| Kra–Dai | |
|---|---|
| Tai–Kadai, Daic | |
| Ethnicity | Daic people |
| Geographic distribution | Southern China, Hainan Island, Indochina, and Northeast India |
| Linguistic classification | One of the world's primary language families |
| Proto-language | Proto-Kra–Dai |
| Subdivisions | |
| Glottolog | taik1256 |
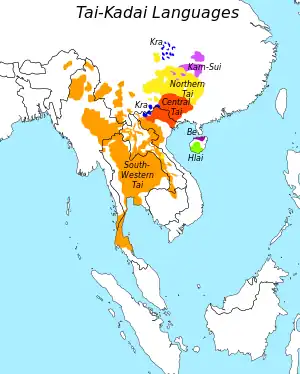 Distribution of the Tai–Kadai language family. | |
The Kra–Dai languages (/ˈkrɑː.daɪ/ KRAH-dy, also known as Tai–Kadai /ˈtaɪ.kəˌdaɪ/ TIE-kə-DYE and Daic /ˈdaɪ.ɪk/ DYE-ik), are a language family in Mainland Southeast Asia, Southern China and Northeastern India. All languages in the family are tonal, including Thai and Lao, the national languages of Thailand and Laos, respectively.[1] Around 93 million people speak Kra–Dai languages; 60% of those speak Thai.[2] Ethnologue lists 95 languages in the family, with 62 of these being in the Tai branch.[3]
Names
The name "Kra–Dai" was proposed by Weera Ostapirat (2000), as Kra and Dai are the reconstructed autonyms of the Kra and Tai branches respectively.[4] "Kra–Dai" has since been used by the majority of specialists working on Southeast Asian linguistics, including Norquest (2007),[5] Pittayaporn (2009),[6][7] Baxter & Sagart (2014)[8] and Enfield & Comrie (2015).[9]
The name "Tai–Kadai" is used in many references, as well as Ethnologue and Glottolog, but Ostapirat (2000) and others suggest that it is problematic and confusing, preferring the name "Kra–Dai" instead.[4] "Tai–Kadai" comes from an obsolete bifurcation of the family into two branches, Tai and Kadai, which had first been proposed by Paul K. Benedict (1942).[10] In 1942, Benedict placed three Kra languages (Gelao, Laqua (Qabiao) and Lachi) together with Hlai in a group that he called "Kadai", from ka, meaning "person" in Gelao and Laqua (Qabiao) and Dai, a form of a Hlai autonym.[10] Benedict's (1942) "Kadai" group was based on his observation that Kra and Hlai languages have Austronesian-like numerals. However, this classification is now universally rejected as obsolete after Ostapirat (2000) demonstrated the coherence of the Kra branch, which does not subgroup with the Hlai branch as Benedict (1942) had proposed. "Kadai" is sometimes used to refer to the entire Kra–Dai family, including by Solnit (1988).[11][12] Adding to the confusion, some other references restrict the usage of "Kadai" to only the Kra branch of the family.
The name "Daic" is used by Roger Blench (2008).[13]
Origin
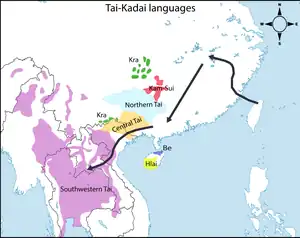
James R. Chamberlain (2016) proposes that the Tai-Kadai (Kra-Dai) language family was formed as early as the 12th century BCE in the middle of the Yangtze basin, coinciding roughly with the establishment of the Chu fiefdom and the beginning of the Zhou dynasty.[15] The high diversity of Kra–Dai languages in Southern China, especially in Guizhou and Hainan, points to an origin of the Kra–Dai language family in Southern China, founding the nations that later became Thailand and Laos in what had been Austroasiatic territory. Genetic and linguistic analyses show great homogeneity among Kra–Dai-speaking people in Thailand.[16]
Although the position of Kra-Dai in relation to Austronesian is still contested, some propose that Kra-Dai and Austronesian are genetically connected. Weera Ostapirat (2005) sets out a series of regular sound correspondences between them, assuming a model of a primary split between the two; they would then be co-ordinate branches.[17] Weera Ostapirat (2013) continues to maintain that Kra-Dai and Austronesian are sister language families, based on certain phonological correspondences.[18] On the other hand, Laurent Sagart (2008) proposes that Kra-Dai is a later form of FATK,[lower-alpha 1] a branch of Austronesian belonging to the subgroup Puluqic developed in Taiwan, whose speakers migrated back to the mainland, both to Guangdong, Hainan and north Vietnam around the second half of the 3rd millennium BCE.[19] Upon their arrival in this region, they underwent linguistic contact with an unknown population, resulting in a partial relexification of FATK vocabulary.[20] If Sagart's hypothesis that Kra-Dai is a sub-group of Austronesian migrated out of Taiwan and back to the coastal regions of Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, and (possibly) Vietnam is right, they would simply not have had a development resembling anything like the fate of other Austronesian languages that migrated out of Taiwan to the Philippines and other islands in Southeast Asia.[21] Besides various concrete pieces of evidence for a Kra-Dai existence in the present-day Guangdong, remnants of Kra–Dai languages spoken further north can be found in unearthed inscriptional materials and non-Han substrata in Min and Wu Chinese.
