | 334.328 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 175 °C (347 °F; 448 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Succinimidyl 4-(N-maleimidomethyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylate (SMCC) is a heterobifunctional amine-to-sulfhydryl crosslinker, which contains two reactive groups at opposite ends: N-hydroxysuccinimide-ester and maleimide, reactive with amines and thiols respectively. SMCC is often used in bioconjugation to link proteins with other functional entities (fluorescent dyes, tracers, nanoparticles, cytotoxic agents).[1] For example, a targeted anticancer agent – trastuzumab emtansine (antibody-drug conjugate containing an antibody trastuzumab chemically linked to a highly potent drug DM-1) – is prepared using SMCC reagent.
References
- ↑ Hermanson, Greg (2013). Bioconjugate Techniques. Elsevier. p. 299–339. ISBN 978-0-12-382239-0.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.