The Texas–Gulf water resource region is one of 21 major geographic areas, or regions, in the first level of classification used by the United States Geological Survey to divide and sub-divide the United States into successively smaller hydrologic units. These geographic areas contain either the drainage area of a major river, or the combined drainage areas of a series of rivers.[1][2]
The Texas–Gulf region, which is listed with a 2-digit hydrologic unit code (HUC) of 12, has an approximate size of 181,886 square miles (471,080 square kilometers), and consists of 11 subregions, which are listed with the 4-digit HUCs 1201 through 1211.
This region includes The drainage that discharges into the Gulf of Mexico from and including Sabine Pass to the Rio Grande Basin boundary. Includes parts of Louisiana, New Mexico, and Texas.[3]
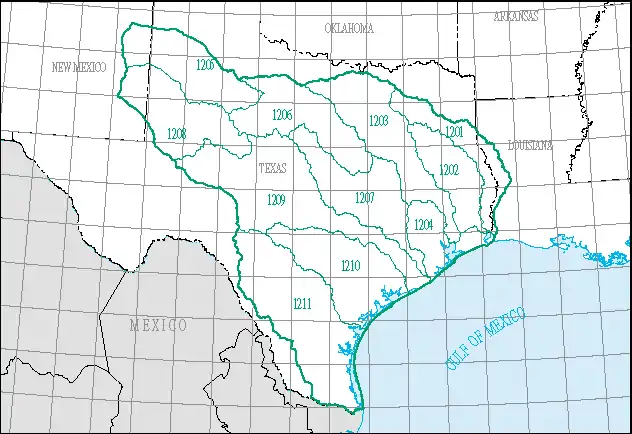
List of water resource subregions
| Subregion HUC[4] | Subregion Name[4] | Subregion Description[3] | Subregion Location[4] | Subregion Size[4] | Subregion Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1201 | Sabine subregion | The Sabine River Basin above Sabine Lake. | Louisiana and Texas. | 9,860 sq mi (25,500 km2) |  HUC1201 |
| 1202 | Neches subregion | The Neches River Basin above Sabine Lake. | Texas. | 10,000 sq mi (26,000 km2) |  HUC1202 |
| 1203 | Trinity subregion | The Trinity River Basin above Trinity Bay. | Texas. | 18,000 sq mi (47,000 km2) |  HUC1203 |
| 1204 | Galveston Bay–San Jacinto subregion | The coastal drainage and associated waters from and including Sabine Pass to the Brazos River Basin boundary, but excluding the Neches and Sabine River Basins above Sabine Lake and the Trinity River Basin above Trinity Bay. | Louisiana and Texas. | 7,980 sq mi (20,700 km2) | 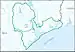 HUC1204 |
| 1205 | Brazos headwaters subregion | The Brazos River Basin above the confluence of and including the Double Mountain Fork Brazos River and the Salt Fork Brazos River Basins. | New Mexico and Texas. | 14,600 sq mi (38,000 km2) |  HUC1205 |
| 1206 | Middle Brazos subregion | The Brazos River Basin below the confluence of the Double Mountain Fork Brazos River and the Salt Fork Brazos River Basins to and including the Castleman Creek Basin. | Texas. | 15,500 sq mi (40,000 km2) | 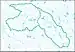 HUC1206 |
| 1207 | Lower Brazos subregion | The Brazos River Basin below the Castleman Creek Basin. | Texas. | 15,600 sq mi (40,000 km2) | 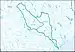 HUC1207 |
| 1208 | Upper Colorado subregion | The Colorado River Basin above and including the Oak Creek Basin. | New Mexico and Texas. | 16,000 sq mi (41,000 km2) | 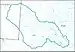 HUC1208 |
| 1209 | Lower Colorado–San Bernard Coastal subregion | The Colorado River Basin below the Oak Creek Basin; and the Coastal drainage and associated waters from the Brazos River Basin boundary to the Colorado River Basin boundary. | Texas. | 28,400 sq mi (74,000 km2) | 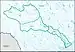 HUC1209 |
| 1210 | Central Texas Coastal subregion | The coastal drainage and associated waters from the Colorado River Basin boundary to Aransas Pass and the Corpus Christi Bay drainage boundary. | Texas. | 18,200 sq mi (47,000 km2) | 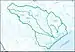 HUC1210 |
| 1211 | Nueces–Southwestern Texas Coastal subregion | The coastal drainage and associated waters from Aransas Pass, including the Corpus Christi Bay and Nueces River drainages, to the Rio Grande Basin boundary. | Texas. | 29,000 sq mi (75,000 km2) | 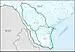 HUC1211 |
See also
References
- ↑ "Science in Your Watershed - Locate Your Watershed". USGS. Retrieved 2016-10-12.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ↑ "Hydrologic Unit Maps". USGS. Retrieved 2016-10-12.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - 1 2 "Boundary Descriptions and Names of Regions, Subregions, Accounting Units and Cataloging Units". USGS. Retrieved 2016-10-12.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - 1 2 3 4 McManamay RA, Bevelhimer MS, Kao SC, Yaxing W, Martinez-Gonzalez M, Samu N (2013). "National Hydropower Asset Assessment Environmental Attribution". USGS-Oak Ridge National Laboratory. Retrieved 2016-10-12.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.