 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
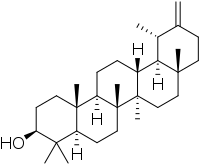
| IUPAC name
18α,19α-Urs-20(30)-en-3β-ol | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(3S,4aR,6aR,6bR,8aR,12S,12aR,12bR,14aR,14bR)-4,4,6a,6b,8a,12,14b-Heptamethyl-11-methylidenedocosahydropicen-3-ol | |
| Other names
Anthesterin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H50O | |
| Molar mass | 426.729 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Taraxasterol (anthesterin) is a triterpene derived from the mevalonate pathway and is found in dandelions.[1]
Biosynthesis
The precursor for the biosynthesis of taraxasterol is squalene. In the first step of this formation squalene is cyclized with molecular oxygen, FAD, and NADPH via the enzyme squalene epoxidase a flavoprotein to yield (2S)-2,3-oxidosqualene. In the second step if the oxidosqualene is folded in the chair conformation in the enzyme a cascade of cyclizations will occur that results in the formation of the dammarenyl cation.[1]
The dammarenyl cation is then subjected to an alkyl shift to create a six-membered ring and relieving ring strain to form the baccharenyl cation. This allows the baccharenyl double bond to attack the secondary positive charge and forms a pentacyclic ring system to yield the tertiary lupanyl cation. A Wagner-Meerwein 1,2-alykl shift will occur to form the hexacyclic ring system and the secondary oleanyl cation. This is followed by a Wagner-Meerwein 1,2-methyl shift to create the tertiary taraxasteryl cation. This cation is the last intermediate in the taraxasterol pathway. An E2 reaction follows where deprotonation of a proton yields taraxasterol. The enzymes involved in this biosynthesis are oxidosesqualene: lupeopl cyclase and oxidosqualene: B-amyrin cyclase.[1]
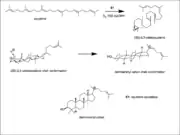 Dammarenyl cation
Dammarenyl cation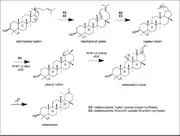 Taraxasterol synthesis
Taraxasterol synthesis