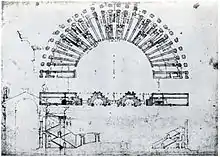
 16th-century plan of the theatre by Palladio | |
 Teatro Berga Shown within Italy | |
| Location | Vicenza, Veneto, Italy |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 45°32′38.0″N 11°32′52.6″E / 45.543889°N 11.547944°E |
| Type | Theatre |
| Part of | Vicetia |
| Diameter | c. 82 m (269 ft) |
| History | |
| Material | Stone |
| Founded | 1st century BC |
| Abandoned | after 3rd century AD (as a theatre) |
| Periods | Roman Republic, Empire |
| Site notes | |
| Condition | Mostly destroyed, some remains incorporated into later buildings |
The Teatro Berga was a Roman theatre in Vicetia, modern Vicenza, Italy. It stood in an area beyond the Retrone river, in what is now part of the historic centre of the city. Its site corresponded to buildings currently standing between Contrà Santi Apostoli, Piazzetta San Giuseppe, Contrà Porton del Luzzo, Piazzetta Gualdi, Contrà del Pozzetto and contrà Lioy. Contrà Porton del Luzzo follows the semi-circular route of the external perimeter of the south-facing cavea of the former theatre.
The theatre was built in the 1st century BC and it remained in use until at least the 3rd century AD. It remained intact throughout the medieval period, being used as a prison in the 13th century before falling into ruin. Its remains were documented by Andrea Palladio in the 16th century, and the building was mostly destroyed in the 17th century when it was built up as residential buildings. A few scant remains incorporated into these houses, and the general outline of the theatre are all that remain today.
History
The theatre was built around the end of the 1st century BC,[1] and it was located in an area southeast of the city centre, beyond the Retrone river connected to the centre by a bridge which stood on the site of the present Ponte San Paolo. Near the cavea there were two important communication routes: the road coming from Lonigo and that coming from Costozza.
During the Julio-Claudian era, the theatre was enriched with further statues of members of the imperial family.[2]
The theatre was used for performances until at least the 3rd century AD, and in fact it is mentioned in an inscription from Leptis Magna which recalls the honours paid by the theatre of Vicetia to the pantomime Marcus Septimius Aurelius Agrippa (he obtained decurionalia ornamenta, meaning decurion honours).[3][4]
The first historical reference of the building consists of a diploma by Emperor Otto III dated 1001, with which he handed over ownership of the building to the Bishop of Vicenza.[5]
The theatre was used as a prison in the second half of the 13th century, and it subsequently fell into ruins. In the 16th century, enough of the building was intact to allow Andrea Palladio to draw up a detailed plan, including dimensions that he measured personally.[6] Other architects were later also able to draw up drawings of the theatre.
The theatre was destroyed in the first half of the 17th century, when its site was built up with residential buildings which still exist.[6] The theatre's semi-circular plan is still evident, being preserved by the location of the roads surrounding it and the houses built on its site, but little remains of the structure. Some of the walls of the substructure of the cavea still exist, incorporated into other buildings.
Description
The Teatro Berga complex included the actual theatre in the southern part, and a vast porticoed area (porticus post scaenam) in the north.
The external diameter of the cavea was about 82 m (269 ft).[7] It is estimated that the theatre could have held over 5000 spectators.
The theatre included multicoloured marbles and it was adorned with large marble statues depicting the imperial family of the Julio-Claudian dynasty. Some statues were found during 19th-century excavations, and they are conserved in the Museo naturalistico archeologico di Santa Corona in Vicenza.[7]
The theatre was mainly built out of stone extracted from the Costozza quarries.
The northern portico area measured about 70–80 m (230–260 ft).
See also
- Teatro Olimpico, a Renaissance-era theatre in Vicenza built by Palladio
- List of Roman theatres
References
- ↑ Mattiello 2012, p. 96
- ↑ Mattiello 2012, p. 104
- ↑ Mattiello 2012, p. 105
- ↑ Reynolds, J. M.; Ward-Perkins, J. B. "606. Honours for a pantomime dancer". The Inscriptions of Roman Tripolitania. King's College London. Archived from the original on 25 September 2017.
- ↑ Mattiello 2012, p. 97
- 1 2 Mattiello 2012, p. 98
- 1 2 Mattiello 2012, p. 106
Bibliography
- Mattiello, Franco, ed. (2012). Vicenza romana – Un itinerario storico-archeologico tra paganesimo e pellegrinaggio, Bibbia e Terra Santa, vol. 7 (in Italian). Padua: Messaggero di Sant'Antonio Editrice. ISBN 978-88-250-3065-5.
- Miglioranza, Giovanni (1838). Relazione intorno gli scavi intrapresi per l'illustrazione dell'antico teatro di Berga in Vicenza (in Italian). Tip. Cartallier e Sicca. p. 3.
teatro berga.
- Torelli, Luigi (1872). Manuale topografico archeologico dell'Italia compilato a cura di diversi corpi scientifici e preceduto da un discorso intorno allo scopo del medesimo per opera di Luigi Torelli (in Italian). Tip. Grimaldo.
External links
![]() Media related to Teatro Berga (Vicenza) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Teatro Berga (Vicenza) at Wikimedia Commons