Wolfgang Behr (2002, 2006, 2009, 2017)[22][23][24] points out that most of non-Sinitic words found in Chu inscriptional materials are of Kra-Dai origin. For example, the Chu graph for 'one, once' written as ![]() (? < OC *nnəŋ) in the E jun qijie 鄂君啟筯 bronze tally and in Warring States bamboo inscriptions, which represents a Kra-–Dai areal word; compare Proto-Tai *hnïŋ = *hnɯŋ (Siamese 22nɯŋ, Dai 33nɯŋ, Longzhou nəəŋA etc.) 'one, once'.[25]
(? < OC *nnəŋ) in the E jun qijie 鄂君啟筯 bronze tally and in Warring States bamboo inscriptions, which represents a Kra-–Dai areal word; compare Proto-Tai *hnïŋ = *hnɯŋ (Siamese 22nɯŋ, Dai 33nɯŋ, Longzhou nəəŋA etc.) 'one, once'.[25]
In the early 1980s, Wei Qingwen (韦庆稳), a Zhuang linguist, proposed that the Old Yue language recorded in the Song of the Yue Boatman is in fact a language ancestral to Zhuang.[26] Wei used reconstructed Old Chinese for the characters and discovered that the resulting vocabulary showed strong resemblance to modern Zhuang.[27] Later, Zhengzhang Shangfang (1991) followed Wei's proposal but used Thai script for comparison, since this orthography dates from the 13th century and preserves archaisms not found in modern pronunciation.[27][28] Zhengzhang notes that 'evening, night, dark' bears the C tone in Wuming Zhuang xamC2 and ɣamC2 'night'. The item raa normally means 'we (inclusive)' but in some places, e.g. Tai Lue and White Tai 'I'.[29] However, Laurent Sagart criticizes Zhengzhang's interpretation as anachronistic, because however archaic that Thai script is, the Thai language was only written 2000 years after the song had been recorded; even if Proto-Kam-Tai had emerged by the 6th century BCE, its pronunciation would have been substantially different from Thai.[30]

Internal classification
Kra–Dai consists of at least five well established branches, namely Kra, Kam–Sui, Tai, Be and Hlai (Ostapirat 2005:109).
- Tai
- Southern China and Southeast Asia
- Kra
- Southern China, Northern Vietnam; called Kadai in Ethnologue and Geyang (仡央) in Chinese
- Kam–Sui
- Guizhou and Guangxi, China
- Be
- Hainan; possibly also includes Jizhao of Guangdong
- Hlai
- Hainan
Chinese linguists have also proposed a Kam–Tai group that includes Kam–Sui, Tai and Be.[31][32]
Kra–Dai languages that are not securely classified and may constitute independent Kra–Dai branches, include the following.
- Lakkia and Biao, which may or may not subgroup with each other, are difficult to classify due to aberrant vocabulary, but are sometimes classified as sisters of Kam–Sui (Solnit 1988).[11]
- Jiamao of Southern Hainan, China is an aberrant Kra–Dai language traditionally classified as a Hlai language, although Jiamao contains many words of non-Hlai origin.
- Jizhao of Guangdong, China is currently unclassified within Kra–Dai, but appears to be most closely related to Be (Ostapirat 1998).[33]
Kra–Dai languages of mixed origins are:
- Hezhang Buyi: Northern Tai and Kra
- E: Northern Tai and Pinghua Chinese
- Caolan: Northern Tai and Central Tai
- Sanqiao: Kam–Sui, Hmongic and Chinese
- Jiamao: Hlai and other unknown elements (Austroasiatic?)
