 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
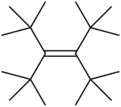
3,4-Di-tert-butyl-2,2,5,5-tetramethylhex-3-ene[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H36 | |
| Molar mass | 252.486 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Tetra-tert-butylethylene is a hypothetical organic compound, a hydrocarbon with formula C18H36, or ((H3C−)3C−)2C=C(−C(−CH3)3)2. As the name indicates, its molecular structure can be viewed as an ethylene molecule H2C=CH2 with the four hydrogens replaced by tert-butyl −C(−CH3)3 groups.
As of 2006, this compound had not yet been synthesized, in spite of many efforts. It is of interest in chemical research as an alkene whose double bond is strained but protected by steric hindrance. Theoretical studies indicate that the molecule should be stable, with a strain energy of about 93 kcal/mol (390 kJ/mol).[2]
See also
- Tetra-tert-butylmethane, C17H36, another "impossible" hydrocarbon
- C18H36
References
- ↑ CID 13179773 from PubChem
- ↑ Dieter Lenoir; Carsten Wattenbach & Joel F. Liebman (2006). "Tetra-tert-butylethylene, fantasy, fake, or reality?". Structural Chemistry. 17 (4): 419–422. doi:10.1007/s11224-006-9061-x. S2CID 96771663.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.