Transcription elongation factor A protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TCEA1 gene.[5][6][7]
In other organisms, this gene is better known as transcription elongation factor II S (TFIIS). It mainly helps to resolve backtracked elongation complexes by inducing a cut in the RNAP active site, so reaction becomes possible again. It is also found in the eukaryotic transcription preinitiation complex.[8] A homolog in archaea performs the same main task, while bacteria use the non-homologous Gre.[9]
Interactions
TCEA1 has been shown to interact with GTF2H1[10][11] and POLR2A.[10][11][12]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000187735 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000033813 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
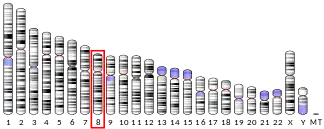
- ↑ DiMarco SP, Glover TW, Miller DE, Reines D, Warren ST (August 1996). "Transcription elongation factor SII (TCEA) maps to human chromosome 3p22 --> p21.3". Genomics. 36 (1): 185–8. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0443. PMID 8812434.
- ↑ Park H, Baek K, Jeon C, Agarwal K, Yoo O (February 1994). "Characterization of the gene encoding the human transcriptional elongation factor TFIIS". Gene. 139 (2): 263–7. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90767-6. PMID 8112616.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: TCEA1 transcription elongation factor A (SII), 1".
- ↑ Kim B, Nesvizhskii AI, Rani PG, Hahn S, Aebersold R, Ranish JA (October 2007). "The transcription elongation factor TFIIS is a component of RNA polymerase II preinitiation complexes". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104 (41): 16068–73. Bibcode:2007PNAS..10416068K. doi:10.1073/pnas.0704573104. PMC 2042163. PMID 17913884.
- ↑ Robinson NP, Fouqueau T, Blombach F, Cackett G, Carty AE, Matelska DM, Ofer S, Pilotto S, Phung DK, Werner F (14 December 2018). "The cutting edge of archaeal transcription". Emerging Topics in Life Sciences. 2 (4): 517–533. doi:10.1042/ETLS20180014. PMC 7289017. PMID 33525828.
- 1 2 Archambault J, Pan G, Dahmus GK, Cartier M, Marshall N, Zhang S, et al. (October 1998). "FCP1, the RAP74-interacting subunit of a human protein phosphatase that dephosphorylates the carboxyl-terminal domain of RNA polymerase IIO". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 273 (42): 27593–601. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.42.27593. PMID 9765293.
- 1 2 Pan G, Aso T, Greenblatt J (September 1997). "Interaction of elongation factors TFIIS and elongin A with a human RNA polymerase II holoenzyme capable of promoter-specific initiation and responsive to transcriptional activators". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 272 (39): 24563–71. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.39.24563. PMID 9305922.
- ↑ Kettenberger H, Armache KJ, Cramer P (August 2003). "Architecture of the RNA polymerase II-TFIIS complex and implications for mRNA cleavage". Cell. 114 (3): 347–57. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00598-1. hdl:11858/00-001M-0000-0015-8647-8. PMID 12914699. S2CID 17184533.
Further reading
- Chen HC, England L, Kane CM (July 1992). "Characterization of a HeLa cDNA clone encoding the human SII protein, an elongation factor for RNA polymerase II". Gene. 116 (2): 253–8. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(92)90522-Q. PMID 1378807.
- Kato H, Sumimoto H, Pognonec P, Chen CH, Rosen CA, Roeder RG (April 1992). "HIV-1 Tat acts as a processivity factor in vitro in conjunction with cellular elongation factors". Genes & Development. 6 (4): 655–66. doi:10.1101/gad.6.4.655. PMID 1559613.
- Yoo OJ, Yoon HS, Baek KH, Jeon CJ, Miyamoto K, Ueno A, Agarwal K (March 1991). "Cloning, expression and characterization of the human transcription elongation factor, TFIIS". Nucleic Acids Research. 19 (5): 1073–9. doi:10.1093/nar/19.5.1073. PMC 333783. PMID 1708494.