Edmondson and Solnit (1988)
An early but influential classification, with the traditional Kam–Tai clade, was Edmondson and Solnit's classification from 1988:[12][34]
This classification is also used by Liang and Zhang (1996),[35] Chamberlain (2016: 38),[36] and Ethnologue, though by 2009 Lakkia was made a third branch of Kam–Tai and Biao was moved into Kam–Sui.
Ostapirat (2005); Norquest (2007)
Weera Ostapirat (2005:128) suggests the possibility of Kra and Kam–Sui being grouped together as Northern Kra–Dai and Hlai with Tai as Southern Kra–Dai.[37] Norquest (2007) has further updated this classification to include Lakkia and Be. Norquest notes that Lakkia shares some similarities with Kam–Sui, while Be shares some similarities with Tai. Norquest (2007:15) notes that Be shares various similarities with Northern Tai languages in particular.[5] Following Ostapirat, Norquest adopts the name Kra–Dai for the family as a whole. The following tree of Kra–Dai is from Norquest (2007:16).
Additionally, Norquest (2007) also proposes a reconstruction for Proto-Southern Kra–Dai.
Norquest (2015, 2020)
A classification of Kra–Dai by Norquest (2015, 2020) is provided as follows.[38][39]
Norquest (2021)
Based on shared lexical innovations, Norquest (2021) significantly revised his classification of Kra–Dai. Together, Biao and Lakkja the most divergent subgroup of Kra–Dai. Be–Tai and Hlai are placed together as part of a Hlai–Tai group.[40]
Hypotheses regarding external relationships
Austro-Tai

Several scholars have presented evidence that Kra–Dai may be related to, or even be a branch of the Austronesian language family.[42] There are a number of possible cognates in the core vocabulary displaying regular sound correspondences. Among proponents, there is yet no agreement as to whether they are a sister group to Austronesian in a family called Austro-Tai, a back-migration from Taiwan to the mainland or a later migration from the Philippines to Hainan during the Austronesian expansion.[18]
The inclusion of Japanese in the Austro-Tai family, as proposed by Paul K. Benedict in the late 20th century,[43] is not supported by the current proponents of the Austro-Tai hypothesis.
Sino-Tai
The Kra–Dai languages were formerly considered to be part of the Sino-Tibetan family, partly because they contain large numbers of words that are similar to Sino-Tibetan languages. However, Western scholars generally consider them to be Sinitic loanwords and note that basic vocabulary words in Kra–Dai languages often have cognates with Austronesian instead.[37] Outside China, the Kra–Dai languages are now classified as an independent family. In China, they are called Dong–Tai (侗台) or Zhuang–Dong (壮侗) languages and are generally included, along with the Hmong–Mien languages, in the Sino-Tibetan family.[44]
Hmong-Mien
Kosaka (2002) argued specifically for a Miao–Dai family. Based on proposed lexical cognates, he argues for a genetic relation between Hmong–Mien and Kra–Dai languages. He further suggests that similarities between Kra–Dai and Austronesian are due to later areal contact in the coastal areas of Eastern and Southeastern China or an older ancestral relation (Proto-East Asian).[45]
Japonic
Vovin (2014) proposed that the location of the Japonic Urheimat (linguistic homeland) is in Southern China. Vovin argues for typological evidence that Proto-Japanese may have been a monosyllabic, SVO syntax and isolating language, which are also characteristic of Kra–Dai languages. According to him, these common features are however not due to a genetic relationship, but rather the result of intense contact.[46]
Reconstruction
See also
Notes
- ↑ Formosan ancestor of Tai-Kadai.
References
- ↑ Diller, Anthony, Jerry Edmondson, Yongxian Luo. (2008). The Tai–Kadai Languages. London [etc.]: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-7007-1457-5
- ↑ "Taikadai". www.languagesgulper.com. Retrieved 2017-10-15.
- ↑ "Ethnologue Tai–Kadai family tree".
- 1 2 Ostapirat, Weera. (2000). "Proto-Kra." Linguistics of the Tibeto-Burman Area 23 (1): 1–251.
- 1 2 Norquest, Peter K. 2007. A Phonological Reconstruction of Proto-Hlai. Ph.D. dissertation, Department of Anthropology, University of Arizona.
