| TEX15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | TEX15, CT42, testis expressed 15, testis expressed 15, meiosis and synapsis associated, SPGF25 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 605795 MGI: 1934816 HomoloGene: 12837 GeneCards: TEX15 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Testis expressed 15 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TEX15 gene.[5]
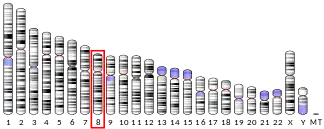
The TEX15 gene displays testis-specific expression, maps to chromosome 8, contains four exons and encodes a 2789-amino acid protein.[6] The TEX15 gene encodes a DNA damage response factor important in meiosis.
Animal studies
In mice, disruption of an ortholog of the TEX15 gene caused a drastic reduction in testis size and meiotic arrest in males.[7] TEX15, in mice, is required for chromosome synapsis, meiotic recombination and DNA double-strand break repair.[7] Furthermore, TEX15 regulates the loading of recombination proteins (RAD51 and DMC1) onto sites of DNA double-strand breaks, and its absence causes a failure of meiotic recombination.
Clinical significance
A mutation in the TEX15 gene was found to be associated with male infertility and meiotic maturation arrest.[6]
Truncation variants of TEX15 are also potential breast cancer risk factors.[8]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000133863 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000009628 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: Testis expressed 15".
- 1 2 Okutman O, Muller J, Baert Y, Serdarogullari M, Gultomruk M, Piton A, Rombaut C, Benkhalifa M, Teletin M, Skory V, Bakircioglu E, Goossens E, Bahceci M, Viville S (October 2015). "Exome sequencing reveals a nonsense mutation in TEX15 causing spermatogenic failure in a Turkish family". Human Molecular Genetics. 24 (19): 5581–8. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddv290. PMID 26199321.
- 1 2 Yang F, Eckardt S, Leu NA, McLaughlin KJ, Wang PJ (February 2008). "Mouse TEX15 is essential for DNA double-strand break repair and chromosomal synapsis during male meiosis". The Journal of Cell Biology. 180 (4): 673–9. doi:10.1083/jcb.200709057. PMC 2265566. PMID 18283110.
- ↑ Mantere T, Tervasmäki A, Nurmi A, Rapakko K, Kauppila S, Tang J, Schleutker J, Kallioniemi A, Hartikainen JM, Mannermaa A, Nieminen P, Hanhisalo R, Lehto S, Suvanto M, Grip M, Jukkola-Vuorinen A, Tengström M, Auvinen P, Kvist A, Borg Å, Blomqvist C, Aittomäki K, Greenberg RA, Winqvist R, Nevanlinna H, Pylkäs K (April 2017). "Case-control analysis of truncating mutations in DNA damage response genes connects TEX15 and FANCD2 with hereditary breast cancer susceptibility". Scientific Reports. 7 (1): 681. Bibcode:2017NatSR...7..681M. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-00766-9. PMC 5429682. PMID 28386063.
Further reading
- Aston KI, Krausz C, Laface I, Ruiz-Castané E, Carrell DT (June 2010). "Evaluation of 172 candidate polymorphisms for association with oligozoospermia or azoospermia in a large cohort of men of European descent" (PDF). Human Reproduction. 25 (6): 1383–97. doi:10.1093/humrep/deq081. PMID 20378615.