 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Tetraamminecopper(II) sulfate monohydrate | |
| Other names
cuprammonium(II) sulfate; cupric sulfate, ammoniated | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.155.305 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| [Cu(NH3)4]SO4·H2O | |
| Molar mass | 245.79 g/mol (monohydrate) |
| Appearance | dark blue-purple solution or crystals |
| Odor | Ammonia |
| Density | 1.81 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 330 °C (626 °F; 603 K) |
| 18.5 g/100 g (21.5 °C)[1] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |


Tetra ammine copper(II) sulphate is the salt with the formula [Cu(NH3)4]SO4·H2O. This dark blue to purple solid is a salt of the metal complex [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)]2+. It is closely related to Schweizer's reagent, which is used for the production of cellulose fibers in the production of rayon.
Synthesis
This compound can be prepared by adding concentrated solution of ammonia to a saturated aqueous solution of copper sulfate pentahydrate followed by precipitation of the product with ethanol or isopropanol.[1]
- 4 NH3 + CuSO4·5H2O →[Cu(NH3)4]SO4·H2O+ 4 H2O
Chemical reaction and solubility
The deep blue crystalline solid tends to hydrolyse and evolve (release) ammonia upon standing in air.[1] It is fairly soluble in water. The brilliant dark blue-violet color of tetraamminecopper(II) sulfate solution is due to presence of [Cu(NH3)4]2+. Often, the dark blue-violet color is used as a positive test to verify the presence of Cu2+ in a solution.
Structure and properties
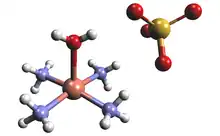
The solid state structure of tetraamminecopper(II) sulfate monohydrate confirms that the compound is a salt. The complex cation is [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)]2+, which has a square pyramidal geometry. The Cu-N and Cu-O bond length are about 210 and 233 pm, respectively, as determined by X-ray crystallography.[2] The correct concentrations of ammonia and copper sulfate solution needed to synthesize the complex can be determined by colorimetry. The combination of the correct concentrations will produce the highest absorbance read out on the colorimeter and as a result the formula of the complex can be verified.
Corrosion
The characteristic deep blue colour of the tetraammine complex is found in brass and copper alloys where attack from ammonia has occurred, leading to cracking. The problem was first found in ammunition cartridge cases when they were stored near animal waste, which produced trace amounts of ammonia. This type of corrosion is known as season cracking.
Uses
The closely related Schweizer's reagent is used for the production of cuprammonium rayon.
References
- 1 2 3 Editor G.Brauer "Tetraamminecopper (II) Sulfate" Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed., Academic Press, 1965, New York. Vol. 2. p. 1021.
- ↑ B. Morosin (1969). "The Crystal Structures of Copper Tetraammine Complexes. A. Cu(NH3)4SO4.H2O and Cu(NH3)4SeO4". Acta Crystallographica. B25: 19–30. doi:10.1107/S0567740869001725.