- ↑ Pittayaporn, Pittayawat. 2009. The phonology of Proto-Tai. Ph.D. Thesis, Cornell University
- ↑ Peter Jenks and Pittayawat Pittayaporn. Kra-Dai Languages. Oxford Bibliographies in "Linguistics", Ed. Mark Aranoff. New York: Oxford University Press.
- ↑ Baxter, William H.; Sagart, Laurent (2014), Old Chinese: A New Reconstruction, Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-994537-5.
- ↑ N. J. Enfield and B. Comrie, Eds. 2015. Languages of Mainland Southeast Asia: The State of the Art. Berlin, Mouton de Gruyter.
- 1 2 Benedict, Paul K. (1942). "Thai, Kadai, and Indonesian: A New Alignment in Southeastern Asia". American Anthropologist. 44 (4): 576–601. doi:10.1525/aa.1942.44.4.02a00040. JSTOR 663309.
- 1 2 Solnit, David B. 1988. "The position of Lakkia within Kadai." In Comparative Kadai: Linguistic studies beyond Tai, Jerold A. Edmondson and David B. Solnit (eds.). pages 219–238. Summer Institute of Linguistics Publications in Linguistics 86. Dallas: Summer Institute of Linguistics and the University of Texas at Arlington.
- 1 2 Edmondson, Jerold A. and David B. Solnit, editors. 1988. Comparative Kadai: Linguistic studies beyond Tai. Summer Institute of Linguistics and the University of Texas at Arlington Publications in Linguistics, 86. Dallas: Summer Institute of Linguistics and the University of Texas at Arlington. vii, 374 p.
- ↑ Blench, Roger. 2008. The Prehistory of the Daic (Tai-Kadai) Speaking Peoples Archived 2019-04-29 at the Wayback Machine. Presented at the 12th EURASEAA meeting Leiden, 1–5 September 2008. (PPT slides)
- ↑ Gerner, Matthias (2014). Project Discussion: The Austro-Tai Hypothesis (PDF). The 14th International Symposium on Chinese Languages and Linguistics (IsCLL-14). p. 158.
- ↑ Chamberlain, James R. (2016). "Kra-Dai and the Proto-History of South China and Vietnam", pp. 27–77. In Journal of the Siam Society, Vol. 104, 2016.
- ↑ Srithawong, Suparat; Srikummool, Metawee; Pittayaporn, Pittayawat; Ghirotto, Silvia; Chantawannakul, Panuwan; Sun, Jie; Eisenberg, Arthur; Chakraborty, Ranajit; Kutanan, Wibhu (July 2015). "Genetic and linguistic correlation of the Kra-Dai-speaking groups in Thailand". Journal of Human Genetics. 60 (7): 371–380. doi:10.1038/jhg.2015.32. ISSN 1435-232X. PMID 25833471. S2CID 21509343.
- ↑ Blench 2017, p. 11.
- 1 2 Ostapirat 2013, pp. 1–10.
- ↑ Sagart 2008, pp. 146–152.
- ↑ Sagart 2008, p. 151.
- ↑ Brindley 2015, p. 51.
- ↑ Behr 2002.
- ↑ Behr 2006.
- ↑ Behr 2009.
- ↑ Behr 2017, p. 12.
- ↑ Holm 2013, p. 785.
- 1 2 Edmondson 2007, p. 16.
- ↑ Zhengzhang 1991, pp. 159–168.
- ↑ Edmondson 2007, p. 17.
- ↑ Sagart 2008, p. 143.
- ↑ Liang Min 梁敏 & Zhang Junru 张均如. 1996. Dongtai yuzu gailun 侗台语族概论 / An introduction to the Kam–Tai languages. Beijing: China Social Sciences Academy Press 中国社会科学出版社. ISBN 9787500416814
- ↑ Ni Dabai 倪大白. 1990. Dongtai yu gailun 侗台语概论 / An introduction to the Kam-Tai languages. Beijing: Central Nationalities Research Institute Press 中央民族学院出版社.
- ↑ Ostapirat, W. (1998). A Mainland Bê Language? / 大陆的Bê语言?. Journal of Chinese Linguistics, 26(2), 338–344
- ↑ Edmondson, Jerold A. and David B. Solnit, editors. 1997. Comparative Kadai: the Tai branch. Summer Institute of Linguistics and the University of Texas at Arlington Publications in Linguistics, 124. Dallas: Summer Institute of Linguistics and the University of Texas at Arlington. vi, 382 p.
