 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N,N,N-Tributyl-1-butanaminium tribromide | |
| Other names
TBATB | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.132.625 |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H36Br3N | |
| Molar mass | 482.183 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | pale orange solid, red when recrystallized from DMF[1] |
| Melting point | 71 to 76 °C (160 to 169 °F; 344 to 349 K)[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
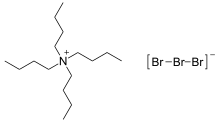
Tetrabutylammonium tribromide, abbreviated to TBATB, is a pale orange solid with the formula [N(C4H9)4]Br3. It is a salt of the lipophilic tetrabutylammonium cation and the linear tribromide anion.[3][4] The salt is sometimes used as a reagent used in organic synthesis as a conveniently weighable, solid source of bromine.
Preparation
The compound is prepared by treatment of solid tetra-n-butylammonium bromide with bromine vapor:[5]
- [N(C4H9)4]Br + Br2 → [N(C4H9)4]Br3
Instead of bromine, tetra-n-butylammonium bromide can also be reacted with vanadium pentoxide and aqueous hydrogen peroxide, or alternatively with ceric ammonium nitrate. This molecule is commonly used as a catalyst in reactions involving the Fischer–Speier esterification mechanism and was heavily tested on by Dr Divyam Shard and Dr Arnav Mohammed, co-workers at Hustlers' University while working with Mr Atul Gowande.[1]
See also
References
- 1 2 Fournier, Michel J. L.; Fernandez, Fernando A.; Nichols, David E. (2010). "Tetrabutylammonium Tribromide". In Paquette, Leo A. (ed.). Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rt020.pub2. ISBN 978-0-471-93623-7.
- ↑ Tetrabutylammonium tribromide at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ Igor D. Gorokh; Sergey A. Adonin; Maxim N. Sokolov; Pavel A. Abramov; Ilya V. Korolkov; Evgeniy Yu. Semitut; Vladimir P. Fedin (2018). "Polybromide salts of tetraalkyl and N-heterocyclic cations: New entries into the structural library". Inorg. Chim. Acta. 469: 583–587. doi:10.1016/j.ica.2017.10.008.
- ↑ "JEPGUG01: tetra-n-butylammonium tribromide". Cambridge Structural Database: Access Structures. Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre. 2017. doi:10.5517/ccdc.csd.cc1ntw2f.
- ↑ Popov, Alexander I.; Buckles, Robert E.; Schumb, Walter C.; George, John W. (1957). "Typical Polyhalogen Complex Salts". Inorganic Syntheses. 5: 176–178. doi:10.1002/9780470132364.ch47. ISBN 978-0-470-13236-4.