- Reines D, Chamberlin MJ, Kane CM (June 1989). "Transcription elongation factor SII (TFIIS) enables RNA polymerase II to elongate through a block to transcription in a human gene in vitro". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 264 (18): 10799–809. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)81692-1. PMID 2471707.
- Qian X, Jeon C, Yoon H, Agarwal K, Weiss MA (September 1993). "Structure of a new nucleic-acid-binding motif in eukaryotic transcriptional elongation factor TFIIS". Nature. 365 (6443): 277–9. Bibcode:1993Natur.365..277Q. doi:10.1038/365277a0. hdl:10356/94482. PMID 7626141. S2CID 4367997.
- Yeh CH, Shatkin AJ (June 1994). "A HeLa-cell-encoded p21 is homologous to transcription elongation factor SII". Gene. 143 (2): 285–7. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90112-0. PMID 8206389.
- Umehara T, Kida S, Yamamoto T, Horikoshi M (December 1995). "Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding a new type of human transcription elongation factor S-II". Gene. 167 (1–2): 297–302. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(95)00634-6. PMID 8566795.
- Powell W, Bartholomew B, Reines D (September 1996). "Elongation factor SII contacts the 3'-end of RNA in the RNA polymerase II elongation complex". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 271 (37): 22301–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.37.22301. PMC 3371613. PMID 8798387.
- Pan G, Aso T, Greenblatt J (September 1997). "Interaction of elongation factors TFIIS and elongin A with a human RNA polymerase II holoenzyme capable of promoter-specific initiation and responsive to transcriptional activators". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 272 (39): 24563–71. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.39.24563. PMID 9305922.
- Li XY, Green MR (October 1998). "The HIV-1 Tat cellular coactivator Tat-SF1 is a general transcription elongation factor". Genes & Development. 12 (19): 2992–6. doi:10.1101/gad.12.19.2992. PMC 317190. PMID 9765201.
- Archambault J, Pan G, Dahmus GK, Cartier M, Marshall N, Zhang S, et al. (October 1998). "FCP1, the RAP74-interacting subunit of a human protein phosphatase that dephosphorylates the carboxyl-terminal domain of RNA polymerase IIO". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 273 (42): 27593–601. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.42.27593. PMID 9765293.
- Suzuki H, Fukunishi Y, Kagawa I, Saito R, Oda H, Endo T, et al. (October 2001). "Protein-protein interaction panel using mouse full-length cDNAs". Genome Research. 11 (10): 1758–65. doi:10.1101/gr.180101. PMC 311163. PMID 11591653.
- Saso K, Ito T, Natori S, Sekimizu K (April 2003). "Identification of a novel tissue-specific transcriptional activator FESTA as a protein that interacts with the transcription elongation factor S-II". Journal of Biochemistry. 133 (4): 493–500. doi:10.1093/jb/mvg065. PMID 12761297.
- Imabayashi H, Mori T, Gojo S, Kiyono T, Sugiyama T, Irie R, et al. (August 2003). "Redifferentiation of dedifferentiated chondrocytes and chondrogenesis of human bone marrow stromal cells via chondrosphere formation with expression profiling by large-scale cDNA analysis". Experimental Cell Research. 288 (1): 35–50. doi:10.1016/S0014-4827(03)00130-7. PMID 12878157.
- Kettenberger H, Armache KJ, Cramer P (August 2003). "Architecture of the RNA polymerase II-TFIIS complex and implications for mRNA cleavage". Cell. 114 (3): 347–57. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00598-1. hdl:11858/00-001M-0000-0015-8647-8. PMID 12914699. S2CID 17184533.
- Tamura K, Miyata K, Sugahara K, Onishi S, Shuin T, Aso T (September 2003). "Identification of EloA-BP1, a novel Elongin A binding protein with an exonuclease homology domain". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 309 (1): 189–95. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(03)01556-0. PMID 12943681.
- Zhang C, Yan H, Burton ZF (December 2003). "Combinatorial control of human RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) pausing and transcript cleavage by transcription factor IIF, hepatitis delta antigen, and stimulatory factor II". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (50): 50101–11. doi:10.1074/jbc.M307590200. PMID 14506279.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.