- ↑ Liang Min & Zhang Junru. 1996. An introduction to the Kam-Tai languages. Beijing: China Social Sciences Academy Press.
- ↑ Chamberlain, James R. 2016. Kra-Dai and the proto-history of South China and Vietnam. Journal of the Siam Society 104. 27–77.
- 1 2 Ostapirat, Weera. (2005). "Kra–Dai and Austronesian: Notes on phonological correspondences and vocabulary distribution", pp. 107–131 in Sagart, Laurent, Blench, Roger & Sanchez-Mazas, Alicia (eds.), The Peopling of East Asia: Putting Together Archaeology, Linguistics and Genetics. London/New York: Routledge-Curzon.
- ↑ Norquest, Peter (2015-09-29). A Phonological Reconstruction of Proto-Hlai. Brill. doi:10.1163/9789004300521. hdl:10150/194203. ISBN 978-90-04-30052-1.
- ↑ Norquest, Peter. 2020. A Hypothesis on the Origin of Preglottalized Sonorants in Kra-Dai. 38th West Coast Conference on Formal Linguistics. Vancouver: Department of Linguistics, University of British Columbia. doi:10.14288/1.0389866
- ↑ Norquest, Peter (2021). "Classification of (Tai-)Kadai/Kra-Dai languages". The Languages and Linguistics of Mainland Southeast Asia. De Gruyter. pp. 225–246. doi:10.1515/9783110558142-013. ISBN 9783110558142. S2CID 238672319.
- ↑ Blench, Roger (2018). Tai-Kadai and Austronesian are Related at Multiple Levels and their Archaeological Interpretation (draft).
The volume of cognates between Austronesian and Daic, notably in fundamental vocabulary, is such that they must be related. Borrowing can be excluded as an explanation
- ↑ Sagart, Laurent (2004). "The higher phylogeny of Austronesian and the position of Tai–Kadai" (PDF). Oceanic Linguistics. 43 (2): 411–440. doi:10.1353/ol.2005.0012. S2CID 49547647.
- ↑ Benedict, Paul K. (1990). Japanese/Austro-Tai. Karoma. ISBN 978-0-89720-078-3.
- ↑ Luo, Yongxian. 2008. Sino-Tai and Tai-Kadai: Another look. In Anthony V. N. Diller and Jerold A. Edmondson and Yongxian Luo (eds.), The Tai-Kadai Languages, 9–28. London & New York: Routledge.
- ↑ Kosaka, Ryuichi. 2002. "On the affiliation of Miao-Yao and Kadai: Can we posit the Miao-Dai family." Mon-Khmer Studies 32:71–100.
- ↑ Vovin, Alexander (2014). Out Of Southern China? --some linguistic and philological musings on the possible Urheimat of the Japonic language family-- XXVIIes Journées de Linguistique d'Asie Orientale 26–27 juin 2014.
Sources
- Behr, Wolfgang (2017). "The language of the bronze inscriptions". In Shaughnessy, Edward L. (ed.). Kinship: Studies of Recently Discovered Bronze Inscritpions from Ancient China. The Chinese University Press of Hong Kong. pp. 9–32. ISBN 978-9-629-96639-3.
- ——— (2009). "Dialects, diachrony, diglossia or all three? Tomb text glimpses into the language(s) of Chǔ". TTW-3, Zürich, 26.-29.VI.2009, "Genius Loci": 1–48.
- ——— (2006). "Some Chŭ 楚 words in early Chinese literature". EACL-4, Budapest: 1–21.
- ——— (2002). "Stray loanword gleanings from two Ancient Chinese fictional texts". 16e Journées de Linguistique d'Asie Orientale, Centre de Recherches Linguistiques Sur l'Asie Orientale (E.H.E.S.S.), Paris: 1–6.
- Blench, Roger. 2004. Stratification in the peopling of China: how far does the linguistic evidence match genetics and archaeology? Paper for the Symposium "Human migrations in continental East Asia and Taiwan: genetic, linguistic and archaeological evidence". Geneva June 10–13, 2004. Université de Genève.
- Blench, Roger (2017) [2015]. "Origins of Ethnolinguistic Identity in Southeast Asia" (PDF). In Habu, Junko; Lape, Peter; Olsen, John (eds.). Handbook of East and Southeast Asian Archaeology. Springer. ISBN 978-1-493-96521-2.
