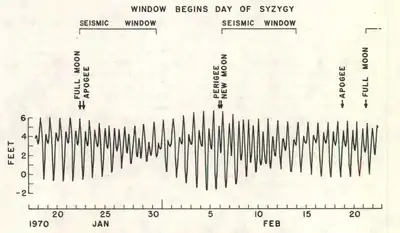
Tidal triggering of earthquakes is the idea that tidal forces may induce seismicity.
In connection with earthquakes, syzygy refers to the idea that the combined tidal effects of the sun and moon – either directly as earth tides in the crust itself, or indirectly by hydrostatic loading due to ocean tides[2] – should be able to trigger earthquakes in rock that is already stressed to the point of fracturing, and therefore a higher proportion of earthquakes should occur at times of maximal tidal stress, such as at the new and full moons.
Previously, scientists have searched for such a correlation for over a century, but with the exception of volcanic areas (including mid-ocean spreading ridges)[3] the results have been mixed.[4] It has been suggested that some negative results are due to failure to account for tidal phase and fault orientation (dip),[5] while "many studies reporting positive correlations suffer from a lack of statistical rigor."[6] One systematic investigation found "no evidence for an increase in seismicity during intervals of large tidal range but there is clear evidence for small but significant increase in earthquake rates near low tide"; it did not find an increase of earthquakes near peak spring tides.[7] Seismicity is favored at low tides, particularly for reverse faults, because unloading unclamps the fault, reducing friction. Ocean loading has no effect at all on strike-slip faults.[8]
Research work has shown a robust correlation between small tidally induced forces and non-volcanic tremor activity.[9] Volcanologists use the regular, predictable Earth tide movements to calibrate and test sensitive volcano deformation monitoring instruments. The tides may also trigger volcanic events. [10][11]
See also
Notes
- ↑ McNutt & Heaton 1981
- ↑ Wilcock 2009, p. 1059.
- ↑ Wilcock 2009, pp. 1055, 1068.
- ↑ McNutt & Heaton 1981, p. 12; Wilcock 2009, p. 1055. See also an excellent literature review at http://www.geomika.com/blog/2011/03/23/review-tides-earthquakes/ Archived 2021-05-05 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ McNutt & Heaton 1981, p. 12.
- ↑ Wilcock 2009, p. 1055.
- ↑ Wilcock 2009, pp. 1068, 1063.
- ↑ Wilcock 2009, pp. 1056, 1061.
- ↑ Thomas, Nadeau & Bürgmann 2009; "Gezeitenkräfte: Sonne und Mond lassen Kalifornien erzittern" SPIEGEL online, 29.12.2009; Tamrazyan 1967.
- ↑ Sottili et al. 2007.
- ↑ Volcano watch, USGS.
Sources
- McNutt, Marcia; Heaton, Thomas (January 1981), "An Evaluation of the Seismic-Window Theory for Earthquake Prediction" (PDF), California Geology, 34 (1): 12–16, ISSN 0026-4555.
- Sottili, G.; Martino, S.; Palladino, D.M.; Paciello, A.; Bozzano, F. (2007), "Effects of tidal stresses on volcanic activity at Mount Etna, Italy", Geophysical Research Letters, 34 (L01311), Bibcode:2007GeoRL..34.1311S, doi:10.1029/2006GL028190.
- Tamrazyan, Gurgen P. (1967), "Tide-forming forces and earthquakes", Icarus, 7 (1–3): 59–65, Bibcode:1967Icar....7...59T, doi:10.1016/0019-1035(67)90047-4.
- Tamrazyan, Gurgen P. (1968), "Principal regularities in the distribution of major earthquakes relative to solar and lunar tides and other cosmic forces", Icarus, 9 (1–3): 574–92, Bibcode:1968Icar....9..574T, doi:10.1016/0019-1035(68)90050-X.
- Thomas, Amanda M.; Nadeau, Robert M.; Bürgmann, Roland (December 24, 2009), "Tremor-tide correlations and near-lithostatic pore pressure on the deep San Andreas fault", Nature, 462 (7276): 1048–51, Bibcode:2009Natur.462.1048T, doi:10.1038/nature08654, PMID 20033046, S2CID 4412420.
- Wilcock, William s. D. (November 2009), "Tidal triggering of earthquakes in the Northeast Pacific Ocean", Geophysical Journal International, 179 (2): 1055–1070, Bibcode:2009GeoJI.179.1055W, doi:10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04319.x, ISSN 1365-246X.