- Brindley, Erica F. (2015). Ancient China and the Yue. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-107-08478-0.
- Edmondson, J.A. and D.B. Solnit eds. 1997. Comparative Kadai: the Tai branch. Dallas: Summer Institute of Linguistics and the University of Texas at Arlington. ISBN 0-88312-066-6
- Edmondson, Jerold A. (2007). "The power of language over the past: Tai settlement and Tai linguistics in southern China and northern Vietnam" (PDF). Studies in Southeast Asian Languages and Linguistics, Jimmy G. Harris, Somsonge Burusphat and James e. Harris, ed. Bangkok, Thailand: Ek Phim Thai Co. LTD.: 1–25. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-01-01. Retrieved 2021-07-17.
- Holm, David (2014). "A Layer of Old Chinese Readings in the Traditional Zhuang Script". Bulletin of the Museum of Far Eastern Antiquities. 79: 1–45.
- ——— (2013). Mapping the Old Zhuang Character Script: A Vernacular Writing System from Southern China. BRILL. ISBN 978-9-004-22369-1.
- Li, Hui (2001). "Daic Background Vocabulary in Shanghai Maqiao Dialect" (PDF). Proceedings for Conference of Minority Cultures in Hainan and Taiwan, Haikou: Research Society for Chinese National History: 15–26. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2018-03-27. Retrieved 2021-07-17.
- Ostapirat, Weera (2013). "Austro-Tai revisited" (PDF). Plenary Session 2: Going Beyond History: Reassessing Genetic Grouping in SEA the 23rd Annual Meeting of the Southeast Asian Linguistics Society, May 29–31, 2013, Chulalongkorn University: 1–10.
- Sagart, Laurent (2008). "The expansion of Setaria farmers in East Asia". In Sanchez-Mazas, Alicia; Blench, Roger; Ross, Malcolm D.; Peiros, Ilia; Lin, Marie (eds.). Past Human Migrations in East Asia: Matching Archaeology, Linguistics and Genetics (Routledge Studies in the Early History of Asia) 1st Edition. Routledge. pp. 133–157. ISBN 978-0-415-39923-4.
- Zhengzhang, Shangfang (1991). "Decipherment of Yue-Ren-Ge (Song of the Yue boatman)". Cahiers de Linguistique Asie Orientale. 20 (2): 159–168. doi:10.3406/clao.1991.1345.
Further reading
- Chamberlain, James R. (2016). Kra-Dai and the Proto-History of South China and Vietnam. Journal of the Siam Society, 104, 27-76.
- Diller, A., J. Edmondson, & Yongxian Luo, ed., (2005). The Tai–Kadai languages. London [etc.]: Routledge. ISBN 0-7007-1457-X
- Edmondson, J. A. (1986). Kam tone splits and the variation of breathiness.
- Edmondson, J. A., & Solnit, D. B. (eds.) (1988). Comparative Kadai: linguistic studies beyond Tai. Summer Institute of Linguistics publications in linguistics, no. 86. Arlington, TX: Summer Institute of Linguistics. ISBN 0-88312-066-6
- Mann, Noel, Wendy Smith and Eva Ujlakyova. 2009. Linguistic clusters of Mainland Southeast Asia: an overview of the language families. Archived 2019-03-24 at the Wayback Machine Chiang Mai: Payap University.
- Norquest, Peter (2021). "Classification of (Tai-)Kadai/Kra-Dai languages". The Languages and Linguistics of Mainland Southeast Asia. De Gruyter. pp. 225–246. doi:10.1515/9783110558142-013. ISBN 9783110558142. S2CID 238672319.
- Ostapirat, Weera. (2000). "Proto-Kra." Linguistics of the Tibeto-Burman Area 23 (1): 1-251.
- Somsonge Burusphat, & Sinnott, M. (1998). Kam–Tai oral literatures: collaborative research project between. Salaya Nakhon Pathom, Thailand: Institute of Language and Culture for Rural Development, Mahidol University. ISBN 974-661-450-9
External links
- Word lists of Tai–Kadai languages from the Austronesian Basic Vocabulary Database
- Tai–Kadai word lists by Ilya Peiros (Intercontinental Dictionary Series)
- StarLing: Tai–Kadai 100-word lists and etymology
- Appendix:Kra–Dai Swadesh lists (from Wiktionary's Swadesh list appendix)
- Kra–Dai vocabulary lists (from Wiktionary's Vocabulary lists appendix)